Social pets often thrive in dyads, where the interaction between two animals fosters strong bonding and clear communication. However, triads introduce complex social dynamics, requiring pets to navigate alliances and conflicts that can enhance cognitive engagement. Understanding the differences between dyad and triad groupings helps optimize social environments for pets, promoting their mental and emotional well-being.
Table of Comparison
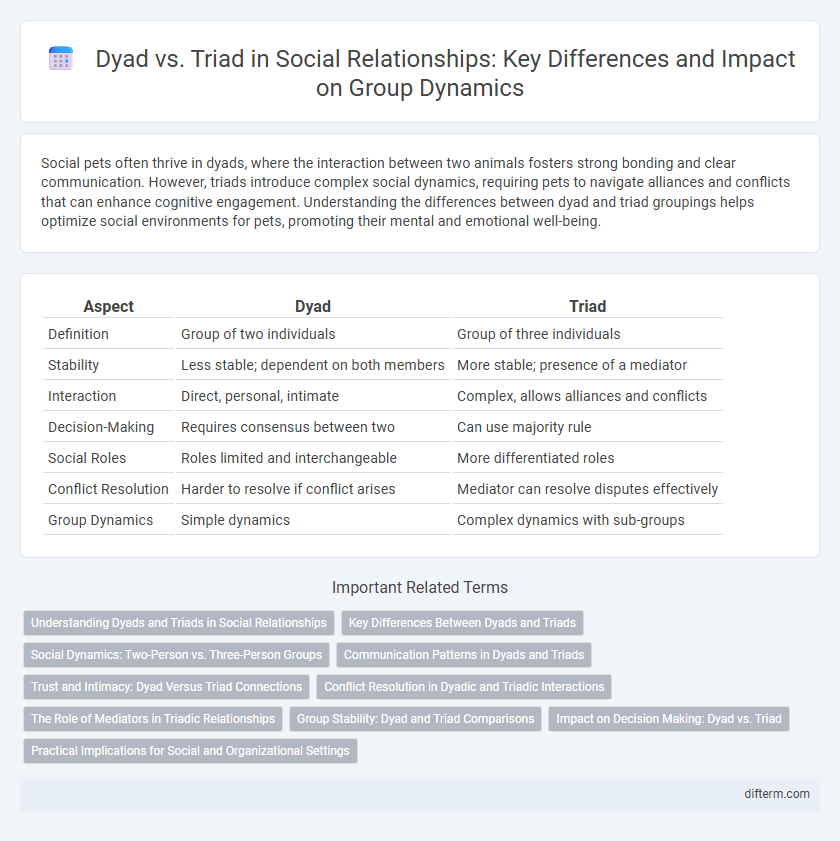
| Aspect | Dyad | Triad |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group of two individuals | Group of three individuals |
| Stability | Less stable; dependent on both members | More stable; presence of a mediator |
| Interaction | Direct, personal, intimate | Complex, allows alliances and conflicts |
| Decision-Making | Requires consensus between two | Can use majority rule |
| Social Roles | Roles limited and interchangeable | More differentiated roles |
| Conflict Resolution | Harder to resolve if conflict arises | Mediator can resolve disputes effectively |
| Group Dynamics | Simple dynamics | Complex dynamics with sub-groups |
Understanding Dyads and Triads in Social Relationships
Dyads consist of two individuals whose interaction is direct and intense, creating a unique and intimate social bond critical for emotional support. Triads introduce a third member, allowing for more complex social dynamics such as mediation, coalition formation, and a diffusion of responsibility. Understanding the distinction between dyads and triads is essential for analyzing the structural and functional differences in social relationships and group behaviors.
Key Differences Between Dyads and Triads
Dyads consist of two individuals engaging in direct and intimate interactions, which fosters strong emotional connections and simpler communication patterns. Triads introduce a third member, creating more complex social dynamics, potential for coalitions, and a shift from one-on-one intimacy to group negotiation. The presence of a third person in triads often stabilizes relationships by distributing social power and enabling conflict mediation.
Social Dynamics: Two-Person vs. Three-Person Groups
Dyads, consisting of two individuals, foster intense, personal interactions where mutual intimacy and direct accountability are prevalent, often resulting in stronger emotional bonds compared to triads. Triads introduce complexity with three individuals, enabling coalition formation, enhanced negotiation, and diversified perspectives that influence group decision-making and social power dynamics. The shift from dyad to triad significantly alters social dynamics by redistributing relational roles and increasing potential for conflict or mediation within the group structure.
Communication Patterns in Dyads and Triads
Communication patterns in dyads typically involve direct, intimate exchanges with clear feedback loops, fostering strong emotional connections and mutual understanding. In triads, communication becomes more complex with the potential for coalition formation, mediation roles, and varied interaction dynamics that can either strengthen group cohesion or create conflict. The presence of a third person introduces negotiation and balancing of perspectives, impacting message clarity and group decision-making processes.
Trust and Intimacy: Dyad Versus Triad Connections
Dyads foster higher levels of trust and intimacy as personalized interactions allow for deeper emotional bonding and mutual understanding. In contrast, triads often experience diluted intimacy due to the divided attention among members, though they can offer more stability and conflict mediation through multiple relational perspectives. Trust in dyads is typically more straightforward to establish and maintain because of direct communication pathways, whereas triads require balancing complex dynamics to sustain trust across all connections.
Conflict Resolution in Dyadic and Triadic Interactions
Conflict resolution in dyadic interactions often relies on direct communication and mutual understanding between two individuals, enabling swift negotiation and compromise. Triadic interactions introduce a third party, which can mediate disputes but may also complicate dynamics by fostering alliances or power imbalances. Effective conflict management in triads requires balancing perspectives to prevent coalition formation and ensure equitable outcomes for all participants.
The Role of Mediators in Triadic Relationships
Mediators play a crucial role in triadic relationships by facilitating communication and resolving conflicts between two other parties, which is less complex than dyadic interactions. Triads enable the emergence of coalitions and social balance, influencing group dynamics and stability through the mediator's ability to negotiate interests. In social networks, this mediation helps prevent breakdowns in trust and fosters cooperation, enhancing overall social cohesion.
Group Stability: Dyad and Triad Comparisons
Dyads, composed of two members, tend to exhibit higher emotional intensity but lower stability compared to triads due to their susceptibility to dissolution if one member withdraws. Triads introduce coalition dynamics and can stabilize group interactions by distributing social roles and responsibilities among three members. The presence of a third member in triads often enhances conflict mediation and continuity, promoting greater overall group stability.
Impact on Decision Making: Dyad vs. Triad
A dyad fosters direct, intimate communication enhancing clarity and trust, but its decision-making can be limited by the absence of diverse perspectives. Triads introduce complexity with three perspectives, encouraging debate and reducing the likelihood of deadlock, which often leads to more balanced and well-rounded decisions. Social scientists note that triads allow coalition-building and dynamic negotiation, significantly impacting group influence and consensus outcomes.
Practical Implications for Social and Organizational Settings
Dyads foster intimate, direct communication and trust, ideal for mentorship and partnerships, while triads introduce complexity with potential alliances and mediation roles, enhancing conflict resolution and group decision-making. Organizations benefit from triads by promoting diverse perspectives and reducing groupthink, improving innovation and problem-solving. Practical application involves leveraging dyads for focused collaboration and triads for dynamic, resilient team structures.
dyad vs triad Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com