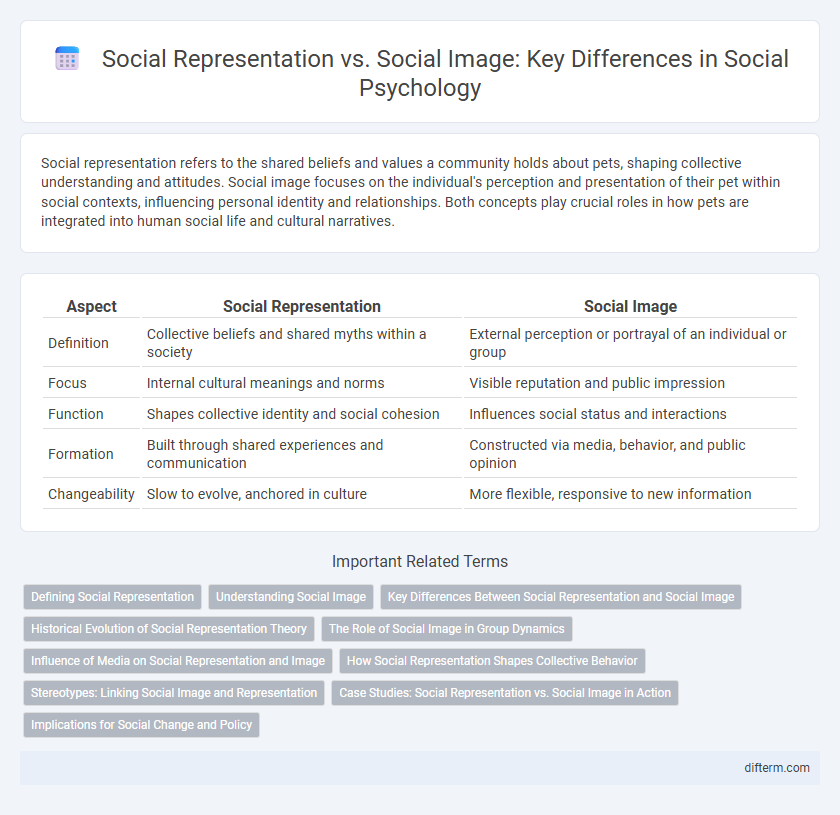
Social representation refers to the shared beliefs and values a community holds about pets, shaping collective understanding and attitudes. Social image focuses on the individual's perception and presentation of their pet within social contexts, influencing personal identity and relationships. Both concepts play crucial roles in how pets are integrated into human social life and cultural narratives.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Representation | Social Image |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collective beliefs and shared myths within a society | External perception or portrayal of an individual or group |
| Focus | Internal cultural meanings and norms | Visible reputation and public impression |
| Function | Shapes collective identity and social cohesion | Influences social status and interactions |
| Formation | Built through shared experiences and communication | Constructed via media, behavior, and public opinion |
| Changeability | Slow to evolve, anchored in culture | More flexible, responsive to new information |
Defining Social Representation
Social representation refers to the collective elaboration of a social object by the community, encompassing shared beliefs, values, and meanings that shape group identity and social reality. It differs from social image, which is an individual's personal perception or impression of a social entity. Understanding social representation involves examining how societal norms and collective memory influence the construction and communication of social knowledge.
Understanding Social Image
Social image refers to the perception and evaluation of an individual or group based on visible behaviors, appearances, and social cues within society. It shapes social interactions by influencing how others interpret identity, status, and belonging. Understanding social image involves analyzing the symbolic meanings attached to external expressions and how these influence acceptance and influence in social contexts.
Key Differences Between Social Representation and Social Image
Social representation refers to the collective beliefs, values, and ideas shared within a community that shape its worldview, while social image pertains to the perception or reputation an individual or group holds in society. The key differences lie in social representation being a broader, culturally embedded framework influencing social norms, whereas social image is a more dynamic and subjective impression influenced by personal behavior and external communication. Understanding these distinctions helps in analyzing how societal values and individual identities interact in social contexts.
Historical Evolution of Social Representation Theory
The historical evolution of Social Representation Theory traces back to Serge Moscovici's pioneering work in the 1960s, emphasizing how collective knowledge shapes social reality. Social representation differs from social image by encompassing shared systems of values, ideas, and practices within groups, rather than merely individual or group reputations. Over time, this theory has expanded to analyze social constructs in various cultural and political contexts, highlighting its dynamic and interactive nature.
The Role of Social Image in Group Dynamics
Social image influences group dynamics by shaping individual behavior to align with perceived collective norms and expectations. It functions as a social regulator, where maintaining a positive social image motivates conformity and cooperation within the group. This dynamic fosters group cohesion and impacts decision-making processes by reinforcing shared values and social identity.
Influence of Media on Social Representation and Image
Media significantly shapes social representation by framing cultural norms and influencing public perceptions through selective portrayal of groups and issues. Social image, constructed by individuals and communities, is heavily impacted by media narratives that reinforce stereotypes or promote idealized identities. This interplay between media influence and social dynamics drives the evolution of collective attitudes and societal behaviors.
How Social Representation Shapes Collective Behavior
Social representation serves as the shared framework through which communities interpret experiences, fundamentally influencing collective behavior by shaping group norms and values. These representations enable individuals to align perceptions and actions within social contexts, reinforcing social cohesion and guiding decision-making processes. The dynamic interplay between social representation and collective behavior underpins social identity formation and drives group responses to external challenges or changes.
Stereotypes: Linking Social Image and Representation
Stereotypes serve as cognitive shortcuts that shape social representation by reinforcing generalized beliefs about groups, thus influencing social images perceived by others. These oversimplified social images perpetuate bias, impacting how individuals and communities are understood and treated within society. Challenging stereotypes is essential for reshaping social representation, promoting inclusivity, and fostering more accurate, diverse social images.
Case Studies: Social Representation vs. Social Image in Action
Case studies reveal that social representation encompasses collective beliefs and shared meaning within a community, while social image reflects individual or group identities projected to others. Instances from public health campaigns demonstrate how social representations influence group attitudes, whereas social image drives personal or organizational branding strategies. Analyzing movements like climate activism showcases the dynamic interplay between societal perceptions and self-presentation in shaping social action.
Implications for Social Change and Policy
Social representation shapes collective perceptions and shared meanings that influence group behavior and societal norms, while social image reflects the public's external perception of an individual or group. Understanding the distinction between these concepts is crucial for policymakers aiming to implement effective social change, as entrenched social representations often drive resistance to policy reforms despite shifts in social image. Strategies targeting social representation can foster deeper attitude changes, promoting sustainable social transformation beyond superficial image adjustments.
social representation vs social image Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com