Social welfare aims to provide immediate support and resources to improve the well-being of individuals and communities, addressing their basic needs and reducing inequality. Social justice seeks to transform underlying social structures and policies to ensure fairness, equal rights, and long-term systemic change. In the context of social issues, social welfare offers practical relief, while social justice demands fundamental reform.
Table of Comparison
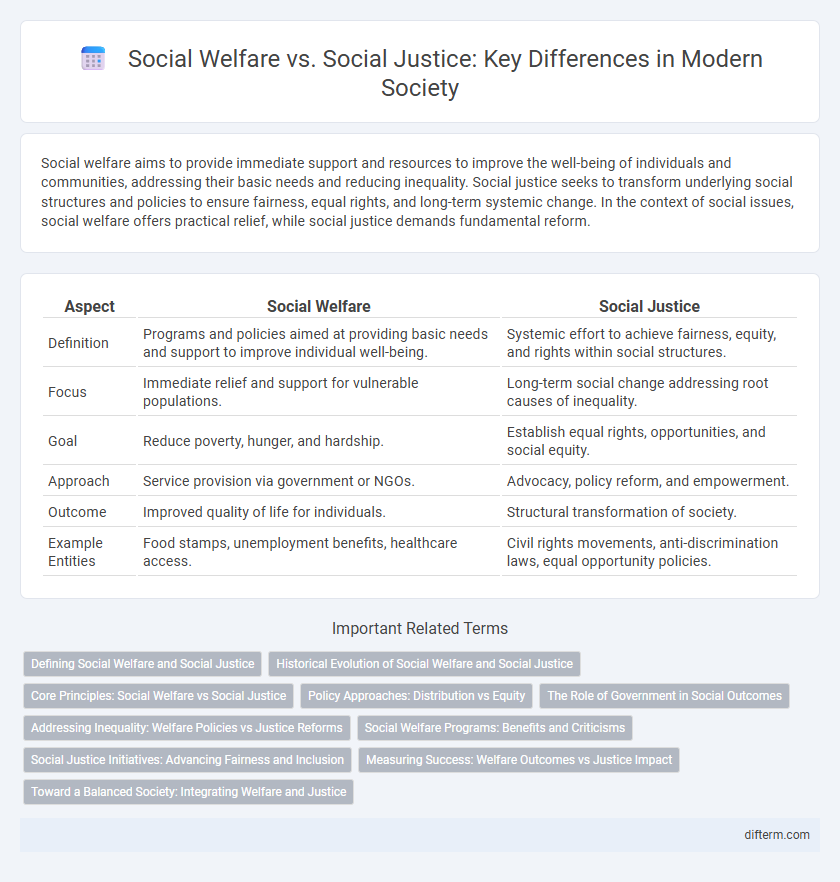
| Aspect | Social Welfare | Social Justice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Programs and policies aimed at providing basic needs and support to improve individual well-being. | Systemic effort to achieve fairness, equity, and rights within social structures. |
| Focus | Immediate relief and support for vulnerable populations. | Long-term social change addressing root causes of inequality. |
| Goal | Reduce poverty, hunger, and hardship. | Establish equal rights, opportunities, and social equity. |
| Approach | Service provision via government or NGOs. | Advocacy, policy reform, and empowerment. |
| Outcome | Improved quality of life for individuals. | Structural transformation of society. |
| Example Entities | Food stamps, unemployment benefits, healthcare access. | Civil rights movements, anti-discrimination laws, equal opportunity policies. |
Defining Social Welfare and Social Justice
Social welfare refers to organized efforts and programs that provide support to improve the well-being of individuals and communities, emphasizing economic assistance, healthcare, and housing. Social justice focuses on the equitable distribution of resources, rights, and opportunities, addressing systemic inequalities and advocating for fairness in social policies. Both concepts aim to enhance quality of life, but social welfare often addresses immediate needs while social justice seeks long-term structural change.
