Private label products in retail pet stores offer exclusive branding controlled by the retailer, ensuring unique formulations and stronger customer loyalty. White label products, however, are manufactured by third parties and sold under multiple retailers' brands, providing cost-effectiveness and faster market entry. Choosing between private label and white label depends on the retailer's goals for differentiation, control, and investment.
Table of Comparison
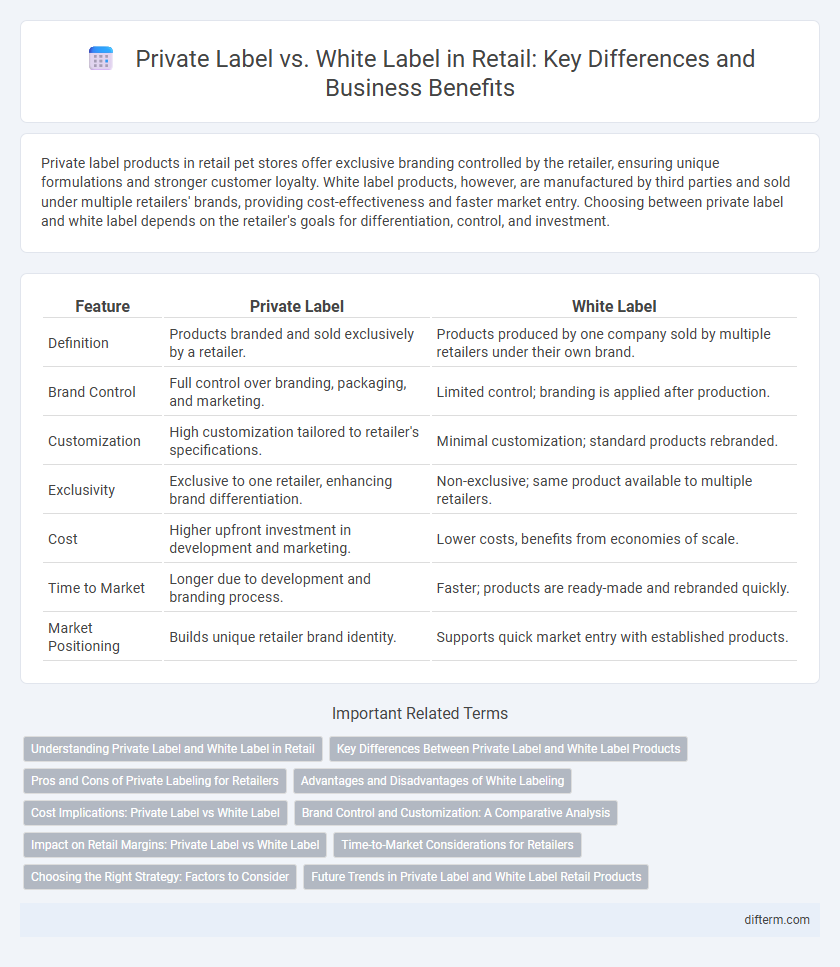
| Feature | Private Label | White Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Products branded and sold exclusively by a retailer. | Products produced by one company sold by multiple retailers under their own brand. |
| Brand Control | Full control over branding, packaging, and marketing. | Limited control; branding is applied after production. |
| Customization | High customization tailored to retailer's specifications. | Minimal customization; standard products rebranded. |
| Exclusivity | Exclusive to one retailer, enhancing brand differentiation. | Non-exclusive; same product available to multiple retailers. |
| Cost | Higher upfront investment in development and marketing. | Lower costs, benefits from economies of scale. |
| Time to Market | Longer due to development and branding process. | Faster; products are ready-made and rebranded quickly. |
| Market Positioning | Builds unique retailer brand identity. | Supports quick market entry with established products. |
Understanding Private Label and White Label in Retail
Private Label products in retail are specifically created and branded by a retailer, offering unique items exclusive to their stores, which enhances brand loyalty and control over quality. White Label products, conversely, are generic goods produced by manufacturers that multiple retailers rebrand and sell under their own store names, allowing for quick market entry and cost efficiency. Understanding these distinctions enables retailers to strategically choose product sourcing methods that align with their branding, pricing, and customer experience goals.
