Social trust forms the foundation of genuine connections in a social pet network by fostering confidence and reliability among users. Social reciprocity encourages mutual exchange and active participation, reinforcing the sense of community and collaboration. Together, social trust and reciprocity create a balanced environment that enhances engagement and strengthens relationships within the platform.
Table of Comparison
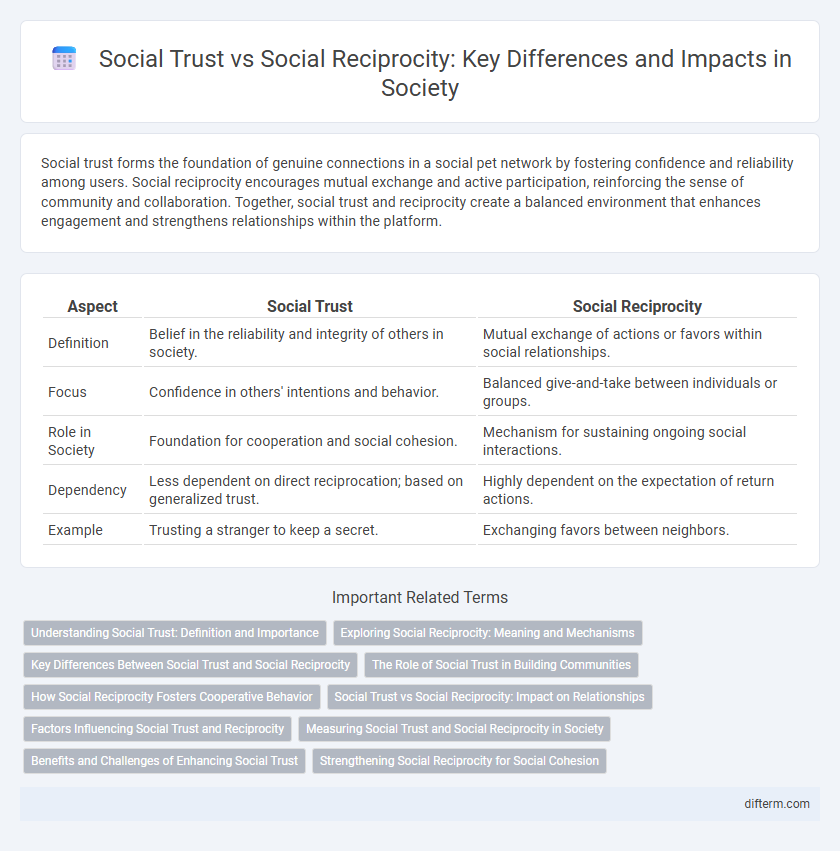
| Aspect | Social Trust | Social Reciprocity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in the reliability and integrity of others in society. | Mutual exchange of actions or favors within social relationships. |
| Focus | Confidence in others' intentions and behavior. | Balanced give-and-take between individuals or groups. |
| Role in Society | Foundation for cooperation and social cohesion. | Mechanism for sustaining ongoing social interactions. |
| Dependency | Less dependent on direct reciprocation; based on generalized trust. | Highly dependent on the expectation of return actions. |
| Example | Trusting a stranger to keep a secret. | Exchanging favors between neighbors. |
Understanding Social Trust: Definition and Importance
Social trust refers to the belief in the reliability, integrity, and honesty of others within a community, serving as a foundation for cooperative behavior and social cohesion. It enables individuals to engage in interactions without constant suspicion, reducing transaction costs and fostering collective action. Understanding social trust is crucial for developing effective policies and initiatives that promote social stability, economic development, and inclusive governance.
Exploring Social Reciprocity: Meaning and Mechanisms
Social reciprocity involves mutual exchange of actions or benefits that reinforce cooperative relationships and enhance social trust within communities. It operates through mechanisms such as norm enforcement, reputation building, and emotional bonding, which encourage individuals to respond to positive behaviors with similar actions. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for fostering social cohesion and sustainable collaboration in diverse social environments.
Key Differences Between Social Trust and Social Reciprocity
Social trust refers to the belief in the reliability and integrity of others within a community, fostering cooperation without immediate exchange expectations. Social reciprocity involves mutual exchange actions where individuals respond to others' behavior with equivalent positive or negative actions, promoting ongoing relational interactions. Key differences lie in trust being a foundational attitude toward others, while reciprocity is behavioral, emphasizing balanced give-and-take in social dynamics.
The Role of Social Trust in Building Communities
Social trust serves as the foundation for cohesive communities by fostering a shared belief in the reliability and integrity of others, which reduces uncertainty and promotes cooperation. High levels of social trust enable more effective social reciprocity, where individuals willingly engage in mutual exchanges, reinforcing community bonds. Research indicates that communities with strong social trust experience enhanced collective action, increased civic participation, and greater resilience in facing social challenges.
How Social Reciprocity Fosters Cooperative Behavior
Social reciprocity, characterized by mutual exchange of actions or favors, significantly strengthens cooperative behavior by creating a cycle of trust and positive reinforcement among individuals. This process encourages participants to act in ways that benefit the group, knowing their contributions will likely be reciprocated, thus enhancing collective welfare. Empirical studies highlight that communities with higher levels of social reciprocity exhibit increased cooperation, leading to more resilient social networks and improved collaboration outcomes.
Social Trust vs Social Reciprocity: Impact on Relationships
Social trust forms the foundation for stable relationships by fostering confidence and predictability between individuals, while social reciprocity emphasizes mutual exchange and fairness that reinforce cooperation. High social trust reduces the need for constant verification, enabling smoother interpersonal interactions, whereas social reciprocity motivates ongoing support through balanced giving and receiving. Understanding the interplay between social trust and social reciprocity is crucial for building resilient social networks and sustaining long-term relational commitment.
Factors Influencing Social Trust and Reciprocity
Social trust and social reciprocity are influenced by factors such as cultural norms, shared values, and past interactions between individuals or groups. Economic stability, transparency in communication, and perceived fairness also play critical roles in strengthening these social constructs. Strong community networks and consistent positive experiences enhance both trust and reciprocal behavior in social settings.
Measuring Social Trust and Social Reciprocity in Society
Measuring social trust involves surveys assessing individuals' confidence in others and institutions, capturing generalized trust and trustworthiness perceptions. Social reciprocity is quantified through behavioral experiments like the trust game, which observe cooperative exchanges and reciprocal actions among participants. Accurate measurement of both constructs provides critical insights into societal cohesion and collective action potential.
Benefits and Challenges of Enhancing Social Trust
Enhancing social trust fosters community cohesion, promotes cooperative behavior, and reduces transaction costs in social interactions, leading to more effective collective problem-solving and economic growth. Challenges include overcoming historical grievances, mitigating misinformation, and addressing unequal power dynamics that may erode trust between different social groups. Sustained efforts in transparent communication, inclusive policies, and mutual accountability are essential to build and maintain high levels of social trust.
Strengthening Social Reciprocity for Social Cohesion
Strengthening social reciprocity enhances community bonds by fostering mutual support and shared responsibilities, which directly contributes to greater social cohesion. Social reciprocity encourages active engagement and cooperation among members, reinforcing trust and collective well-being. By promoting reciprocal interactions, societies can effectively build resilience and solidarity, essential for addressing common challenges and sustaining harmonious relationships.
social trust vs social reciprocity Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com