Social engineering manipulates human behavior to exploit vulnerabilities for malicious purposes, often compromising security and trust within communities. Social innovation focuses on creating novel solutions to societal challenges by fostering collaboration and positive change. While social engineering undermines social systems, social innovation strengthens them through ethical and sustainable practices.
Table of Comparison
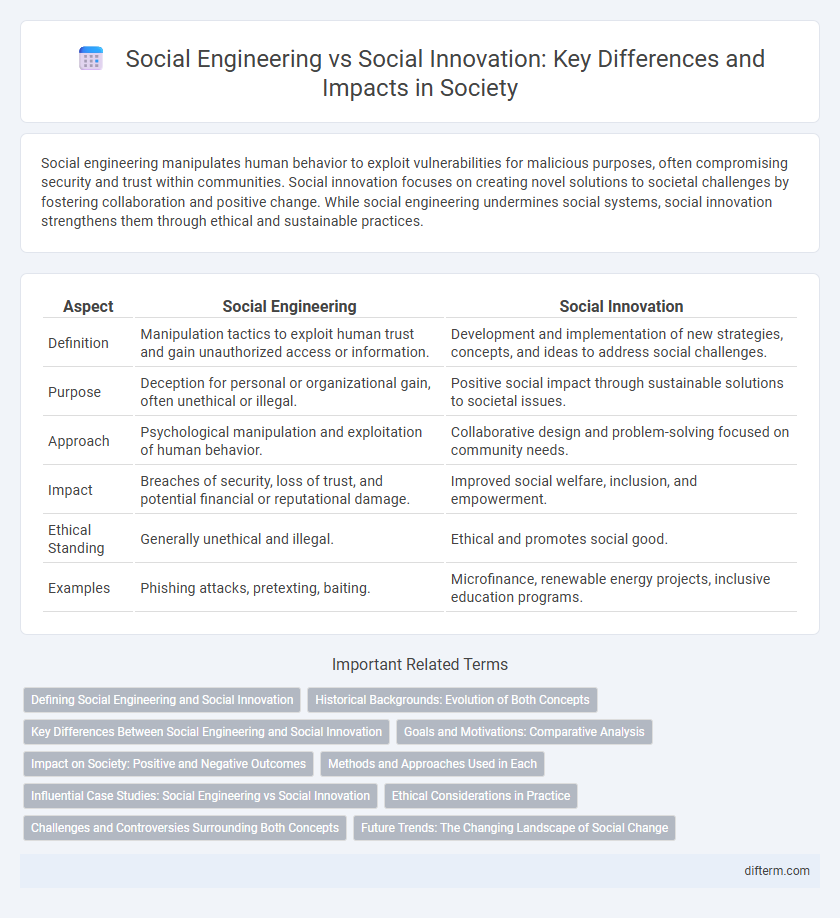
| Aspect | Social Engineering | Social Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manipulation tactics to exploit human trust and gain unauthorized access or information. | Development and implementation of new strategies, concepts, and ideas to address social challenges. |
| Purpose | Deception for personal or organizational gain, often unethical or illegal. | Positive social impact through sustainable solutions to societal issues. |
| Approach | Psychological manipulation and exploitation of human behavior. | Collaborative design and problem-solving focused on community needs. |
| Impact | Breaches of security, loss of trust, and potential financial or reputational damage. | Improved social welfare, inclusion, and empowerment. |
| Ethical Standing | Generally unethical and illegal. | Ethical and promotes social good. |
| Examples | Phishing attacks, pretexting, baiting. | Microfinance, renewable energy projects, inclusive education programs. |
Defining Social Engineering and Social Innovation
Social engineering involves manipulating individuals or groups to achieve specific goals, often exploiting psychological tactics to influence behavior. Social innovation refers to the development and implementation of new strategies, concepts, or ideas that address social needs and improve community well-being. Distinguishing these concepts highlights social engineering's focus on behavior manipulation and social innovation's emphasis on sustainable, positive social change.
Historical Backgrounds: Evolution of Both Concepts
Social engineering originated during the early 20th century as a method to manipulate human behavior for economic or political gain, rooted in psychological and sociological studies. Social innovation emerged in the late 20th century, driven by the need to address systemic social problems through creative solutions and collaborative efforts. Both concepts evolved through different historical contexts, with social engineering often linked to control and influence, while social innovation focuses on empowerment and positive social change.
Key Differences Between Social Engineering and Social Innovation
Social engineering manipulates human behavior through deceptive tactics to achieve specific objectives, often compromising trust and security. In contrast, social innovation involves creating novel solutions to social challenges by fostering community engagement and sustainable development. The key difference lies in intent: social engineering exploits, while social innovation empowers sustainable positive change.
Goals and Motivations: Comparative Analysis
Social engineering seeks to manipulate individuals or groups to achieve specific, often exploitative objectives, focusing on control and influence for personal or organizational gain. Social innovation aims to create sustainable solutions addressing societal challenges, motivated by altruism and the desire to improve community well-being. These contrasting goals highlight social engineering's intent on manipulation versus social innovation's commitment to positive systemic change.
Impact on Society: Positive and Negative Outcomes
Social engineering often manipulates human behavior to achieve specific goals, which can result in negative societal consequences such as loss of trust and increased vulnerability to fraud. In contrast, social innovation drives positive change by developing new strategies and solutions that address social issues, promoting inclusivity and sustainability. Both approaches significantly impact society, but social innovation tends to foster empowerment and long-term improvements, whereas social engineering can undermine social cohesion and ethical standards.
Methods and Approaches Used in Each
Social engineering employs psychological manipulation techniques such as phishing, pretexting, and baiting to exploit human vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to information or systems. Social innovation involves collaborative methods including participatory design, co-creation, and community engagement to develop sustainable solutions addressing social challenges. While social engineering leverages deception for malicious intent, social innovation uses inclusive strategies to foster positive social change.
Influential Case Studies: Social Engineering vs Social Innovation
Social engineering cases such as the Cambridge Analytica scandal demonstrate how manipulation of online data can influence political behavior on a massive scale. In contrast, social innovation examples like the Grameen Bank showcase sustainable solutions to poverty through microfinance, empowering marginalized communities. These influential case studies highlight the contrasting impacts of social engineering's deceptive tactics versus social innovation's collaborative, systemic change.
Ethical Considerations in Practice
Social engineering often raises ethical concerns due to its manipulative tactics that exploit human psychology for personal or organizational gain, risking privacy violations and trust erosion. Social innovation emphasizes ethical practice by fostering inclusive, transparent, and community-centered solutions that prioritize social good and equity. Navigating these ethical considerations requires clear guidelines, stakeholder engagement, and continuous evaluation to ensure responsible implementation and positive societal impact.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Both Concepts
Social engineering often faces ethical challenges due to its manipulation of behaviors for strategic purposes, raising concerns about consent and privacy, while social innovation struggles with scalability and equitable impact, as solutions may not benefit all communities equally. Both concepts encounter controversies regarding their implementation effectiveness and the potential unintended consequences on vulnerable populations. Navigating these complexities requires balancing innovation with ethical considerations and inclusive stakeholder engagement.
Future Trends: The Changing Landscape of Social Change
Social engineering increasingly leverages data analytics and AI to manipulate behaviors, raising ethical concerns while reshaping societal interactions. Social innovation drives sustainable solutions by fostering collaboration across sectors, emphasizing inclusivity and technology-driven empowerment. Future trends highlight a convergence where ethically guided social innovation counters manipulation risks, promoting adaptive, resilient communities.
social engineering vs social innovation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com