Historical Evolution of Social Welfare and Social Justice
The historical evolution of social welfare and social justice reveals distinct yet interconnected paths, with social welfare emerging from charitable traditions aimed at alleviating poverty, while social justice developed from movements centered on equity, human rights, and systemic reform. Key milestones include the establishment of welfare states in the early 20th century, influenced by industrialization and urbanization, and the civil rights movements of the mid-20th century that emphasized social justice principles. This evolution highlights a shift from basic relief efforts toward comprehensive policies addressing structural inequalities and promoting equal opportunities.
Core Principles: Social Welfare vs Social Justice
Social welfare emphasizes providing immediate support and resources to improve individuals' well-being, focusing on alleviating poverty and meeting basic needs through programs like healthcare, housing, and food assistance. Social justice centers on addressing systemic inequalities by promoting fairness, equity, and equal rights across institutions, advocating for policy reform and structural changes that dismantle discrimination and oppression. Both frameworks aim to enhance quality of life but differ in approach: social welfare targets short-term relief, while social justice pursues long-term societal transformation.
Policy Approaches: Distribution vs Equity
Social welfare policies primarily emphasize the distribution of resources to ensure basic needs are met, aiming to alleviate immediate hardships through programs like unemployment benefits and food assistance. Social justice approaches focus on equity, targeting systemic inequalities by addressing root causes such as discrimination and unequal power structures to create fair opportunities for all. Effective policy design integrates both distributional support and equity-driven reforms to balance immediate relief with long-term structural change.
The Role of Government in Social Outcomes
Government plays a critical role in shaping social outcomes by implementing policies that promote social welfare through direct assistance programs such as healthcare, housing, and unemployment benefits. Social justice efforts require government action to address systemic inequities related to race, gender, and economic status, ensuring fair access to resources and opportunities. Effective governance balances social welfare initiatives with social justice reforms to create inclusive, equitable communities that foster long-term societal well-being.
Addressing Inequality: Welfare Policies vs Justice Reforms
Social welfare policies primarily focus on alleviating immediate needs through financial aid, healthcare, and housing support, aiming to reduce the effects of inequality. Social justice reforms target systemic inequalities by advocating for legal changes, equal rights, and institutional restructuring to create lasting equitable opportunities. Combining welfare measures with justice reforms ensures both short-term relief and long-term transformation in addressing social disparities.
Social Welfare Programs: Benefits and Criticisms
Social welfare programs provide essential support such as food assistance, housing subsidies, and healthcare access, aiming to reduce poverty and improve quality of life for vulnerable populations. Critics argue these programs may foster dependency, strain government budgets, and sometimes fail to address underlying systemic issues. Balancing immediate relief with long-term empowerment remains a central debate in shaping effective social welfare policies.
Social Justice Initiatives: Advancing Fairness and Inclusion
Social justice initiatives prioritize equitable access to resources, opportunities, and rights, striving to dismantle systemic barriers that marginalize vulnerable populations. These programs emphasize inclusion by promoting policies that address discrimination, economic inequality, and social exclusion. By advancing fairness, social justice efforts foster a more inclusive society where all individuals have the chance to thrive regardless of their background.
Measuring Success: Welfare Outcomes vs Justice Impact
Measuring success in social welfare focuses on quantifiable outcomes like poverty reduction rates, access to healthcare, and improved living standards. Social justice impact, however, emphasizes systemic change by evaluating policy reforms, equity in resource distribution, and the empowerment of marginalized communities. Both approaches require distinct metrics: social welfare relies on statistical indicators, while social justice demands qualitative analysis of power dynamics and societal transformation.
Toward a Balanced Society: Integrating Welfare and Justice
Balancing social welfare and social justice requires integrating policies that address immediate needs while promoting long-term equality and fairness. Effective social welfare programs provide essential support such as healthcare, housing, and education, which lay the foundation for social justice by reducing systemic disparities. Achieving a balanced society depends on collaborative efforts that ensure equitable resource distribution and empower marginalized communities to participate fully in social and economic life.
social welfare vs social justice Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com