Social pets thrive on narratives that emphasize cooperation, empathy, and shared experiences, contrasting sharply with the dominant narrative that often highlights competition and control. This social narrative fosters stronger bonds between pets and their owners by prioritizing mutual respect and understanding over dominance and hierarchy. Embracing a social narrative encourages healthier, more fulfilling interactions that enhance the well-being of both pets and humans.
Table of Comparison
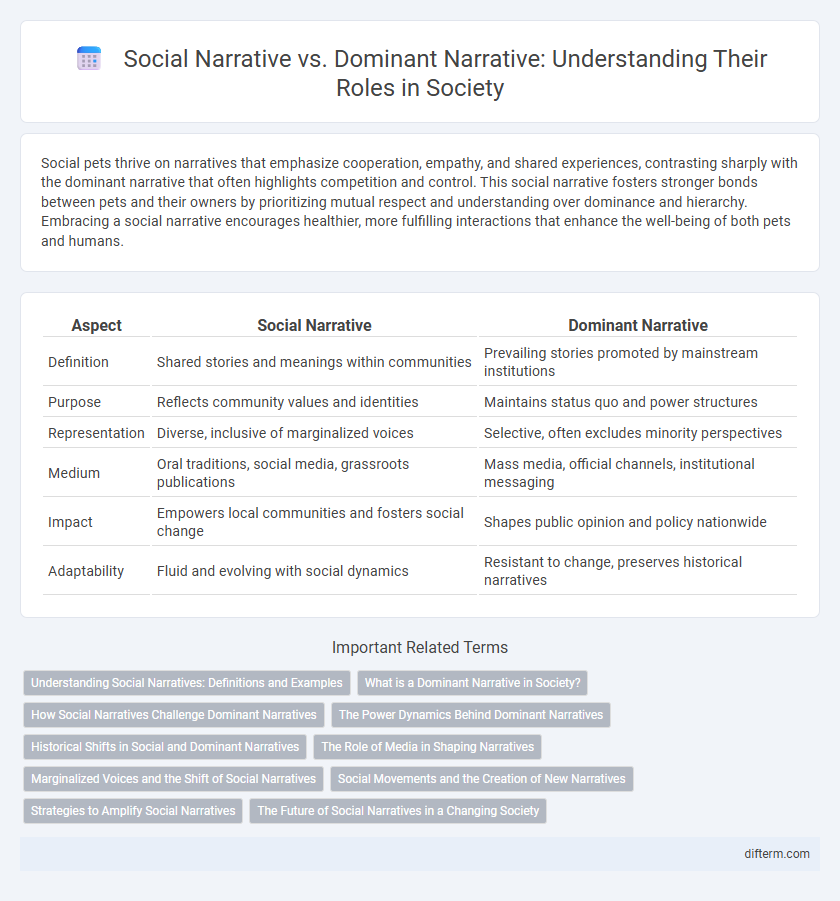
| Aspect | Social Narrative | Dominant Narrative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared stories and meanings within communities | Prevailing stories promoted by mainstream institutions |
| Purpose | Reflects community values and identities | Maintains status quo and power structures |
| Representation | Diverse, inclusive of marginalized voices | Selective, often excludes minority perspectives |
| Medium | Oral traditions, social media, grassroots publications | Mass media, official channels, institutional messaging |
| Impact | Empowers local communities and fosters social change | Shapes public opinion and policy nationwide |
| Adaptability | Fluid and evolving with social dynamics | Resistant to change, preserves historical narratives |
Understanding Social Narratives: Definitions and Examples
Social narratives are the shared stories and meanings constructed within communities that reflect collective experiences and identities, often providing marginalized groups a voice distinct from the dominant narrative. The dominant narrative represents the prevailing story shaped by those in power, influencing public perception and social norms through mainstream media, education, and policy. Understanding these narratives requires analyzing how social contexts, historical events, and power dynamics shape the acceptance and perpetuation of certain stories over others.
What is a Dominant Narrative in Society?
A dominant narrative in society refers to the prevailing story or perspective that shapes collective understanding, often reflecting the values and beliefs of those in power. It influences social norms, cultural identities, and political agendas, marginalizing alternative viewpoints and experiences. Examining dominant narratives reveals the mechanisms through which social inequalities and hegemonic ideologies are maintained.
How Social Narratives Challenge Dominant Narratives
Social narratives challenge dominant narratives by amplifying marginalized voices and exposing overlooked perspectives, thereby disrupting established power structures. These counter-narratives foster inclusivity and promote critical dialogue, enabling societies to question and redefine accepted truths. Through storytelling and collective experiences, social narratives catalyze social change by highlighting diversity and resisting hegemony.
The Power Dynamics Behind Dominant Narratives
Dominant narratives in society are shaped by power structures that prioritize the perspectives and interests of influential groups, often marginalizing alternative social narratives. These prevailing stories reinforce existing hierarchies by controlling which histories and experiences are validated or erased. Challenging dominant narratives requires amplifying marginalized voices and critically examining the mechanisms of ideological control embedded in media, education, and policy.
Historical Shifts in Social and Dominant Narratives
Historical shifts in social and dominant narratives reveal evolving power dynamics and cultural transformations, where marginalized voices increasingly challenge and reshape mainstream historical accounts. Social narratives often emerge from grassroots movements, reflecting lived experiences and collective memory that contrast with dominant narratives rooted in institutional authority and traditional frameworks. These shifts highlight the critical role of interpretive frameworks in redefining identity, inequality, and social justice across different periods.
The Role of Media in Shaping Narratives
Media outlets play a pivotal role in shaping social narratives by selecting which stories are amplified and whose voices are marginalized, thereby influencing public perception and social discourse. Dominant narratives often reflect the interests of powerful groups, reinforcing existing social hierarchies while sidelining alternative perspectives. Social narratives emerge in response, contesting mainstream portrayals and fostering diverse viewpoints that challenge dominant media frameworks.
Marginalized Voices and the Shift of Social Narratives
Marginalized voices increasingly challenge the dominant narrative by highlighting overlooked experiences and systemic injustices, fostering a more inclusive social discourse. This shift in social narratives amplifies diverse perspectives, reshaping public consciousness and policy-making toward equity and representation. The ongoing transformation underscores the critical role of storytelling in empowering marginalized communities and disrupting traditional power structures.
Social Movements and the Creation of New Narratives
Social movements challenge dominant narratives by amplifying marginalized voices and reshaping collective memory. These movements craft new narratives that highlight systemic inequalities, fostering critical awareness and inspiring societal change. The creation of alternative social narratives is crucial for promoting inclusivity and redefining cultural norms.
Strategies to Amplify Social Narratives
Strategies to amplify social narratives include harnessing grassroots movements, leveraging diverse media platforms, and engaging community influencers to challenge dominant narratives. Employing storytelling techniques that center marginalized voices enhances authenticity and fosters emotional connections, driving broader social awareness and change. Data-driven approaches combined with collaborative partnerships ensure sustained visibility and impact of alternative social narratives.
The Future of Social Narratives in a Changing Society
The future of social narratives in a changing society hinges on amplifying marginalized voices to challenge the dominant narrative that traditionally shapes cultural norms and values. Emerging platforms and digital technologies facilitate the democratization of storytelling, enabling diverse perspectives to influence social discourse and policy development. This shift promises a more inclusive and dynamic societal narrative that reflects the complexities of contemporary identities and experiences.
social narrative vs dominant narrative Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com