Tokenism in social pet communities often reduces pets to mere symbols without real inclusion or influence, undermining genuine diversity. Authentic representation ensures pets of all breeds and backgrounds are valued equitably, fostering a more inclusive and meaningful social environment. True representation promotes respect and understanding, moving beyond superficial inclusion to celebrate every pet's unique role.
Table of Comparison
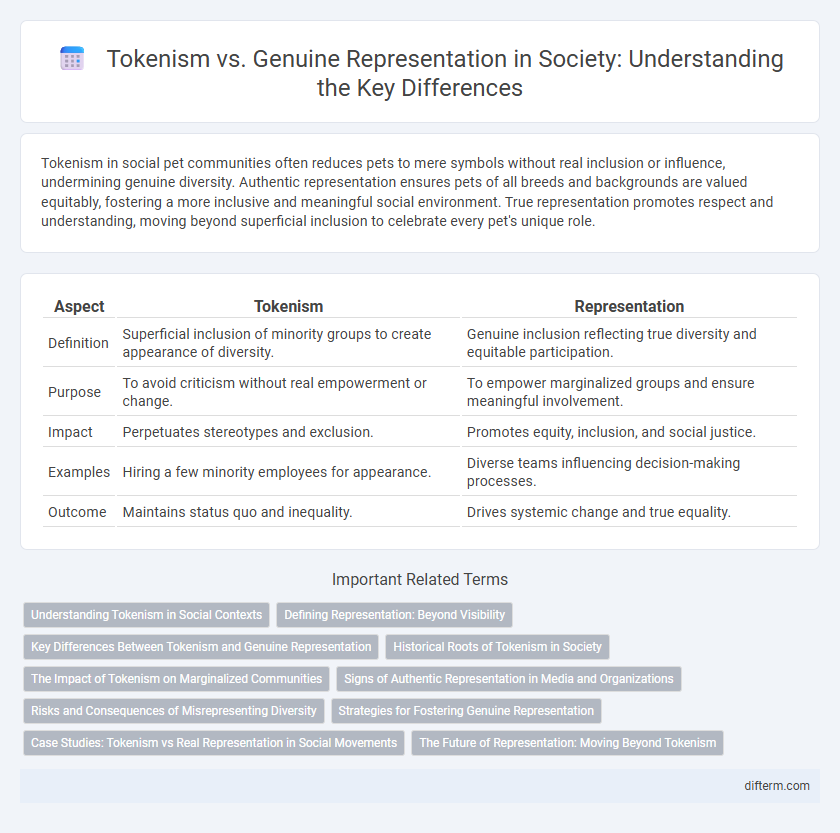
| Aspect | Tokenism | Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Superficial inclusion of minority groups to create appearance of diversity. | Genuine inclusion reflecting true diversity and equitable participation. |
| Purpose | To avoid criticism without real empowerment or change. | To empower marginalized groups and ensure meaningful involvement. |
| Impact | Perpetuates stereotypes and exclusion. | Promotes equity, inclusion, and social justice. |
| Examples | Hiring a few minority employees for appearance. | Diverse teams influencing decision-making processes. |
| Outcome | Maintains status quo and inequality. | Drives systemic change and true equality. |
Understanding Tokenism in Social Contexts
Tokenism in social contexts occurs when marginalized groups are included superficially to give the appearance of diversity without meaningful empowerment or influence. This practice often results in symbolic gestures rather than genuine representation, limiting the ability of individuals to affect change within institutions or communities. True representation requires authentic inclusion that values diverse perspectives and promotes equitable participation beyond mere token presence.
Defining Representation: Beyond Visibility
Representation extends beyond mere visibility by ensuring the meaningful inclusion and empowerment of diverse groups within social, political, and organizational contexts. Unlike tokenism, which often reduces individuals to symbolic roles without real influence, true representation advocates for equitable participation and the acknowledgment of varied perspectives. This depth of engagement fosters authentic inclusion, driving systemic change and social justice.
Key Differences Between Tokenism and Genuine Representation
Tokenism involves superficial inclusion of marginalized groups to create an illusion of diversity without granting real power or influence. Genuine representation means authentic participation where individuals from diverse backgrounds have decision-making authority and their perspectives shape policies or culture. The key difference lies in intent and impact: tokenism emphasizes appearance and compliance, while representation fosters equity and meaningful change.
Historical Roots of Tokenism in Society
Tokenism has deep historical roots dating back to periods of systemic inequality where minority groups were superficially included to give the appearance of diversity without offering real power or influence. This practice emerged as a means to maintain existing social hierarchies by allowing minimal representation that avoids structural change. Understanding this legacy is crucial to distinguishing tokenism from genuine representation, which involves meaningful inclusion and equity.
The Impact of Tokenism on Marginalized Communities
Tokenism often leads to superficial inclusion of marginalized communities without granting real power or influence, perpetuating feelings of invisibility and token validation. It undermines authentic representation by reducing individuals to symbols rather than valuing their diverse perspectives and contributions. This practice hampers social equity efforts and deepens systemic inequalities by masking exclusion behind a facade of diversity.
Signs of Authentic Representation in Media and Organizations
Authentic representation in media and organizations is evidenced by diverse voices in leadership roles, equitable portrayal of communities without stereotypes, and consistent inclusivity across all levels of content creation and decision-making. Genuine representation prioritizes lived experiences, fosters cultural sensitivity, and implements measurable diversity goals beyond surface-level appearances. These signs differentiate meaningful inclusion from tokenism, which often manifests as performative gestures lacking substantial impact or power sharing.
Risks and Consequences of Misrepresenting Diversity
Misrepresenting diversity through tokenism often leads to superficial inclusion that fails to address deeper systemic inequalities, resulting in alienation and reduced trust among marginalized groups. This practice risks perpetuating stereotypes and undermines genuine representation, limiting diverse voices in decision-making processes. The consequences include diminished organizational credibility, reduced social cohesion, and hindered progress toward equitable and inclusive environments.
Strategies for Fostering Genuine Representation
Effective strategies for fostering genuine representation emphasize inclusive decision-making processes and equitable resource allocation that empower marginalized communities. Organizations should implement transparent accountability measures and prioritize authentic engagement over symbolic gestures to avoid tokenism. Continuous education on cultural competence and intersectionality further strengthens representation by addressing systemic barriers and promoting diverse leadership.
Case Studies: Tokenism vs Real Representation in Social Movements
Case studies reveal that tokenism in social movements often involves superficial inclusion of marginalized groups without meaningful power or decision-making roles, undermining genuine representation. Real representation is characterized by active participation and leadership from marginalized communities, leading to tangible policy changes and social impact. Examples include the contrast between performative diversity in corporate-sponsored events and grassroots organizations where leaders from underrepresented groups drive the agenda.
The Future of Representation: Moving Beyond Tokenism
True representation requires meaningful inclusion of diverse voices in decision-making processes, reflecting demographics and experiences authentically. Moving beyond tokenism involves creating equitable platforms where underrepresented groups wield real influence rather than symbolic presence. Advancements in policy reforms and organizational culture shifts demonstrate promising strides toward genuine representation in social, political, and corporate spheres.
Tokenism vs Representation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com