Social justice emphasizes the fair distribution of resources and opportunities to address systemic inequalities, while social equity focuses on achieving fairness through tailored support and accommodations that meet individuals' specific needs. Both concepts aim to create inclusive communities, but social equity ensures that marginalized groups receive the necessary tools to participate fully in society. In the context of a social pet community, fostering social justice requires equitable practices that recognize diverse owner experiences and provide support accordingly.
Table of Comparison
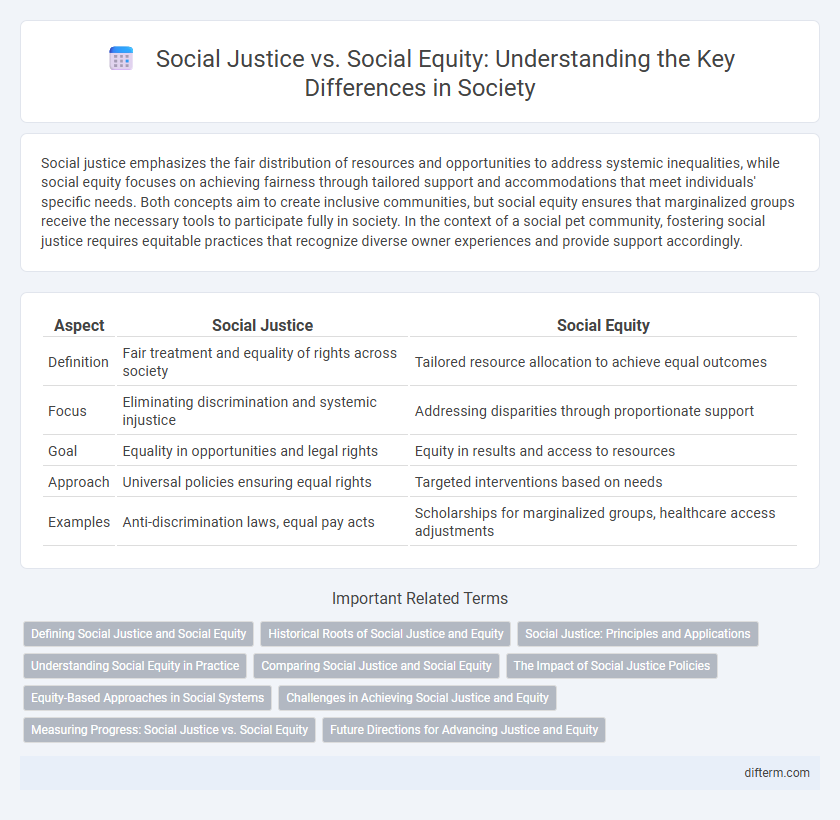
| Aspect | Social Justice | Social Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fair treatment and equality of rights across society | Tailored resource allocation to achieve equal outcomes |
| Focus | Eliminating discrimination and systemic injustice | Addressing disparities through proportionate support |
| Goal | Equality in opportunities and legal rights | Equity in results and access to resources |
| Approach | Universal policies ensuring equal rights | Targeted interventions based on needs |
| Examples | Anti-discrimination laws, equal pay acts | Scholarships for marginalized groups, healthcare access adjustments |
Defining Social Justice and Social Equity
Social justice entails the fair distribution of resources, opportunities, and privileges within a society, emphasizing the removal of systemic barriers and promoting equal rights for all individuals. Social equity focuses on tailored approaches to address historical and structural inequalities, ensuring marginalized groups receive the support needed to achieve comparable outcomes. Understanding the distinction highlights social justice as the overarching ideal of fairness and social equity as the practical means to attain it through targeted interventions.
Historical Roots of Social Justice and Equity
Social justice originates from 18th and 19th-century movements advocating for equal rights and the redistribution of wealth and power, emphasizing universal fairness in law and society. Social equity emerged later, focusing on addressing disparities by recognizing diverse needs and providing tailored resources to marginalized groups. Historical analysis reveals that social justice sought broad systemic change, while social equity targets specific inequalities to achieve balanced opportunities.
Social Justice: Principles and Applications
Social justice encompasses the principles of fairness, human rights, and equal access to resources and opportunities for all individuals regardless of background. It emphasizes dismantling systemic inequalities through policies that promote redistribution and protection of marginalized groups. Practical applications include advocating for inclusive education, equitable healthcare, and labor rights reforms to ensure societal fairness and dignity.
Understanding Social Equity in Practice
Social equity emphasizes fair treatment, access, and opportunities tailored to diverse community needs, aiming to correct systemic inequalities rather than providing uniform solutions. Practical implementation of social equity involves targeted policies that address specific barriers faced by marginalized groups, ensuring resources and support are distributed based on historical and social contexts. This approach contrasts with social justice's broader goal of achieving overall fairness, positioning social equity as a vital mechanism for measurable and inclusive social progress.
Comparing Social Justice and Social Equity
Social justice emphasizes the fair distribution of resources and opportunities by addressing systemic inequalities rooted in race, class, and gender. Social equity focuses on creating tailored policies and practices that recognize diverse needs to achieve equal outcomes across different communities. Both frameworks aim to dismantle discrimination, but social justice targets the broader structural changes while social equity seeks practical, context-specific solutions.
The Impact of Social Justice Policies
Social justice policies aim to dismantle systemic inequalities by promoting equal rights and opportunities across diverse populations, fundamentally altering societal power dynamics. These policies result in measurable improvements in access to education, healthcare, and employment for historically marginalized groups, fostering greater social cohesion. Evaluations reveal that sustained investment in social justice initiatives reduces poverty rates and narrows racial and economic disparities, advancing overall community well-being.
Equity-Based Approaches in Social Systems
Equity-based approaches in social systems prioritize the allocation of resources and opportunities tailored to individual needs, aiming to rectify historical and structural inequalities. By addressing systemic barriers and providing targeted support, these approaches foster inclusive environments that enable marginalized communities to achieve parity with more advantaged groups. Implementing equity-driven policies enhances social cohesion and promotes sustainable development through fairness rather than equal treatment.
Challenges in Achieving Social Justice and Equity
Challenges in achieving social justice and social equity include systemic inequality, limited access to resources, and deeply ingrained discriminatory practices. Disparities in education, healthcare, and economic opportunities perpetuate cycles of poverty and marginalization. Effective policy implementation and inclusive community engagement are critical to overcoming these barriers and promoting fair treatment for all individuals.
Measuring Progress: Social Justice vs. Social Equity
Measuring progress in social justice involves evaluating the dismantling of systemic barriers and ensuring equal rights and opportunities for all individuals. Social equity measurement focuses on the equitable distribution of resources and outcomes tailored to meet diverse community needs, addressing disparities rooted in historical and social contexts. Both approaches require comprehensive data analysis and community engagement to track changes in access, representation, and fairness effectively.
Future Directions for Advancing Justice and Equity
Future directions for advancing social justice and social equity emphasize integrating data-driven policies that address systemic inequalities in education, healthcare, and housing. Empowering marginalized communities through participatory decision-making fosters more equitable resource distribution and policy outcomes. Investment in technology and transparent governance frameworks will play a crucial role in monitoring progress and ensuring accountability in social reform efforts.
social justice vs social equity Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com