Key Differences Between Private Label and White Label Products
Private label products are exclusively manufactured for a specific retailer, allowing unique branding and greater control over product design and quality, while white label products are generic goods produced by one manufacturer and rebranded by multiple retailers. Private label brands often invest heavily in marketing and product innovation, leading to stronger brand loyalty and differentiation, whereas white label products focus on cost efficiency and faster market entry. Retailers choosing between them weigh factors like customization, exclusivity, pricing strategy, and supply chain control to align with their business goals.
Pros and Cons of Private Labeling for Retailers
Private labeling offers retailers higher profit margins and greater control over product quality and brand identity, allowing for differentiation in a competitive market. However, it requires significant investment in product development, marketing, and inventory management, posing potential risks if consumer demand falls short. Unlike white labeling, private labels demand more time and resources but yield stronger customer loyalty and brand equity over time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of White Labeling
White labeling offers retailers the advantage of rapid market entry with pre-developed products, reducing time and development costs while allowing customization under a retailer's brand. However, reliance on third-party manufacturers can lead to limited control over product quality, potential supply chain disruptions, and challenges in differentiating from competitors using the same products. White labeling is ideal for retailers seeking to expand product lines quickly but may risk brand dilution and lower profit margins compared to private labeling.
Cost Implications: Private Label vs White Label
Private label products typically involve higher upfront costs due to custom branding and exclusive product development, while white label options offer lower initial expenses by providing pre-made products that retailers rebrand. Private label strategies enable greater control over pricing and profit margins, often resulting in higher long-term profitability despite larger initial investments. White label models reduce risk and complexity, making them cost-effective for retailers seeking quick market entry without significant product differentiation.
Brand Control and Customization: A Comparative Analysis
Private label products offer retailers full brand control and extensive customization options, allowing tailored product design, packaging, and marketing strategies that align closely with their target audience. White label products, while faster to market and cost-effective, provide limited customization and brand control since the same product is sold under various retailer brands with minimal alterations. This distinction influences retailer strategies, where private labels enhance brand identity and customer loyalty, whereas white labels prioritize expediency and broad product availability.
Impact on Retail Margins: Private Label vs White Label
Private label products typically yield higher retail margins due to greater control over branding and pricing strategies, reducing dependency on third-party suppliers. White label products offer moderate margins, leveraging established brand recognition but often facing constraints in customization and price flexibility. Retailers prioritizing margin maximization often prefer private labels for exclusivity and margin expansion opportunities.
Time-to-Market Considerations for Retailers
Private label products offer retailers greater control over development and branding, often resulting in longer time-to-market due to product design, manufacturing, and quality assurance processes. White label products provide faster time-to-market as retailers rebrand existing products, minimizing development time and accelerating shelf availability. In highly competitive retail markets, selecting white label solutions can help retailers respond swiftly to consumer trends, while private label strategies support long-term differentiation.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right strategy between private label and white label in retail depends on brand control, product differentiation, and cost considerations. Private label offers exclusive branding and higher margins but requires investment in product development, while white label allows quicker market entry with less customization. Evaluating target audience preferences, competitive landscape, and supply chain capabilities is essential for making an informed decision.
Future Trends in Private Label and White Label Retail Products
Future trends in private label and white label retail products emphasize enhanced brand differentiation through advanced product customization and sustainable packaging innovations. Artificial intelligence-driven consumer insights enable retailers to rapidly adapt offerings, boosting private label competitiveness against national brands. The growing consumer demand for transparency and ethical sourcing accelerates the expansion of eco-friendly private label and white label product lines.
Private Label vs White Label Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com