Social activism involves direct, often public actions aimed at challenging societal issues and provoking change, while social advocacy focuses on supporting and promoting causes through education, awareness, and policy influence. In the context of social pets, activism might include organizing community events to confront animal cruelty, whereas advocacy could entail lobbying for better animal welfare laws. Both approaches are crucial for advancing the rights and well-being of pets in society.
Table of Comparison
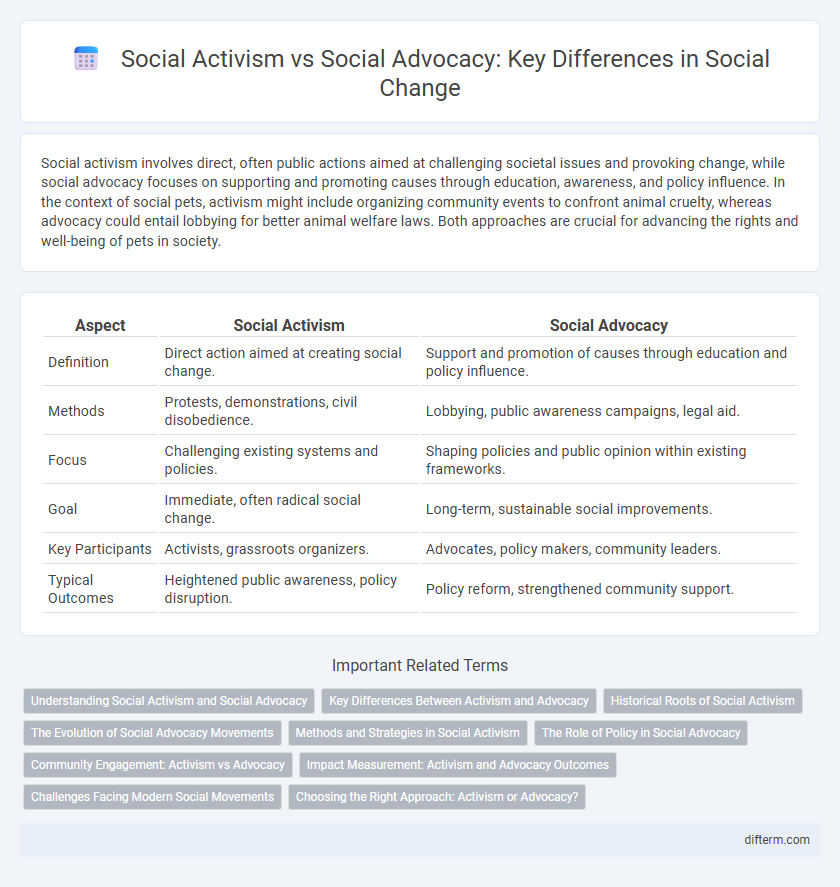
| Aspect | Social Activism | Social Advocacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct action aimed at creating social change. | Support and promotion of causes through education and policy influence. |
| Methods | Protests, demonstrations, civil disobedience. | Lobbying, public awareness campaigns, legal aid. |
| Focus | Challenging existing systems and policies. | Shaping policies and public opinion within existing frameworks. |
| Goal | Immediate, often radical social change. | Long-term, sustainable social improvements. |
| Key Participants | Activists, grassroots organizers. | Advocates, policy makers, community leaders. |
| Typical Outcomes | Heightened public awareness, policy disruption. | Policy reform, strengthened community support. |
Understanding Social Activism and Social Advocacy
Social activism involves direct actions and organized efforts to bring about social or political change, often through protests, demonstrations, or campaigns. Social advocacy focuses on supporting and promoting specific causes or policies by influencing public opinion and decision-makers through education, lobbying, and community engagement. Both approaches aim to address social issues but differ in methods and scope of impact.
Key Differences Between Activism and Advocacy
Social activism involves direct, often public actions such as protests or campaigns aimed at creating immediate social or political change, whereas social advocacy focuses on influencing decision-makers through strategic communication, policy recommendations, and education efforts. Activism is typically more confrontational and grassroots-driven, emphasizing mobilization and public pressure, while advocacy relies on negotiation, expertise, and building relationships within established systems. Understanding these distinctions helps organizations and individuals choose effective approaches to address social issues and promote justice.
Historical Roots of Social Activism
Social activism traces its roots to early movements such as the abolitionist campaigns of the 18th and 19th centuries, which sought to dismantle slavery and promote civil rights. Key historical events like the civil rights movement and women's suffrage further shaped the strategies and goals of social activists dedicated to systemic change. Social advocacy, while related, often involves supporting existing policies and raising awareness through organized efforts rather than direct action.
The Evolution of Social Advocacy Movements
Social advocacy movements have evolved from grassroots campaigns championing civil rights to comprehensive initiatives addressing systemic inequalities across race, gender, and environmental justice. The integration of digital platforms and data analytics has amplified the reach and impact, enabling real-time mobilization and global solidarity. Contemporary advocacy increasingly emphasizes intersectionality and collaborative policymaking to drive sustainable societal change.
Methods and Strategies in Social Activism
Social activism employs direct action methods such as protests, sit-ins, and public demonstrations to create immediate visibility for social issues. Strategies often include grassroots organizing, digital campaigns, and coalition-building to mobilize communities and pressure policymakers for systemic change. These approaches prioritize urgent, collective participation over institutional negotiation, distinguishing activism from social advocacy's more policy-oriented tactics.
The Role of Policy in Social Advocacy
Social advocacy leverages policy to drive systemic change by influencing legislation, regulations, and public resource allocation to address social inequalities. Policy serves as a strategic tool for advocates to institutionalize rights, improve social services, and promote equity across communities. Effective social advocacy often requires collaboration with lawmakers, research-backed evidence, and mobilizing public support to achieve sustainable policy reforms.
Community Engagement: Activism vs Advocacy
Community engagement in social activism often involves direct action such as protests, rallies, and grassroots organizing to challenge societal issues and demand change. Social advocacy, by contrast, emphasizes sustained efforts to influence policy, educate stakeholders, and build coalitions through dialogue and lobbying. Both approaches mobilize community members, but activism typically seeks immediate impact while advocacy aims for long-term systemic reform.
Impact Measurement: Activism and Advocacy Outcomes
Social activism often drives immediate, grassroots changes by mobilizing communities, whereas social advocacy tends to focus on long-term policy reform and systemic improvements. Measuring the impact of activism includes evaluating tangible community engagement and direct societal shifts, while advocacy outcomes are assessed through legislative advancements and sustained institutional changes. Effective impact measurement integrates both qualitative community insights and quantitative policy achievements to capture the full scope of social change.
Challenges Facing Modern Social Movements
Modern social movements encounter challenges such as digital misinformation campaigns that undermine credibility and hinder community mobilization. Resource limitations, including funding and volunteer burnout, constrain sustained activism efforts. Navigating complex policy environments and achieving measurable legislative changes remain significant obstacles for both social activism and social advocacy initiatives.
Choosing the Right Approach: Activism or Advocacy?
Choosing between social activism and social advocacy depends on the desired impact and method of engagement; activism typically involves direct action and public demonstrations to challenge societal issues, while advocacy focuses on influencing policy and promoting change through dialogue and education. Activism often generates immediate visibility and mobilizes communities rapidly, whereas advocacy builds sustainable change by working within legal and institutional frameworks. Evaluating the urgency of the issue, target audience, and long-term goals helps determine the most effective approach for social change.
social activism vs social advocacy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com