Social influence shapes behavior through positive encouragement and shared values within a community, promoting healthy and supportive interactions among pet owners. Peer pressure, however, often yields negative effects by compelling individuals to conform to expectations that may not align with their genuine beliefs or the best interests of their pets. Understanding the distinction helps pet owners foster authentic connections and make informed choices based on mutual respect rather than coercion.
Table of Comparison
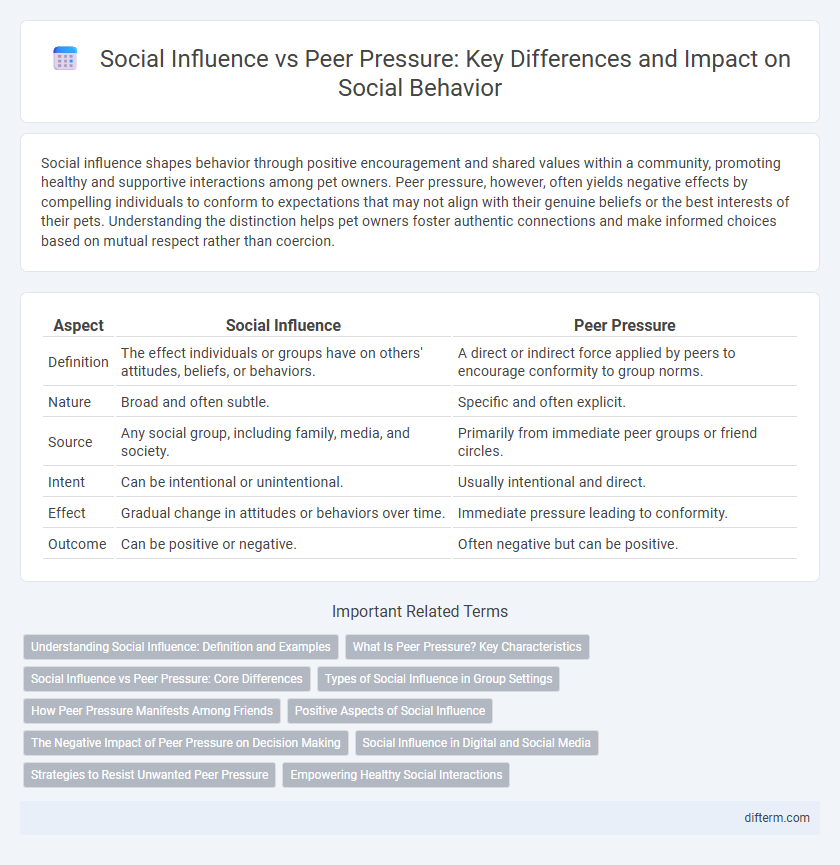
| Aspect | Social Influence | Peer Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The effect individuals or groups have on others' attitudes, beliefs, or behaviors. | A direct or indirect force applied by peers to encourage conformity to group norms. |
| Nature | Broad and often subtle. | Specific and often explicit. |
| Source | Any social group, including family, media, and society. | Primarily from immediate peer groups or friend circles. |
| Intent | Can be intentional or unintentional. | Usually intentional and direct. |
| Effect | Gradual change in attitudes or behaviors over time. | Immediate pressure leading to conformity. |
| Outcome | Can be positive or negative. | Often negative but can be positive. |
Understanding Social Influence: Definition and Examples
Social influence encompasses various ways individuals' thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are affected by others, including conformity, compliance, and obedience, distinct from peer pressure which specifically involves influence from equals. Examples of social influence include informational social influence, where individuals adopt behaviors based on credible information, and normative social influence, driven by the desire for social acceptance. Understanding these mechanisms highlights how social influence shapes decision-making in contexts such as marketing, group dynamics, and social interactions.
What Is Peer Pressure? Key Characteristics
Peer pressure is a social influence exerted by a peer group encouraging individuals to adopt certain behaviors, attitudes, or values to conform with group norms. Key characteristics include the desire for acceptance, direct or indirect persuasion, and the risk of negative or positive behavioral change. Peer pressure often involves subtle coercion and can significantly impact decision-making, especially during adolescence.
Social Influence vs Peer Pressure: Core Differences
Social influence involves subtle shifts in behavior or attitudes due to others' presence, driven by internal motivation and social norms. Peer pressure exerts direct, often coercive, demands to conform, frequently linked to fear of rejection or punishment. Core differences lie in voluntariness, with social influence fostering voluntary adaptation, while peer pressure enforces conformity through external pressure or threats.
Types of Social Influence in Group Settings
Compliance, identification, and internalization represent key types of social influence in group settings, each varying in depth and motivation. Compliance occurs when individuals conform publicly without changing private beliefs, often driven by a desire for acceptance. Identification involves adopting behaviors or attitudes to maintain relationships within the group, while internalization reflects a genuine acceptance of group norms as one's own values.
How Peer Pressure Manifests Among Friends
Peer pressure manifests among friends through subtle cues such as implicit expectations to conform to group behaviors, shared norms that discourage dissent, and indirect encouragement to engage in specific activities to gain acceptance. This influence often relies on emotional bonds and the desire for social validation, where individuals feel compelled to align their choices with the group to avoid rejection or ridicule. Understanding these dynamics highlights how peer pressure operates not only through overt demands but also through nuanced social interactions within friend circles.
Positive Aspects of Social Influence
Social influence enhances personal development by encouraging individuals to adopt beneficial behaviors such as healthy habits and ethical decision-making. Peer support in positive social environments fosters confidence, motivation, and resilience, contributing to overall well-being. Constructive social influence promotes collaboration, community engagement, and the spread of innovative ideas that drive social progress.
The Negative Impact of Peer Pressure on Decision Making
Peer pressure often leads individuals to make decisions that conflict with their personal values, increasing the likelihood of risky behaviors such as substance abuse or delinquency. The desire to conform to group norms can impair critical thinking and reduce resistance to negative influences. This erosion of autonomous decision-making undermines long-term well-being and personal development.
Social Influence in Digital and Social Media
Social influence in digital and social media shapes user behavior through algorithms, targeted content, and viral trends, significantly impacting opinions and decision-making processes. Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Twitter amplify social proof and expert endorsements, driving conformity and shaping cultural norms. Understanding digital social influence helps marketers and policymakers design effective communication strategies and counter misinformation.
Strategies to Resist Unwanted Peer Pressure
Developing strong self-awareness helps individuals recognize and resist unwanted peer pressure by clarifying personal values and boundaries. Practicing assertive communication empowers people to confidently express their decisions without aggression, reducing susceptibility to negative influence. Building supportive social networks with like-minded individuals reinforces positive behavior and provides alternative sources of social validation.
Empowering Healthy Social Interactions
Social influence shapes individual behaviors through positive reinforcement and shared values, fostering supportive environments that encourage personal growth. Unlike peer pressure, which often compels conformity through coercion, healthy social interactions promote autonomy and informed decision-making. Empowering these interactions strengthens self-confidence and cultivates resilience, enabling individuals to navigate social dynamics constructively.
social influence vs peer pressure Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com