Social signaling involves deliberate behaviors animals use to communicate intentions or status to others, such as a dog wagging its tail to indicate friendliness. Social cues are the subtle, often involuntary signals perceived by pets that influence their social interactions, like a cat's flattened ears signaling discomfort. Understanding the distinction between social signaling and social cues helps pet owners interpret their pets' behavior and foster healthier social environments.
Table of Comparison
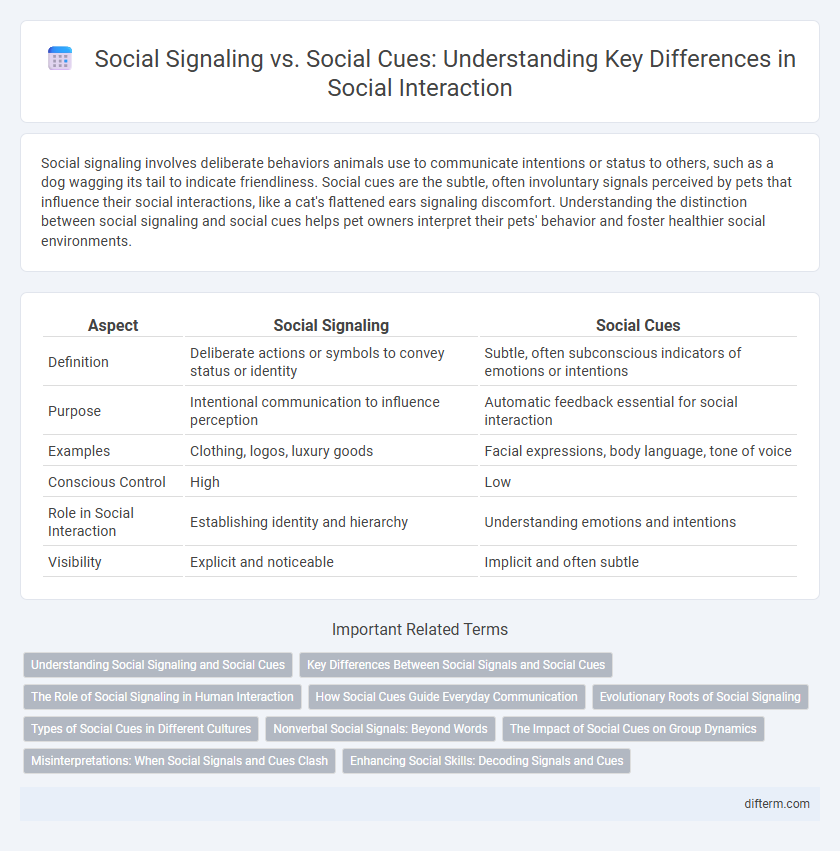
| Aspect | Social Signaling | Social Cues |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate actions or symbols to convey status or identity | Subtle, often subconscious indicators of emotions or intentions |
| Purpose | Intentional communication to influence perception | Automatic feedback essential for social interaction |
| Examples | Clothing, logos, luxury goods | Facial expressions, body language, tone of voice |
| Conscious Control | High | Low |
| Role in Social Interaction | Establishing identity and hierarchy | Understanding emotions and intentions |
| Visibility | Explicit and noticeable | Implicit and often subtle |
Understanding Social Signaling and Social Cues
Social signaling involves deliberate actions or behaviors intended to convey specific information or intentions to others, such as gestures, facial expressions, or vocal tones. Social cues are the subtle, often unconscious environmental or interpersonal signals that individuals interpret to guide their social interactions, including body language, eye contact, and contextual context. Understanding the distinction and interplay between social signaling and social cues is essential for decoding human communication and enhancing social intelligence in everyday interactions.
Key Differences Between Social Signals and Social Cues
Social signals are deliberate behaviors or communications, such as facial expressions or tone of voice, intended to influence others' perceptions or actions. Social cues are often subtle, involuntary indicators like body language, eye contact, or posture that provide context and inform social interactions. The key difference lies in social signals being purposeful messages, while social cues are subconscious or environmental hints that guide interpretation and response.
The Role of Social Signaling in Human Interaction
Social signaling plays a crucial role in human interaction by conveying intentions, emotions, and social status through deliberate behaviors such as facial expressions, body language, and vocal tone. Unlike subtle social cues, social signals are often more intentional and recognized by others as indicators of social identity or group membership. This dynamic facilitates effective communication, cooperation, and relationship-building within social groups.
How Social Cues Guide Everyday Communication
Social cues, including facial expressions, body language, and tone of voice, guide everyday communication by providing nonverbal signals that convey emotions and intentions. These cues help individuals interpret messages more accurately, enabling smoother social interactions and reducing misunderstandings. Effective use of social cues enhances empathy and strengthens relationships by aligning verbal content with context and emotional states.
Evolutionary Roots of Social Signaling
Social signaling originates from evolutionary mechanisms that enhance group cohesion and individual survival by conveying intentions, emotions, or status through observable behaviors. These signals, such as vocalizations, facial expressions, and body posture, have evolved to facilitate communication without explicit language. Understanding the distinction between social signaling and social cues reveals how innate behaviors guide social interactions in human and animal societies.
Types of Social Cues in Different Cultures
Social cues vary significantly across cultures, encompassing nonverbal signals such as eye contact, gestures, facial expressions, and proxemics, which serve as essential tools for communication and social signaling. In Western cultures, direct eye contact often conveys confidence and honesty, whereas in many Asian cultures, prolonged eye contact may be perceived as disrespectful. Gestures like the thumbs-up sign can indicate approval in some regions but are offensive in others, highlighting the importance of understanding cultural variations in social cues for effective intercultural interactions.
Nonverbal Social Signals: Beyond Words
Nonverbal social signals, such as facial expressions, body posture, and eye contact, convey complex emotions and intentions beyond spoken language, shaping interpersonal interactions and social dynamics. Unlike social cues, which are often context-dependent hints prompting specific responses, nonverbal signals function as continuous, subconscious communication channels influencing trust, empathy, and group cohesion. Understanding these subtle behaviors enhances social intelligence and improves effectiveness in both personal relationships and professional environments.
The Impact of Social Cues on Group Dynamics
Social cues such as facial expressions, body language, and tone of voice play a critical role in shaping group dynamics by influencing interpersonal communication and emotional resonance among members. These subtle signals facilitate trust-building, conflict resolution, and coordinated cooperation, thereby enhancing overall group cohesion and performance. Understanding and interpreting social cues accurately can significantly improve social interactions and collective decision-making processes within groups.
Misinterpretations: When Social Signals and Cues Clash
Social signaling and social cues often clash, leading to misinterpretations that impact interpersonal communication and relationships. Social signals, such as explicit verbal messages, can contradict subtle social cues like body language or facial expressions, causing confusion about true intentions or emotions. This mismatch can result in misunderstandings, reduced trust, and impaired social interactions across diverse cultural and social contexts.
Enhancing Social Skills: Decoding Signals and Cues
Social signaling involves intentional behaviors used to convey information, while social cues are subtle, often unconscious indicators like facial expressions or body language. Enhancing social skills requires recognizing and accurately interpreting these signals and cues to respond appropriately in various social contexts. Mastery of decoding social signals improves communication effectiveness, empathy, and relationship-building.
social signaling vs social cues Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com