A social pet's digital identity captures curated behaviors and interactions tailored for online communities, often differing from their real identity, which encompasses genuine personality traits and offline interactions. Understanding the contrast between these identities helps in managing expectations and fostering authentic connections both virtually and in the physical world. Bridging the gap between digital and real identities enhances trust and enriches social experiences for pets and their owners alike.
Table of Comparison
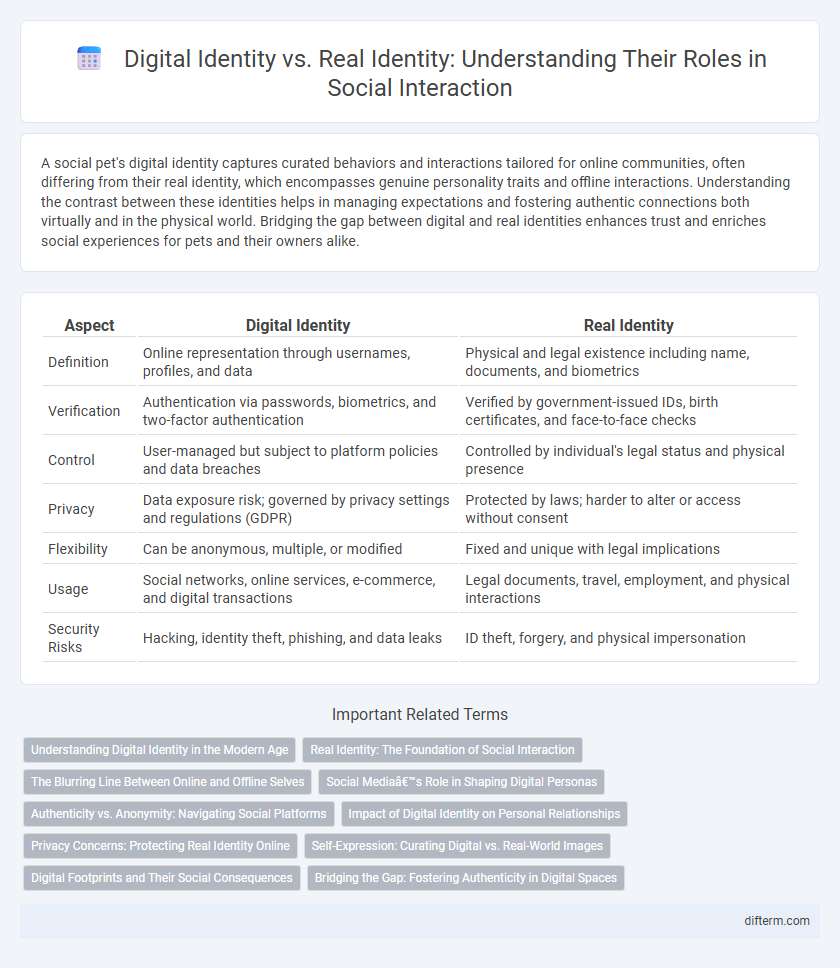
| Aspect | Digital Identity | Real Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Online representation through usernames, profiles, and data | Physical and legal existence including name, documents, and biometrics |
| Verification | Authentication via passwords, biometrics, and two-factor authentication | Verified by government-issued IDs, birth certificates, and face-to-face checks |
| Control | User-managed but subject to platform policies and data breaches | Controlled by individual's legal status and physical presence |
| Privacy | Data exposure risk; governed by privacy settings and regulations (GDPR) | Protected by laws; harder to alter or access without consent |
| Flexibility | Can be anonymous, multiple, or modified | Fixed and unique with legal implications |
| Usage | Social networks, online services, e-commerce, and digital transactions | Legal documents, travel, employment, and physical interactions |
| Security Risks | Hacking, identity theft, phishing, and data leaks | ID theft, forgery, and physical impersonation |
Understanding Digital Identity in the Modern Age
Digital identity encompasses the online representation of an individual through data, credentials, and interactions across various platforms, distinct from their real-world identity. Modern digital identity management involves authentication methods, privacy controls, and the protection of personal information against cyber threats. Understanding the implications of digital identities allows individuals and organizations to navigate social media, e-commerce, and digital services securely and effectively.
Real Identity: The Foundation of Social Interaction
Real identity serves as the cornerstone of genuine social interaction, providing authenticity and trust that digital identities often lack. It encompasses an individual's true characteristics, experiences, and values, which are essential for meaningful connections and effective communication. Rooted in physical presence and verified through tangible interactions, real identity fosters deeper empathy and mutual understanding in social relationships.
The Blurring Line Between Online and Offline Selves
The blurring line between digital identity and real identity challenges traditional concepts of self as online personas increasingly influence offline behaviors and social interactions. Digital footprints, curated profiles, and virtual communities contribute to complex identity narratives that intertwine with physical-world experiences. This convergence raises critical questions about authenticity, privacy, and the psychological impact of maintaining multiple selves across digital and real environments.
Social Media’s Role in Shaping Digital Personas
Social media platforms significantly influence the construction of digital identities by enabling users to curate and project idealized versions of themselves, often prioritizing engagement metrics over authenticity. Algorithms amplify content that aligns with popular trends, reinforcing selective self-presentation and creating feedback loops that shape user behavior and perception. This dynamic results in digital personas that may diverge substantially from real identities, affecting social interactions and psychological well-being.
Authenticity vs. Anonymity: Navigating Social Platforms
Digital identity on social platforms often challenges the balance between authenticity and anonymity, where users craft online personas that may differ significantly from their real identities. Authenticity builds trust and fosters genuine connections, while anonymity provides privacy and freedom from judgment, yet can lead to misrepresentation or cyberbullying. Navigating these dynamics requires platforms to implement features that encourage truthful self-expression while protecting users' rights to anonymity and security.
Impact of Digital Identity on Personal Relationships
Digital identity shapes how individuals present themselves online, often influencing trust and communication patterns in personal relationships. Misalignment between digital and real identities can lead to misunderstandings, diminished emotional connection, and challenges in authenticity. Social platforms and digital footprints also affect relationship dynamics by altering privacy expectations and social interactions.
Privacy Concerns: Protecting Real Identity Online
Protecting real identity online requires robust privacy measures to prevent unauthorized access and identity theft in digital spaces. Users must employ strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and privacy-focused platforms to mitigate risks associated with digital identity exposure. Safeguarding personal data ensures greater control over online presence and limits potential misuse or surveillance by malicious actors.
Self-Expression: Curating Digital vs. Real-World Images
Digital identity allows individuals to selectively showcase aspects of their personality and achievements, often highlighting idealized versions to shape social perceptions. Real-world identity encompasses a fuller, more nuanced set of traits shaped by direct experiences, relationships, and context-specific behaviors. The contrast between curated digital self-expression and authentic real-world presence creates complex dynamics in how people connect, trust, and communicate socially.
Digital Footprints and Their Social Consequences
Digital footprints, comprising online activities such as social media interactions, browsing history, and digital transactions, significantly shape an individual's digital identity, often diverging from their real identity. These footprints contribute to social consequences like privacy invasion, reputation management challenges, and the risk of digital discrimination in employment or social circles. Understanding the disparity between digital and real identities is crucial for mitigating negative social impacts and fostering responsible online behavior.
Bridging the Gap: Fostering Authenticity in Digital Spaces
Bridging the gap between digital identity and real identity requires cultivating genuine self-expression and trust in online interactions. Encouraging platforms to implement transparent verification methods enhances authenticity while safeguarding privacy. Emphasizing consistent and honest communication promotes deeper connections, reducing misrepresentation in social digital spaces.
digital identity vs real identity Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com