Social roles define the expected behaviors and responsibilities individuals assume in a social pet environment, guiding interactions within the community. Social scripts provide structured scenarios or dialogues that shape predictable responses and facilitate smoother communication among pets and their owners. Differentiating social roles from social scripts helps optimize engagement by clarifying behavior expectations versus contextual interaction patterns.
Table of Comparison
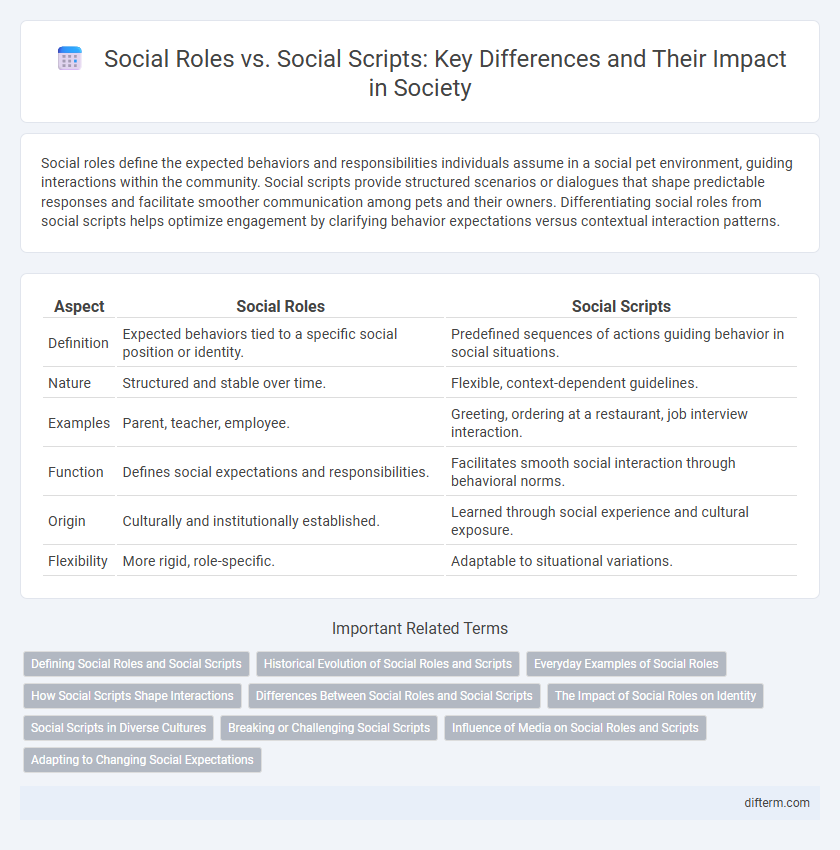
| Aspect | Social Roles | Social Scripts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expected behaviors tied to a specific social position or identity. | Predefined sequences of actions guiding behavior in social situations. |
| Nature | Structured and stable over time. | Flexible, context-dependent guidelines. |
| Examples | Parent, teacher, employee. | Greeting, ordering at a restaurant, job interview interaction. |
| Function | Defines social expectations and responsibilities. | Facilitates smooth social interaction through behavioral norms. |
| Origin | Culturally and institutionally established. | Learned through social experience and cultural exposure. |
| Flexibility | More rigid, role-specific. | Adaptable to situational variations. |
Defining Social Roles and Social Scripts
Social roles are predefined expectations tied to a person's position within a group, guiding consistent behavior patterns such as those of a teacher or parent. Social scripts are cognitive frameworks that outline situational behaviors, helping individuals navigate interactions like greeting someone or attending a meeting. Understanding the distinction between social roles and social scripts clarifies how societal norms influence both identity and everyday actions.
Historical Evolution of Social Roles and Scripts
Social roles and social scripts have evolved significantly throughout history, adapting to changing cultural norms and societal structures. Early human communities relied on rigid social roles to maintain order, while social scripts began to guide interactions in more complex societies. Over time, these roles and scripts became more flexible, reflecting shifts in gender, class, and occupational expectations across different historical periods.
Everyday Examples of Social Roles
Social roles define expected behaviors tied to a person's position in society, such as a teacher instructing students or a parent caring for children. Social scripts guide interactions within these roles, like greeting colleagues in a workplace or following conversational norms during a family dinner. Everyday examples include a cashier scanning items and politely engaging customers, illustrating how social roles and scripts shape routine social behavior.
How Social Scripts Shape Interactions
Social scripts provide structured expectations that guide individuals' behaviors in specific contexts, facilitating smoother and more predictable social interactions. These scripts influence communication patterns, decision-making processes, and role adoption, enabling people to navigate complex social environments efficiently. By internalizing social scripts, individuals anticipate responses and align their actions to maintain social harmony and fulfill societal norms.
Differences Between Social Roles and Social Scripts
Social roles define expected behaviors, responsibilities, and norms associated with a specific position within a group or society, such as being a teacher or parent. Social scripts are predefined sequences of actions or interactions that guide how individuals perform their roles in particular social situations, like greeting a guest or attending a meeting. The key difference lies in social roles representing broader identity-based expectations, while social scripts specify situational behavior patterns to enact those roles.
The Impact of Social Roles on Identity
Social roles significantly shape individual identity by providing structured expectations and behaviors within various contexts, influencing how people perceive themselves and are perceived by others. These roles act as frameworks that guide interactions, reinforcing social norms and contributing to a sense of belonging and self-understanding. The internalization of social roles directly impacts personal identity development, often determining life choices and social dynamics.
Social Scripts in Diverse Cultures
Social scripts in diverse cultures provide structured guides for behavior based on shared values, norms, and expectations within specific communities. These scripts influence interpersonal interactions and help individuals navigate complex social environments by prescribing appropriate responses and roles in various situations. Understanding cultural variations in social scripts enhances cross-cultural communication and fosters social cohesion in multicultural settings.
Breaking or Challenging Social Scripts
Breaking or challenging social scripts disrupts established patterns of behavior that dictate societal expectations based on social roles, such as gender or professional identities. This disruption allows individuals to redefine norms, fostering social change and promoting inclusivity by questioning stereotypes embedded in traditional roles. Examples include challenging gender norms through non-binary expressions or altering workplace hierarchies to encourage collaborative leadership styles.
Influence of Media on Social Roles and Scripts
Media significantly shapes social roles and social scripts by disseminating norms, behaviors, and expectations across diverse audiences. Through repeated exposure to television, film, and digital content, individuals internalize prescribed social scripts that influence their interactions and societal roles. This media-driven construction of social reality affects identity formation and reinforces cultural stereotypes within communities.
Adapting to Changing Social Expectations
Social roles provide structured guidelines for behavior in specific contexts, while social scripts represent the dynamic, culturally shared expectations that evolve with societal changes. Adapting to changing social expectations requires individuals to reinterpret and modify both roles and scripts to maintain social coherence and personal identity. This flexibility enhances social integration and helps navigate complexities in diverse social environments.
social roles vs social scripts Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com