Open source software offers pet technology developers the flexibility to customize and improve applications without licensing restrictions, fostering innovation and community collaboration. Proprietary software provides dedicated support, polished interfaces, and guaranteed updates, which can enhance reliability and user experience in pet tech products. Choosing between open source and proprietary depends on factors like budget, technical expertise, and desired control over software features.
Table of Comparison
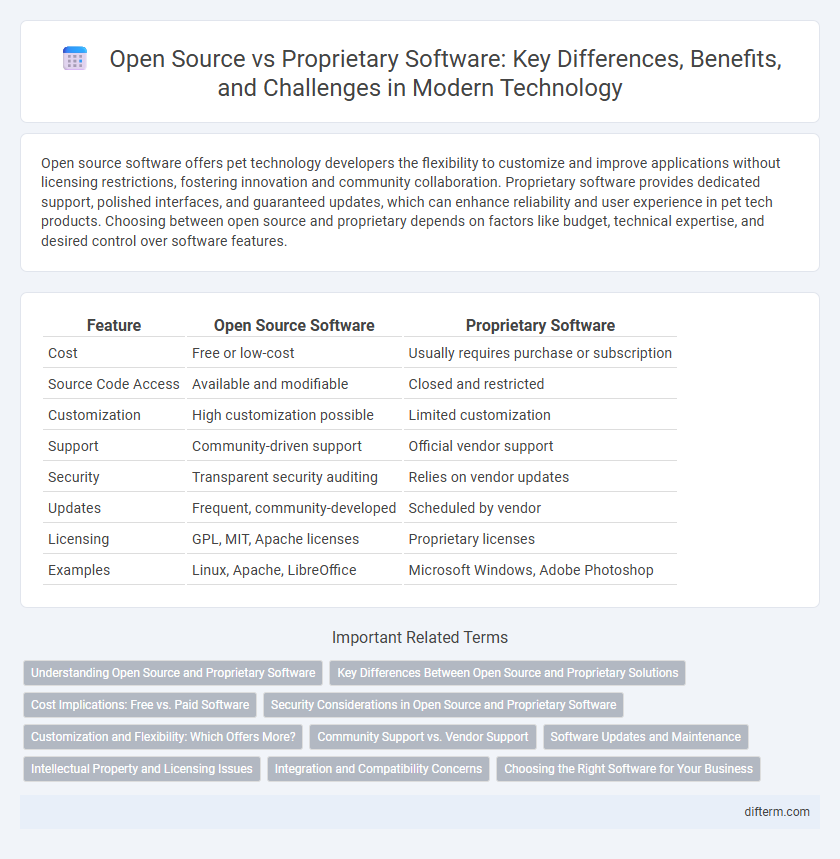
| Feature | Open Source Software | Proprietary Software |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free or low-cost | Usually requires purchase or subscription |
| Source Code Access | Available and modifiable | Closed and restricted |
| Customization | High customization possible | Limited customization |
| Support | Community-driven support | Official vendor support |
| Security | Transparent security auditing | Relies on vendor updates |
| Updates | Frequent, community-developed | Scheduled by vendor |
| Licensing | GPL, MIT, Apache licenses | Proprietary licenses |
| Examples | Linux, Apache, LibreOffice | Microsoft Windows, Adobe Photoshop |
Understanding Open Source and Proprietary Software
Open source software offers access to its source code, enabling users to modify, distribute, and improve the software freely, which fosters collaboration and transparency within developer communities. Proprietary software, developed and owned by companies, restricts access to its source code, providing users with licenses that limit modification and redistribution, ensuring controlled innovation and revenue generation. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for businesses and individuals when selecting software solutions based on factors like cost, customization, security, and support.
Key Differences Between Open Source and Proprietary Solutions
Open source software allows users to access, modify, and distribute its source code freely, fostering collaboration and rapid innovation, while proprietary software restricts access to its source code, maintaining control over features and distribution. Open source solutions often have lower upfront costs and enhanced security through transparency, whereas proprietary software typically offers dedicated customer support and streamlined user experiences. Licensing models differ significantly, with open source relying on public licenses like GPL, and proprietary software governed by restrictive commercial licenses.
Cost Implications: Free vs. Paid Software
Open source software offers significant cost savings by eliminating licensing fees, making it an attractive choice for startups and small businesses focused on budget constraints. Proprietary software, while requiring upfront payments and ongoing subscription costs, typically provides dedicated support, regular updates, and enhanced security features. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including maintenance and training expenses, is essential when choosing between free open source options and paid proprietary solutions.
Security Considerations in Open Source and Proprietary Software
Open source software offers transparency that enables continuous security auditing by a global community, potentially leading to faster identification and patching of vulnerabilities. Proprietary software relies on internal teams for security, which may limit external scrutiny but provides controlled and consistent updates with dedicated support. Evaluating security considerations requires balancing open collaboration benefits against the structured accountability and confidentiality inherent in proprietary models.
Customization and Flexibility: Which Offers More?
Open source software offers significantly greater customization and flexibility by providing access to its source code, allowing developers to modify, enhance, and tailor applications to specific needs. Proprietary software typically restricts access to its code, limiting users to predefined features and customization options dictated by the vendor. Enterprises seeking adaptable solutions often prefer open source platforms due to their collaborative development model and extensive customization potential.
Community Support vs. Vendor Support
Open source software thrives on robust community support, offering collaborative problem-solving, rapid updates, and extensive user-contributed resources that enhance innovation and flexibility. Proprietary software relies on vendor support, providing structured customer service, guaranteed stability, and dedicated troubleshooting from specialized teams. Understanding the trade-offs between community-driven assistance and professional vendor support is crucial for choosing software solutions that align with organizational needs and risk tolerance.
Software Updates and Maintenance
Open source software offers frequent updates and transparent maintenance driven by a global community of developers, ensuring rapid bug fixes and feature improvements. Proprietary software updates are controlled by the vendor, often released on a fixed schedule with limited user insight into the underlying code changes. Maintenance in open source is typically cost-effective due to community support, whereas proprietary software maintenance may require costly licenses and vendor dependency.
Intellectual Property and Licensing Issues
Open source software grants users the freedom to modify, distribute, and examine the source code, fostering collaborative innovation but requiring adherence to licenses like GPL or MIT that enforce copyleft or permissive terms. Proprietary software restricts access to source code and prohibits unauthorized copying or modification, protecting intellectual property through strict licensing agreements that safeguard revenue and control over software distribution. Both models present distinct challenges in intellectual property management, with open source emphasizing community-driven rights and proprietary software focusing on exclusive ownership and monetization.
Integration and Compatibility Concerns
Open source software offers extensive integration capabilities due to transparent code and community-driven plugins, enhancing compatibility across diverse systems and platforms. Proprietary software often restricts integration options, relying on vendor-specific APIs that can limit interoperability with third-party applications. Enterprises must evaluate integration flexibility and long-term compatibility to ensure seamless workflows and reduce vendor lock-in risks.
Choosing the Right Software for Your Business
Selecting the right software for your business depends on factors such as cost, customization, security, and support. Open source software offers greater flexibility and lower upfront costs, making it ideal for businesses with technical expertise and a need for customization. Proprietary software provides dedicated support and enhanced security features, often suitable for companies requiring reliable service and compliance with industry standards.
Open Source vs Proprietary Software Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com