Social proof and normative influence play key roles in shaping pet owners' behavior within social pet communities. Social proof relies on observing the actions and approvals of others to validate one's choices, such as adopting popular pet products or behaviors seen in peers. Normative influence exerts pressure to conform to group standards and expectations, driving pet owners to align their actions with what is considered socially acceptable or desirable in their community.
Table of Comparison
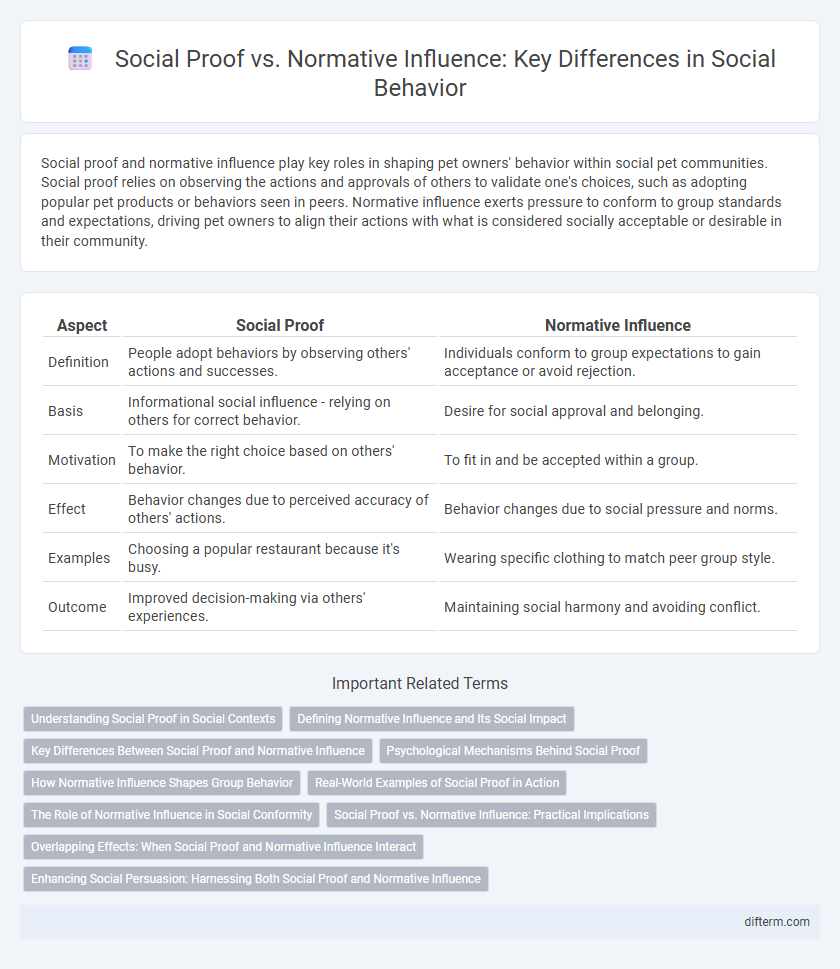
| Aspect | Social Proof | Normative Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | People adopt behaviors by observing others' actions and successes. | Individuals conform to group expectations to gain acceptance or avoid rejection. |
| Basis | Informational social influence - relying on others for correct behavior. | Desire for social approval and belonging. |
| Motivation | To make the right choice based on others' behavior. | To fit in and be accepted within a group. |
| Effect | Behavior changes due to perceived accuracy of others' actions. | Behavior changes due to social pressure and norms. |
| Examples | Choosing a popular restaurant because it's busy. | Wearing specific clothing to match peer group style. |
| Outcome | Improved decision-making via others' experiences. | Maintaining social harmony and avoiding conflict. |
Understanding Social Proof in Social Contexts
Social proof operates as a psychological phenomenon where individuals look to the behavior of others to guide their own actions in uncertain social contexts. It differs from normative influence, which emphasizes conformity driven by the desire for social acceptance and approval. Understanding social proof highlights how people rely on observed behaviors and social cues to make decisions, especially in unfamiliar or ambiguous situations.
