5G NR offers significantly faster data speeds and lower latency compared to LTE, enabling seamless connectivity for smart pet devices. Enhanced capacity and reliability of 5G NR support real-time tracking and high-definition video streaming for pet monitoring. LTE remains widely available but is gradually being outpaced by the advanced performance of 5G NR in pet technology applications.
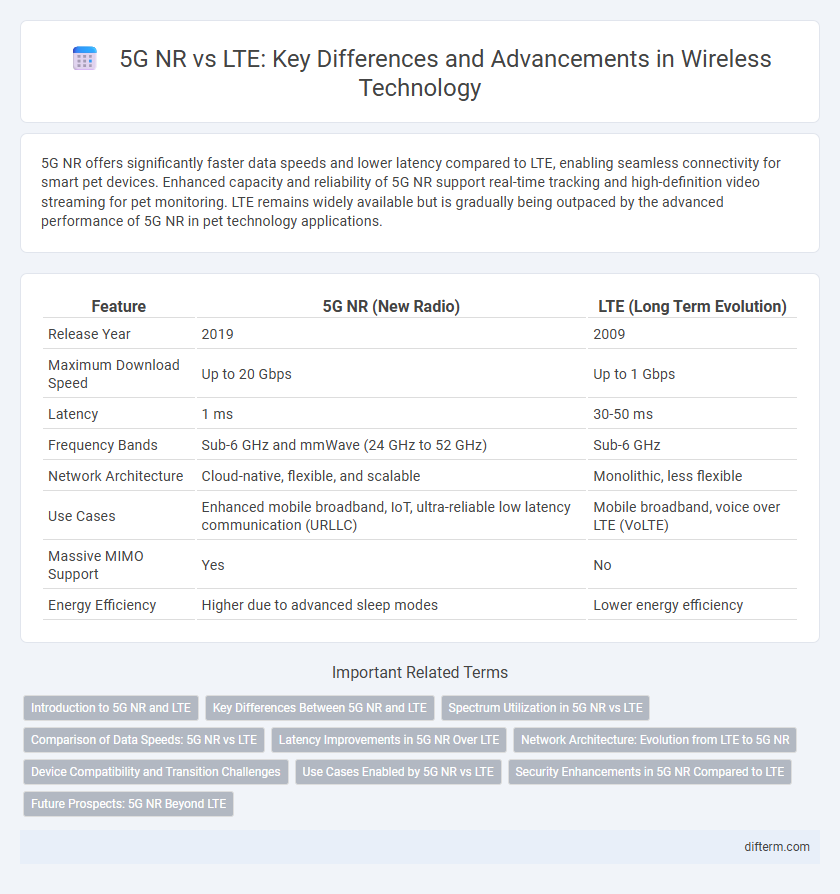
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 5G NR (New Radio) | LTE (Long Term Evolution) |
|---|---|---|
| Release Year | 2019 | 2009 |
| Maximum Download Speed | Up to 20 Gbps | Up to 1 Gbps |
| Latency | 1 ms | 30-50 ms |
| Frequency Bands | Sub-6 GHz and mmWave (24 GHz to 52 GHz) | Sub-6 GHz |
| Network Architecture | Cloud-native, flexible, and scalable | Monolithic, less flexible |
| Use Cases | Enhanced mobile broadband, IoT, ultra-reliable low latency communication (URLLC) | Mobile broadband, voice over LTE (VoLTE) |
| Massive MIMO Support | Yes | No |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher due to advanced sleep modes | Lower energy efficiency |
Introduction to 5G NR and LTE
5G NR (New Radio) represents the next generation of wireless technology, designed to provide significantly higher speeds, lower latency, and enhanced capacity compared to LTE (Long-Term Evolution). LTE, widely deployed since 2009, serves as a 4G standard offering reliable broadband connectivity but with limitations in supporting massive IoT and ultra-reliable communication. 5G NR introduces advanced features like flexible numerology, massive MIMO, and beamforming to meet the demands of diverse applications including smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality.
