Social pets thrive by fostering connections that enhance emotional well-being and reduce feelings of loneliness. Embracing social integration encourages interactive play and companionship, which supports mental and physical health. In contrast, social isolation often leads to behavioral issues and diminished quality of life for pets.
Table of Comparison
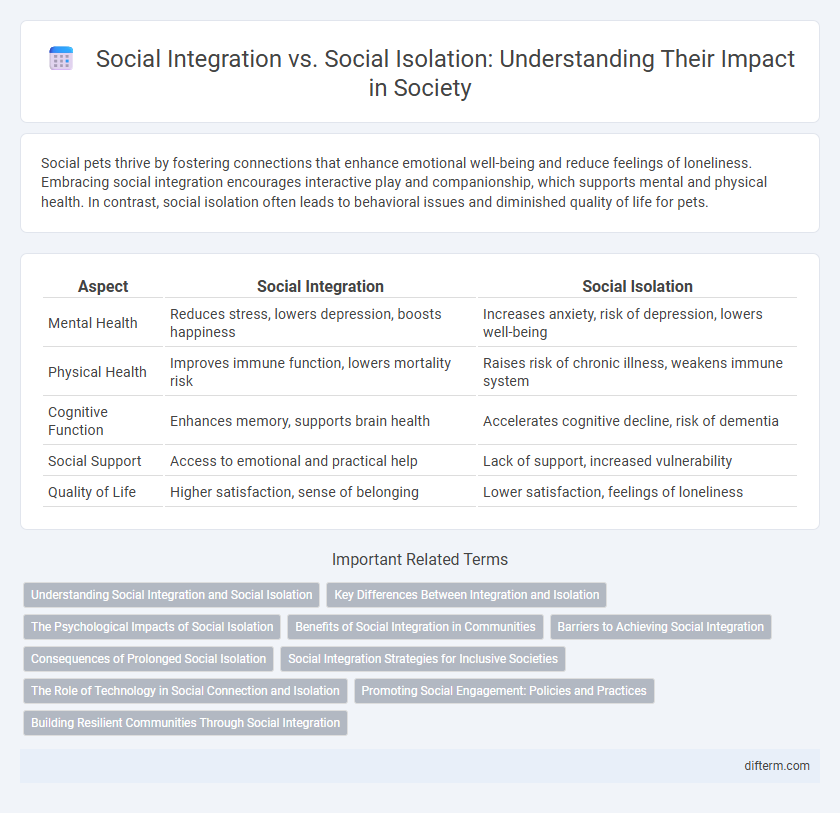
| Aspect | Social Integration | Social Isolation |
|---|---|---|
| Mental Health | Reduces stress, lowers depression, boosts happiness | Increases anxiety, risk of depression, lowers well-being |
| Physical Health | Improves immune function, lowers mortality risk | Raises risk of chronic illness, weakens immune system |
| Cognitive Function | Enhances memory, supports brain health | Accelerates cognitive decline, risk of dementia |
| Social Support | Access to emotional and practical help | Lack of support, increased vulnerability |
| Quality of Life | Higher satisfaction, sense of belonging | Lower satisfaction, feelings of loneliness |
Understanding Social Integration and Social Isolation
Social integration involves active participation in community life, fostering connections that enhance emotional well-being and reduce feelings of loneliness. In contrast, social isolation occurs when individuals lack meaningful social interactions, leading to negative impacts on mental health and higher risks of depression. Recognizing the importance of social bonds is essential for promoting inclusivity and improving overall quality of life.
Key Differences Between Integration and Isolation
Social integration involves active participation in community activities, fostering a sense of belonging and support, whereas social isolation is characterized by limited interaction and feelings of loneliness. Integration enhances mental health, promotes access to resources, and builds social networks, while isolation increases risks of depression, anxiety, and physical health decline. Effective social integration relies on inclusive environments and strong interpersonal connections that counteract the negative impacts of isolation.
The Psychological Impacts of Social Isolation
Social isolation significantly increases the risk of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline by disrupting essential human connections and support networks. Prolonged loneliness triggers heightened stress responses and lowers immune function, exacerbating mental health vulnerabilities. In contrast, social integration fosters emotional resilience, healthier stress management, and improved psychological well-being.
Benefits of Social Integration in Communities
Social integration fosters a strong sense of belonging, improves mental health, and enhances emotional resilience by providing individuals with support networks. Communities with higher social integration experience reduced crime rates, increased civic participation, and stronger economic development. Access to diverse social connections promotes cultural exchange, shared resources, and overall societal well-being.
Barriers to Achieving Social Integration
Barriers to achieving social integration include economic disparities, cultural differences, and limited access to education or social services, which hinder individuals from participating fully in community life. Social stigma and discrimination based on race, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status further exacerbate exclusion and isolation. Overcoming these obstacles requires targeted policies promoting inclusivity, equitable resource distribution, and community engagement initiatives.
Consequences of Prolonged Social Isolation
Prolonged social isolation significantly increases the risk of mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline, particularly among older adults. Research links extended isolation to heightened mortality rates and impaired immune function, exacerbating physical health conditions like cardiovascular disease. Social integration, by contrast, fosters emotional support and resilience, reducing these adverse health effects and promoting overall well-being.
Social Integration Strategies for Inclusive Societies
Social integration strategies for inclusive societies emphasize the implementation of community programs that foster interaction among diverse social groups to reduce social isolation. Policies promoting equal access to education, employment, and social services play a crucial role in creating environments where marginalized populations feel valued and connected. Leveraging digital platforms and local networks enhances communication and support systems, facilitating stronger social cohesion and participation.
The Role of Technology in Social Connection and Isolation
Technology serves as a double-edged sword in social integration, enabling instant communication and access to vast social networks while also fostering potential isolation through superficial interactions. Platforms like social media and messaging apps facilitate relationship building across distances, enhancing inclusivity for marginalized groups and individuals with mobility challenges. However, excessive reliance on digital connections can lead to reduced face-to-face engagement, contributing to feelings of loneliness and social withdrawal.
Promoting Social Engagement: Policies and Practices
Promoting social engagement through inclusive policies and community-driven practices enhances social integration by facilitating meaningful interactions and reducing feelings of social isolation. Implementing accessible public spaces, support groups, and targeted outreach programs strengthens social networks and fosters a sense of belonging among diverse populations. Evidence shows that these strategies improve mental health outcomes and encourage active participation in civic life.
Building Resilient Communities Through Social Integration
Building resilient communities relies on fostering social integration by promoting inclusive participation, mutual support, and shared resources among diverse groups. Strong social networks enhance collective well-being and reduce the risks of social isolation, which often leads to mental health challenges and weakened community cohesion. Empowering individuals through social connections creates adaptive capacities that strengthen community resilience in times of crisis.
social integration vs social isolation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com