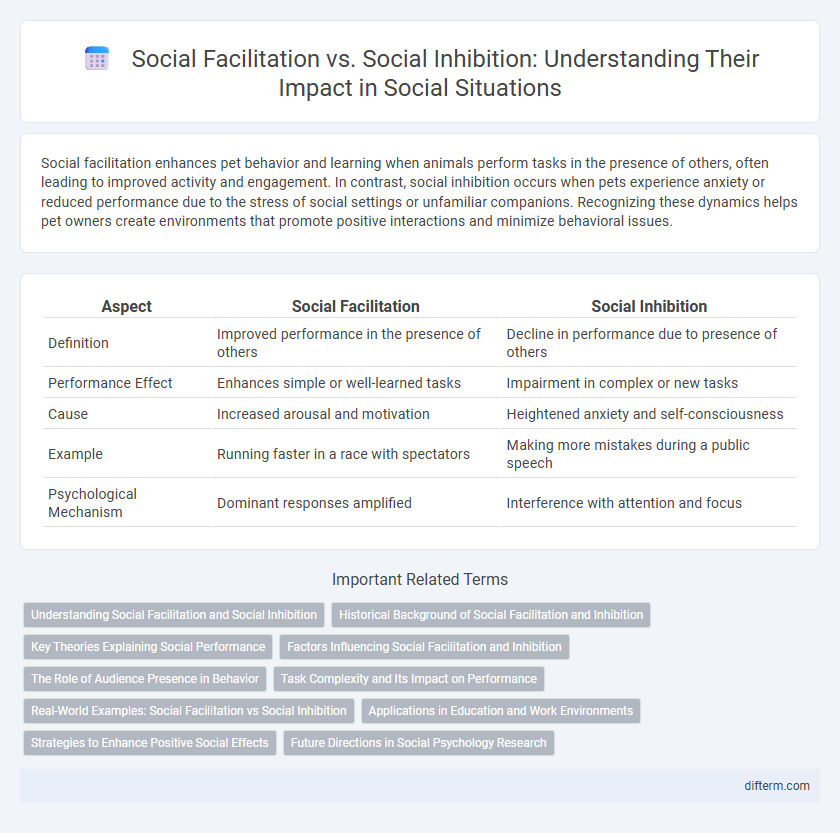
Social facilitation enhances pet behavior and learning when animals perform tasks in the presence of others, often leading to improved activity and engagement. In contrast, social inhibition occurs when pets experience anxiety or reduced performance due to the stress of social settings or unfamiliar companions. Recognizing these dynamics helps pet owners create environments that promote positive interactions and minimize behavioral issues.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Facilitation | Social Inhibition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Improved performance in the presence of others | Decline in performance due to presence of others |
| Performance Effect | Enhances simple or well-learned tasks | Impairment in complex or new tasks |
| Cause | Increased arousal and motivation | Heightened anxiety and self-consciousness |
| Example | Running faster in a race with spectators | Making more mistakes during a public speech |
| Psychological Mechanism | Dominant responses amplified | Interference with attention and focus |
Understanding Social Facilitation and Social Inhibition
Social facilitation enhances performance on simple or well-practiced tasks when in the presence of others, driven by increased arousal and motivation. In contrast, social inhibition occurs when the presence of others decreases performance on complex or unfamiliar tasks due to heightened anxiety or pressure. Understanding these phenomena is crucial for optimizing group dynamics and individual productivity in social and work settings.
Historical Background of Social Facilitation and Inhibition
The historical background of social facilitation and social inhibition traces back to Norman Triplett's 1898 study, which first observed enhanced performance in cyclists when racing alongside others. Subsequent research by Robert Zajonc in 1965 formalized the theory by demonstrating that the presence of an audience increases arousal, improving simple task performance (social facilitation) while impairing complex tasks (social inhibition). These foundational studies established the dual effects of social presence on individual behavior within social psychology.
Key Theories Explaining Social Performance
Social facilitation, explained by Zajonc's Drive Theory, posits that the presence of others enhances performance on simple or well-learned tasks by increasing arousal levels. In contrast, social inhibition occurs when heightened arousal interferes with complex or novel task execution, resulting in impaired performance. The Evaluation Apprehension Theory further suggests that fear of negative judgment leads to increased arousal, intensifying social facilitation or inhibition effects depending on task difficulty.
Factors Influencing Social Facilitation and Inhibition
The presence of an audience or co-actors significantly influences social facilitation and inhibition, with well-learned or simple tasks typically enhancing performance, while complex or new tasks often suffer deterioration. Arousal levels and individual differences, such as self-confidence and anxiety, also moderate whether an individual's performance improves or declines in social contexts. Environmental factors like the observer's familiarity, evaluation apprehension, and the nature of the social setting further impact the facilitative or inhibitive effects on task execution.
The Role of Audience Presence in Behavior
Audience presence significantly impacts individual performance through social facilitation, where familiar or simple tasks improve due to heightened arousal, while social inhibition occurs when complex or unfamiliar tasks suffer under observation. Research shows that the mere presence of others triggers physiological changes such as increased heart rate and adrenaline, intensifying focus or anxiety based on task difficulty. Understanding the nuanced role of audience presence helps optimize environments in workplaces, sports, and education to enhance productivity and reduce performance anxiety.
Task Complexity and Its Impact on Performance
Task complexity plays a critical role in determining whether social facilitation or social inhibition occurs during performance. Simple or well-practiced tasks tend to benefit from the presence of others, enhancing speed and accuracy due to increased arousal and motivation. Complex or unfamiliar tasks often experience social inhibition, where performance deteriorates under observation because of heightened anxiety and cognitive overload.
Real-World Examples: Social Facilitation vs Social Inhibition
Athletes often experience social facilitation when performing well in front of a supportive home crowd, leading to improved speed and precision. Conversely, individuals may face social inhibition during public speaking, where anxiety caused by an audience results in decreased performance and memory lapses. Workplace meetings illustrate both phenomena, as confident employees may excel with peer presence, while those less comfortable might struggle to communicate their ideas effectively.
Applications in Education and Work Environments
Social facilitation enhances individual performance in education and work settings by increasing motivation and focus when tasks are simple or well-learned, resulting in improved productivity and learning outcomes. Social inhibition, however, can reduce performance on complex or new tasks due to anxiety or self-consciousness in the presence of others, necessitating strategies like situational awareness and stress management to mitigate its effects. Educational institutions and workplaces implement collaborative activities and private practice sessions to balance these phenomena, optimizing performance and skill development.
Strategies to Enhance Positive Social Effects
Implementing strategies such as setting clear individual goals and providing positive reinforcement can enhance social facilitation, boosting performance in group settings. Encouraging supportive peer interactions and reducing evaluation apprehension minimizes social inhibition. Structuring tasks to match skill levels and fostering a collaborative environment optimize social dynamics for improved productivity.
Future Directions in Social Psychology Research
Future directions in social psychology research emphasize exploring neural mechanisms underlying social facilitation and inhibition effects using advanced neuroimaging techniques. Investigating cross-cultural differences and situational variables that modulate performance in group settings will enhance understanding of social influence on behavior. Integrating digital social contexts such as virtual reality and social media platforms offers new avenues to study real-time social facilitation and inhibition phenomena.
social facilitation vs social inhibition Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com