Defining Normative Influence and Its Social Impact
Normative influence refers to the pressure individuals feel to conform to the expectations of a group to gain social acceptance and avoid rejection. This social impact shapes behaviors by encouraging adherence to norms, often leading to conformity even when personal beliefs differ. Understanding normative influence highlights its role in maintaining social cohesion and driving group dynamics within communities and organizations.
Key Differences Between Social Proof and Normative Influence
Social proof relies on individuals observing others' behaviors in uncertain situations to guide their own actions, while normative influence stems from the desire to conform and be accepted within a social group. Social proof typically operates through informational cues, whereas normative influence involves internalizing group norms to avoid social rejection. Understanding these distinctions clarifies how social behaviors are shaped by observation versus the need for social approval.
Psychological Mechanisms Behind Social Proof
Social proof operates through observational learning, where individuals adopt behaviors seen in others to reduce uncertainty and enhance decision-making confidence. This psychological mechanism relies heavily on the perception of consensus and credibility, leveraging cognitive biases such as the bandwagon effect and informational conformity. Normative influence, distinct from social proof, involves compliance driven by the desire for social approval and avoidance of rejection, emphasizing emotional rather than informational motives.
How Normative Influence Shapes Group Behavior
Normative influence shapes group behavior by driving individuals to conform to social norms to gain acceptance and avoid rejection within a group. This influence operates through internalized expectations, where the desire for social approval leads to alignment with group behaviors, attitudes, and values. Unlike social proof, which relies on evidential cues from others' actions, normative influence is rooted in the psychological need for belonging and social cohesion.
Real-World Examples of Social Proof in Action
Social proof manifests in real-world scenarios such as restaurant recommendations on Yelp, where positive reviews influence dining choices, demonstrating how individuals mimic group behavior to assume correctness. In retail, high sales volumes or "best-seller" tags serve as social proof, guiding consumers toward popular products based on collective approval. Online platforms like Instagram amplify social proof through follower counts and likes, shaping trends and user preferences by reflecting normative influence within digital communities.
The Role of Normative Influence in Social Conformity
Normative influence plays a critical role in social conformity by driving individuals to align their behaviors with group expectations to gain acceptance and avoid social rejection. Unlike social proof, which relies on informational cues about correct behavior, normative influence emphasizes adherence to social norms even when privately disagreeing. This mechanism reinforces social cohesion and maintains group stability by promoting uniformity in attitudes and actions.
Social Proof vs. Normative Influence: Practical Implications
Social proof drives individuals to mimic the actions of others based on perceived popularity or success, while normative influence compels conformity to group expectations to gain acceptance. Understanding these mechanisms assists marketers and policymakers in crafting strategies that either highlight widespread adoption to increase products' appeal or emphasize social norms to foster behaviors aligned with community values. Leveraging social proof can boost immediate engagement, whereas normative influence promotes long-term adherence to desired social behaviors.
Overlapping Effects: When Social Proof and Normative Influence Interact
Social proof and normative influence often overlap, intensifying their impact on individual behavior within social contexts. Social proof, based on observing others' actions, validates choices, while normative influence taps into the desire for social acceptance and belonging. Their interaction creates a powerful dynamic where individuals align behaviors both to follow perceived evidence and to meet group expectations, shaping decision-making and conformity in social environments.
Enhancing Social Persuasion: Harnessing Both Social Proof and Normative Influence
Leveraging social proof involves showcasing actual behaviors or endorsements from others to build credibility and trust in social persuasion efforts. Normative influence taps into individuals' desires to conform to social norms and gain acceptance within a group, driving behavior change through perceived social expectations. Integrating both strategies enhances social persuasion by simultaneously validating actions and aligning them with group values, thus maximizing behavioral compliance.
social proof vs normative influence Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com