Key Differences Between 5G NR and LTE
5G NR (New Radio) offers significantly higher data rates, lower latency, and greater network capacity compared to LTE, enabling advanced applications like IoT and enhanced mobile broadband. Unlike LTE's reliance on sub-6 GHz bands, 5G NR utilizes a wider spectrum including millimeter-wave frequencies for faster speeds and reduced congestion. Key differences also include 5G NR's flexible numerology and advanced Massive MIMO technology, which improve spectral efficiency and support diverse use cases beyond LTE's capabilities.
Spectrum Utilization in 5G NR vs LTE
5G NR significantly enhances spectrum utilization compared to LTE by supporting a broader range of frequency bands, including millimeter wave (mmWave) bands above 24 GHz for ultra-high capacity. The dynamic spectrum sharing (DSS) feature in 5G NR allows simultaneous use of the same spectrum for LTE and 5G, improving efficiency and reducing fragmentation. Advanced technologies such as beamforming and massive MIMO in 5G NR optimize spectrum use by directing signals more precisely, resulting in higher throughput and lower latency.
Comparison of Data Speeds: 5G NR vs LTE
5G NR delivers peak download speeds up to 10 Gbps, significantly surpassing LTE's maximum of around 1 Gbps. The enhanced bandwidth and advanced modulation techniques in 5G NR enable faster data transmission and lower latency compared to LTE's 4G technology. This speed improvement drives better support for high-demand applications like ultra-high-definition streaming, virtual reality, and real-time gaming.
Latency Improvements in 5G NR Over LTE
5G NR significantly reduces latency compared to LTE, achieving end-to-end delays as low as 1 millisecond, whereas LTE typically experiences latencies around 30 to 50 milliseconds. This latency improvement is enabled by 5G NR's advanced air interface design, flexible frame structure, and enhanced scheduling algorithms. Lower latency in 5G NR supports critical applications like autonomous driving, augmented reality, and real-time industrial automation, which require near-instantaneous communication.
Network Architecture: Evolution from LTE to 5G NR
The network architecture has evolved significantly from LTE to 5G NR, introducing a flexible and modular design that supports diverse use cases and improved efficiency. Unlike the monolithic EPC (Evolved Packet Core) in LTE, 5G NR employs a service-based architecture (SBA) with a cloud-native core network called 5GC, enabling dynamic resource allocation and network slicing. This evolution enhances scalability, reduces latency, and supports massive IoT connectivity and ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC).
Device Compatibility and Transition Challenges
5G NR devices require advanced chipsets supporting new radio frequencies and modulation schemes, resulting in limited backward compatibility with LTE-only hardware. Transition challenges include the need for dual-mode devices capable of seamless handover between 5G NR and LTE networks to ensure consistent connectivity. Network operators must address interoperability issues and optimize spectrum allocation to support coexistence during the migration phase.
Use Cases Enabled by 5G NR vs LTE
5G NR enables ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC) essential for autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and remote surgery, surpassing LTE's capabilities. Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) in 5G NR supports immersive AR/VR experiences and 8K video streaming, which LTE networks cannot efficiently handle due to bandwidth constraints. Massive machine-type communications (mMTC) in 5G facilitate large-scale IoT deployments, offering higher device density and energy efficiency compared to LTE.
Security Enhancements in 5G NR Compared to LTE
5G NR introduces advanced security features such as enhanced encryption algorithms and improved integrity protection, surpassing LTE's capabilities in safeguarding data confidentiality and user privacy. Network slicing in 5G NR enables isolated and secure virtual networks, reducing the risk of cross-network attacks that LTE architecture cannot effectively mitigate. Furthermore, 5G NR incorporates robust authentication mechanisms like 5G-AKA, offering stronger resistance against impersonation and replay attacks compared to LTE's EPS-AKA protocol.
Future Prospects: 5G NR Beyond LTE
5G NR leverages advanced technologies such as massive MIMO, beamforming, and network slicing to deliver ultra-low latency, higher throughput, and improved energy efficiency beyond LTE capabilities. The integration of mmWave frequencies and enhanced mobile broadband features positions 5G NR as the foundation for emerging applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and Industry 4.0. Continuous evolution through releases like 3GPP Release 17 and beyond ensures 5G NR supports scalable IoT networks and paves the way for 6G innovations.
5G NR vs LTE Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com