In social pet dynamics, status refers to the hierarchical standing an animal holds within the group, often linked to dominance or leadership. Role involves the specific functions or behaviors an individual consistently performs, such as caregiver or protector. Understanding the distinction between status and role is crucial for managing group interactions and ensuring harmony among social pets.
Table of Comparison
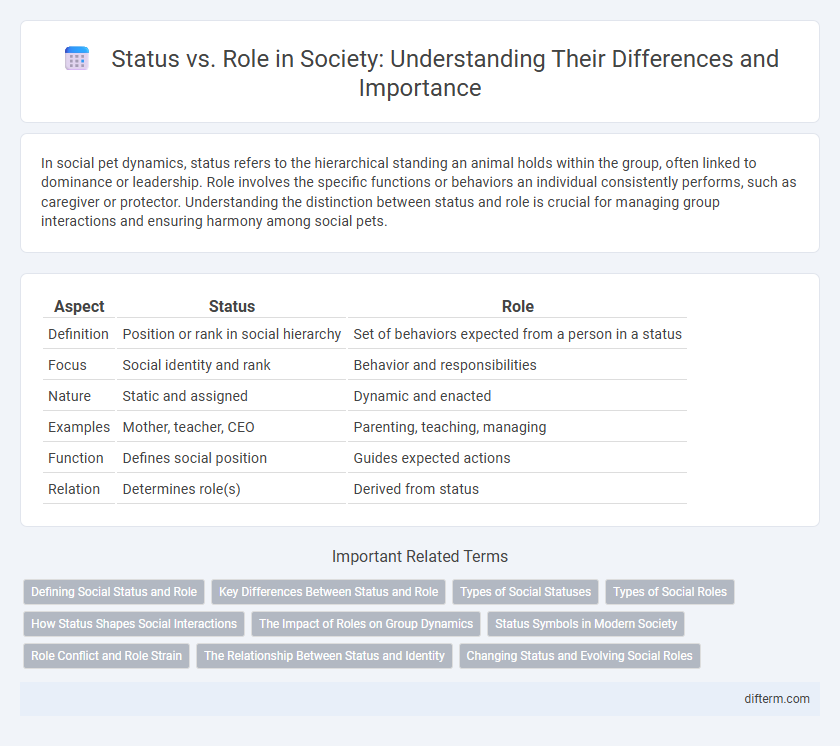
| Aspect | Status | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Position or rank in social hierarchy | Set of behaviors expected from a person in a status |
| Focus | Social identity and rank | Behavior and responsibilities |
| Nature | Static and assigned | Dynamic and enacted |
| Examples | Mother, teacher, CEO | Parenting, teaching, managing |
| Function | Defines social position | Guides expected actions |
| Relation | Determines role(s) | Derived from status |
Defining Social Status and Role
Social status refers to the recognized position an individual holds within a social hierarchy, often influencing their access to resources and social power. A social role encompasses the expected behaviors, responsibilities, and norms associated with that status in specific contexts. Understanding the distinction between status and role is essential for analyzing social dynamics and individual identity within groups.
Key Differences Between Status and Role
Status represents an individual's hierarchical position within a social structure, while role refers to the expected behaviors associated with that position. Status is often static and recognized by society, whereas roles are dynamic and involve specific duties and responsibilities. Understanding the distinction between status and role is essential for analyzing social interactions and organizational behavior.
Types of Social Statuses
Social statuses can be categorized into ascribed statuses, which are assigned at birth such as race, gender, or family heritage, and achieved statuses, earned through personal effort like education or occupation. Master status dominates an individual's identity and influences how others perceive them, often overshadowing other statuses. Understanding these types clarifies social dynamics and individual behaviors within various societal structures.
Types of Social Roles
Social roles encompass a variety of types including ascribed roles, achieved roles, and role expectations that guide individual behavior within a society. Ascribed roles, such as gender or ethnicity, are assigned at birth and remain relatively fixed, while achieved roles, like occupation or education level, are acquired through personal effort and experience. Understanding these types clarifies the dynamic interaction between an individual's status and their expected social behaviors.
How Status Shapes Social Interactions
Status profoundly influences social interactions by defining power dynamics and expectations within groups. Higher status individuals often command more attention, resources, and deference, shaping conversational roles and decision-making processes. This hierarchy affects communication patterns, access to social networks, and the distribution of privileges among members of society.
The Impact of Roles on Group Dynamics
Roles significantly shape group dynamics by defining expectations, responsibilities, and interactions among members. Clear role assignments enhance coordination and cooperation, leading to increased group cohesion and productivity. Conversely, ambiguous or conflicting roles often result in misunderstandings and reduced collective performance.
Status Symbols in Modern Society
Status symbols in modern society serve as visible indicators of social standing, reflecting wealth, power, and prestige through possessions like luxury cars, designer clothing, and high-end technology. These symbols transcend traditional roles by shaping perceptions and influencing social interactions, often signaling success and identity in competitive environments. The shift from role-based respect to symbol-based recognition highlights how material culture increasingly defines social hierarchy.
Role Conflict and Role Strain
Role conflict occurs when an individual faces incompatible demands from different social roles, such as balancing the expectations of a parent and employee simultaneously. Role strain arises from tension within a single role, like a manager struggling to meet both organizational goals and employees' needs. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for comprehending stressors impacting social behavior and identity management.
The Relationship Between Status and Identity
Status significantly shapes an individual's social identity by influencing how they are perceived and how they perceive themselves within a community. Roles associated with specific statuses provide behavioral expectations that reinforce identity and social structure. Understanding the dynamic relationship between status and identity is crucial for analyzing social interactions and the formation of self-concept.
Changing Status and Evolving Social Roles
Changing status reshapes individual identity within social hierarchies, reflecting shifts in power, privilege, or reputation. Evolving social roles adapt to cultural, economic, and technological transformations, influencing expectations and behaviors across communities. These dynamics underscore the fluid interplay between personal status and collective roles in society.
status vs role Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com