Social assimilation involves individuals or groups adopting the cultural norms and behaviors of the dominant society, often leading to the loss of original cultural identities. Social amalgamation, in contrast, emphasizes the blending of diverse cultural traits into a new, cohesive social structure where multiple identities coexist and interact. In the context of social pets, understanding these concepts helps in creating inclusive environments where different social behaviors and interactions merge seamlessly.
Table of Comparison
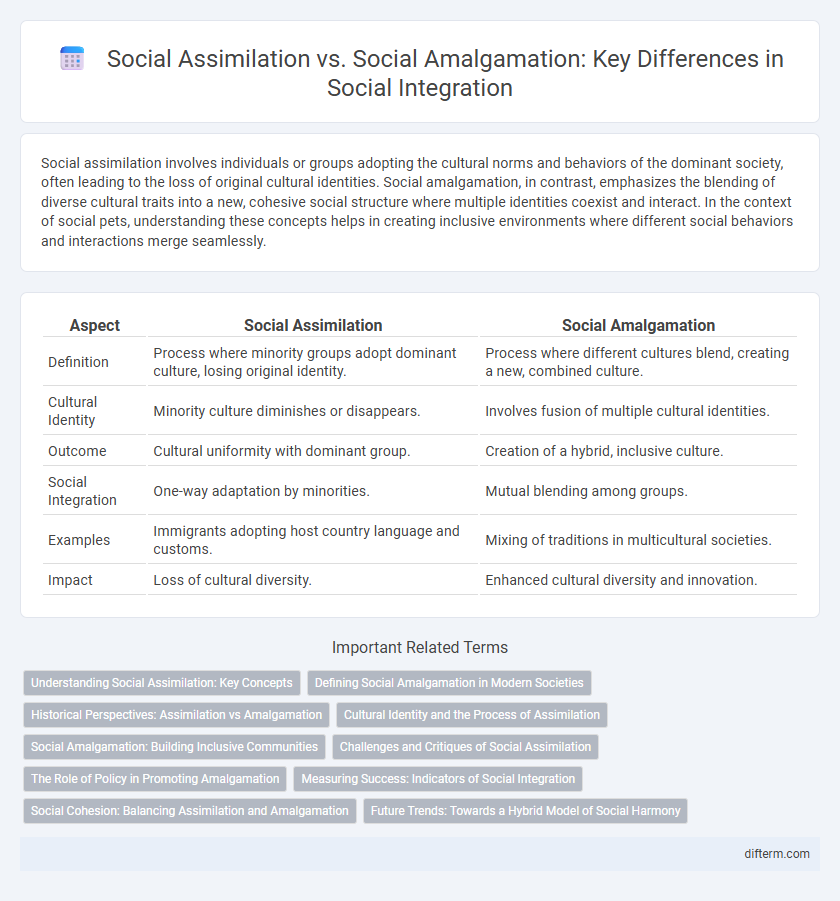
| Aspect | Social Assimilation | Social Amalgamation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process where minority groups adopt dominant culture, losing original identity. | Process where different cultures blend, creating a new, combined culture. |
| Cultural Identity | Minority culture diminishes or disappears. | Involves fusion of multiple cultural identities. |
| Outcome | Cultural uniformity with dominant group. | Creation of a hybrid, inclusive culture. |
| Social Integration | One-way adaptation by minorities. | Mutual blending among groups. |
| Examples | Immigrants adopting host country language and customs. | Mixing of traditions in multicultural societies. |
| Impact | Loss of cultural diversity. | Enhanced cultural diversity and innovation. |
Understanding Social Assimilation: Key Concepts
Social assimilation involves individuals or groups adopting the cultural norms, values, and behaviors of a dominant society, leading to a unified social identity while often reducing diversity. It contrasts with social amalgamation, where distinct groups blend to form a new, hybrid culture without one dominating the other. Understanding social assimilation requires examining processes such as acculturation, integration, and the loss of original cultural traits, highlighting the dynamics of identity transformation within social structures.
Defining Social Amalgamation in Modern Societies
Social amalgamation in modern societies refers to the process where distinct cultural or ethnic groups blend to form a unified social identity, transcending original differences. This phenomenon emphasizes the creation of shared norms, values, and institutions that foster cohesion without erasing individual group identities. Unlike assimilation, amalgamation promotes mutual respect and integration, leading to diverse yet harmonious communities.
Historical Perspectives: Assimilation vs Amalgamation
Historical perspectives on social assimilation reveal a process where minority groups gradually adopt the cultural traits of the dominant society, often resulting in loss of original identity. In contrast, social amalgamation emphasizes the blending of diverse cultural elements to form a new, unified social identity, preserving distinct heritages within a collective whole. Key historical examples include the assimilation policies in the United States during the early 20th century compared to the multicultural amalgamation approaches seen in modern Canadian society.
Cultural Identity and the Process of Assimilation
Social assimilation involves individuals or groups adopting the cultural norms and practices of a dominant society, often resulting in the gradual loss of their original cultural identity. In contrast, social amalgamation emphasizes the blending of different cultural identities into a new, unified culture while preserving distinct elements from each group. The process of assimilation can lead to cultural homogenization, whereas amalgamation supports multicultural coexistence and diversity within a society.
Social Amalgamation: Building Inclusive Communities
Social amalgamation fosters inclusive communities by merging diverse cultural identities into a unified social fabric without erasing individual uniqueness. This process promotes mutual respect, shared values, and collaborative participation among different groups, enhancing social cohesion. Research shows that communities embracing social amalgamation experience lower levels of social tension and greater collective resilience.
Challenges and Critiques of Social Assimilation
Social assimilation often faces challenges such as cultural erosion and identity loss, leading to resistance from minority groups reluctant to abandon their heritage. Critics argue that assimilation imposes a dominant culture's norms, resulting in social exclusion and inequality rather than genuine integration. These issues highlight the need for alternative approaches like social amalgamation, which promotes mutual respect and blending of diverse cultural identities.
The Role of Policy in Promoting Amalgamation
Policy frameworks play a critical role in promoting social amalgamation by encouraging integrated communities where diverse cultural identities coexist and interact. Multicultural policies that support inclusive education, equitable resource distribution, and anti-discrimination laws create environments conducive to blending social groups while preserving cultural uniqueness. Effective governance ensures that social amalgamation fosters cohesion and mutual respect, reducing societal fragmentation.
Measuring Success: Indicators of Social Integration
Measuring success in social integration involves assessing indicators such as equal participation in civic activities, equitable access to education and employment, and the degree of cross-cultural interactions within communities. Social assimilation is often evaluated by the extent to which minority groups adopt dominant cultural norms, while social amalgamation considers the creation of new, blended cultural identities. Data on social cohesion, incidence of intergroup relationships, and reduction in discrimination also serve as key metrics to differentiate between assimilation and amalgamation outcomes.
Social Cohesion: Balancing Assimilation and Amalgamation
Social cohesion thrives when communities strike a balance between assimilation and amalgamation, allowing diverse groups to integrate while preserving unique cultural identities. Assimilation promotes uniformity and shared norms, enhancing social harmony but risking cultural erasure. Amalgamation encourages blending of traditions and values, fostering mutual respect and innovation without demanding complete uniformity.
Future Trends: Towards a Hybrid Model of Social Harmony
Future trends in social integration lean towards a hybrid model that blends elements of social assimilation and social amalgamation. This emerging approach fosters cultural preservation while promoting shared identities, encouraging both unity and diversity within communities. Advances in technology and increased global connectivity are driving this balanced social harmony, facilitating dialogue and collaboration across diverse groups.
social assimilation vs social amalgamation Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com