Social pets thrive through cooperation, enhancing their well-being by forming strong bonds and working together for common goals. While competition can stimulate natural instincts, excessive rivalry often leads to stress and conflict within groups. Balanced social interaction prioritizes collaboration, fostering a harmonious environment that benefits all pets.
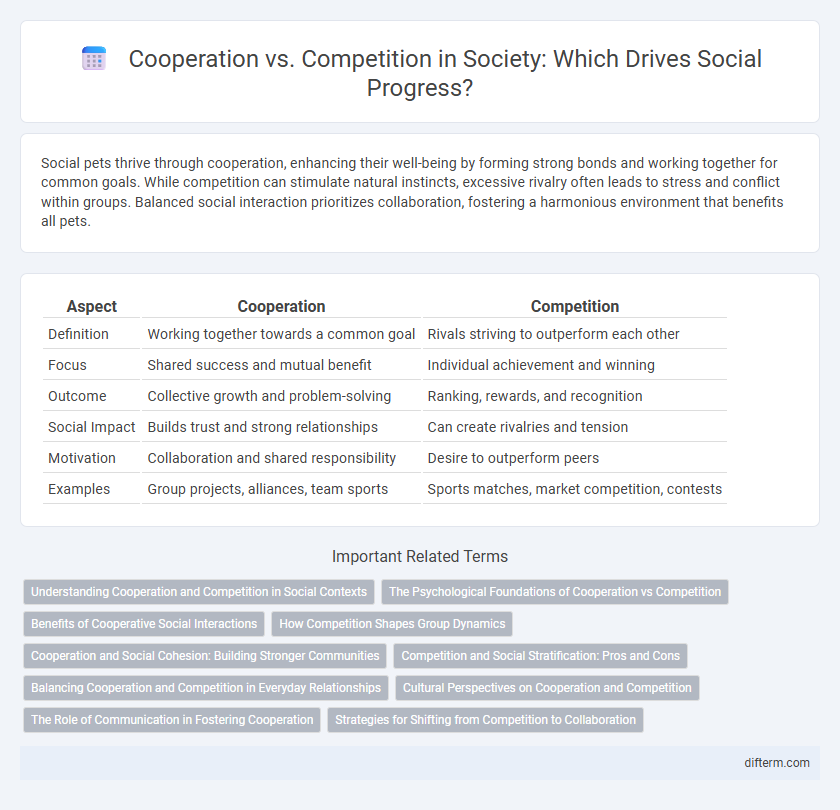
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cooperation | Competition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Working together towards a common goal | Rivals striving to outperform each other |
| Focus | Shared success and mutual benefit | Individual achievement and winning |
| Outcome | Collective growth and problem-solving | Ranking, rewards, and recognition |
| Social Impact | Builds trust and strong relationships | Can create rivalries and tension |
| Motivation | Collaboration and shared responsibility | Desire to outperform peers |
| Examples | Group projects, alliances, team sports | Sports matches, market competition, contests |
Understanding Cooperation and Competition in Social Contexts
Cooperation in social contexts fosters mutual support, shared goals, and collective problem-solving, enhancing group cohesion and trust among members. Competition drives individuals to improve performance, innovate, and achieve personal or group advantages, but excessive rivalry can lead to conflict and reduced collaboration. Balancing cooperation and competition is crucial for optimizing social dynamics, promoting both individual growth and communal well-being.
The Psychological Foundations of Cooperation vs Competition
Cooperation and competition stem from distinct psychological mechanisms influencing human behavior. Cooperation relies on empathy, trust, and prosocial motivation, fostering collective goals and mutual benefits. Competition activates self-interest and social comparison processes, driving individuals to achieve personal success often at the expense of others.
Benefits of Cooperative Social Interactions
Cooperative social interactions foster trust, enhance communication skills, and promote mutual support, leading to stronger community bonds. These interactions facilitate knowledge sharing and collective problem-solving, boosting innovation and resilience in social groups. Increased cooperation correlates with higher overall well-being and reduced social conflict across diverse populations.
How Competition Shapes Group Dynamics
Competition intensifies group dynamics by driving individuals to enhance performance and innovate, often leading to the emergence of clear hierarchies and roles within the group. This dynamic can foster motivation and goal orientation but might also create tensions that challenge group cohesion and trust. Understanding how competitive pressures influence cooperation is essential for balancing productivity with harmonious social interactions.
Cooperation and Social Cohesion: Building Stronger Communities
Cooperation fosters social cohesion by encouraging trust, shared goals, and collective problem-solving, which are essential for building resilient communities. Strong cooperation reduces conflicts and enables diverse groups to work together, enhancing social support networks and overall well-being. Research shows communities with high cooperation levels experience improved economic outcomes and greater community participation.
Competition and Social Stratification: Pros and Cons
Competition drives innovation and personal growth by motivating individuals to improve skills and achieve higher social status, often leading to economic advancement and societal progress. However, excessive competition can deepen social stratification, creating unequal access to resources and opportunities that marginalize lower socioeconomic groups. Balancing competitive dynamics with inclusive policies is essential to minimize social disparities and promote equitable development.
Balancing Cooperation and Competition in Everyday Relationships
Balancing cooperation and competition in everyday relationships enhances mutual growth and resilience by fostering trust while encouraging individual achievement. Effective social dynamics depend on recognizing when to collaborate for shared goals and when to engage in healthy competition to motivate personal development. This equilibrium supports stronger connections and creates an environment where all parties feel valued and challenged.
Cultural Perspectives on Cooperation and Competition
Cultural perspectives on cooperation and competition vary significantly, influencing social behaviors and group dynamics across societies. Collectivist cultures, such as those in East Asia, prioritize cooperation, emphasizing community goals and harmony over individual achievement. In contrast, individualistic cultures like the United States often promote competition, valuing personal success and innovation as drivers of progress.
The Role of Communication in Fostering Cooperation
Effective communication serves as a foundational element in fostering cooperation by enabling clarity, trust, and mutual understanding among participants. Transparent and consistent information exchange reduces conflicts and aligns goals, facilitating collaborative efforts in social groups. Enhanced dialogue channels help in resolving differences promptly, promoting a cooperative rather than competitive environment.
Strategies for Shifting from Competition to Collaboration
Shifting from competition to collaboration involves adopting strategies such as fostering open communication channels, emphasizing shared goals, and building trust among stakeholders. Encouraging transparency and mutual respect creates a foundation where cooperative problem-solving can thrive, reducing adversarial dynamics. Implementing team-based incentives aligns individual efforts with collective success, promoting a culture of collaboration over rivalry in social and organizational settings.
cooperation vs competition Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com