Social anxiety is a more intense and persistent fear of social situations, often causing significant distress and avoidance, while shyness is a milder, temporary feeling of discomfort or hesitation in social interactions. Pets, especially social ones like dogs and cats, can help alleviate social anxiety by providing companionship and reducing feelings of isolation. Understanding the difference between social anxiety and shyness is crucial for addressing behavioral needs and enhancing emotional support through pet interaction.
Table of Comparison
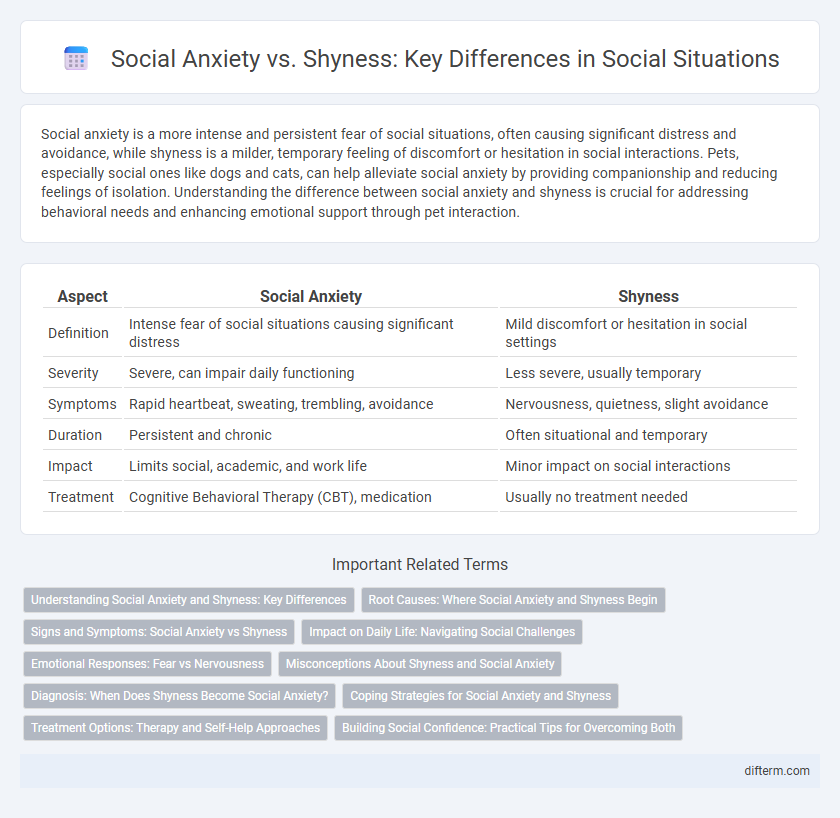
| Aspect | Social Anxiety | Shyness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intense fear of social situations causing significant distress | Mild discomfort or hesitation in social settings |
| Severity | Severe, can impair daily functioning | Less severe, usually temporary |
| Symptoms | Rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, avoidance | Nervousness, quietness, slight avoidance |
| Duration | Persistent and chronic | Often situational and temporary |
| Impact | Limits social, academic, and work life | Minor impact on social interactions |
| Treatment | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), medication | Usually no treatment needed |
Understanding Social Anxiety and Shyness: Key Differences
Social anxiety involves intense fear and avoidance of social situations due to concerns about judgment and embarrassment, affecting daily functioning. Shyness is a personality trait characterized by discomfort or awkwardness in social settings but does not typically impair normal activities. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment strategies.
Root Causes: Where Social Anxiety and Shyness Begin
Social anxiety often stems from deep-rooted fears of judgment or rejection, influenced by genetic predisposition and early negative social experiences. Shyness generally originates from temperament traits and unfamiliarity in social settings, causing discomfort but not intense fear. Understanding these distinct root causes helps tailor effective coping strategies for each condition.
Signs and Symptoms: Social Anxiety vs Shyness
Social anxiety manifests through intense fear of social situations, leading to symptoms such as sweating, trembling, rapid heartbeat, and avoidance of social interactions, significantly impairing daily functioning. In contrast, shyness is characterized by mild discomfort or nervousness in social settings without extreme physiological reactions or severe avoidance behavior. Recognizing symptoms like persistent worry about being judged, panic attacks, or debilitating fear distinguishes social anxiety disorder from normal shyness.
Impact on Daily Life: Navigating Social Challenges
Social anxiety significantly disrupts daily life by causing intense fear and avoidance of social situations, leading to difficulties in work, school, and personal relationships. Shyness, while involving discomfort in social settings, generally allows for more manageable interactions and less impairment in routine activities. Understanding these differences is crucial for developing effective coping strategies and seeking appropriate support.
Emotional Responses: Fear vs Nervousness
Social anxiety triggers intense fear and dread of social situations, often leading to avoidance and physical symptoms like sweating and rapid heartbeat. Shyness primarily involves nervousness and self-consciousness without the overwhelming fear present in social anxiety. Understanding these emotional responses helps distinguish between typical social discomfort and a more debilitating anxiety disorder.
Misconceptions About Shyness and Social Anxiety
Shyness is often misunderstood as mere introversion or temporary nervousness, while social anxiety is a clinical condition characterized by intense fear of social situations. Many believe shy individuals can easily overcome their discomfort with encouragement, but social anxiety involves persistent, overwhelming anxiety that disrupts daily functioning. Confusing these terms leads to underestimating the severity of social anxiety and ignoring the need for specialized treatment.
Diagnosis: When Does Shyness Become Social Anxiety?
Shyness becomes social anxiety when feelings of nervousness in social situations intensify into persistent fear and avoidance that disrupt daily functioning. Unlike shyness, social anxiety disorder involves excessive worry about judgment or humiliation, often diagnosed through clinical assessment based on duration, severity, and impact on social or occupational activities. Early diagnosis helps differentiate normal shyness from social anxiety disorder, enabling targeted cognitive-behavioral therapy and possible medication for effective management.
Coping Strategies for Social Anxiety and Shyness
Effective coping strategies for social anxiety include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to challenge negative thought patterns and gradual exposure to social situations to build confidence. For shyness, building social skills through practice and seeking supportive social environments can reduce discomfort. Mindfulness and relaxation techniques help manage anxiety symptoms in both conditions.
Treatment Options: Therapy and Self-Help Approaches
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a widely effective treatment for social anxiety, targeting negative thought patterns and gradual exposure to social situations. Self-help approaches such as mindfulness meditation and social skills training can complement therapy by enhancing emotional regulation and building confidence. Combining professional therapy with consistent self-help practice often results in significant improvement and long-term management of social anxiety symptoms.
Building Social Confidence: Practical Tips for Overcoming Both
Building social confidence involves recognizing that social anxiety and shyness, while related, manifest differently; social anxiety includes intense fear of judgment, whereas shyness is a natural hesitation in social settings. Practical tips include gradual exposure to social situations, practicing mindfulness to manage anxious thoughts, and developing conversational skills through role-playing or social skills training. Consistent practice and positive self-reinforcement reduce avoidance behavior, empowering individuals to navigate social interactions with greater ease and confidence.
social anxiety vs shyness Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com