Inventory shrinkage in retail pet stores results in lost revenue and disrupted supply chains due to theft, damage, or errors, while overstock ties up capital and increases storage costs, leading to reduced profitability. Balancing inventory levels is essential to maintain product availability without incurring excess holding costs or risking stockouts. Implementing accurate demand forecasting and real-time inventory tracking minimizes shrinkage and overstock, enhancing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
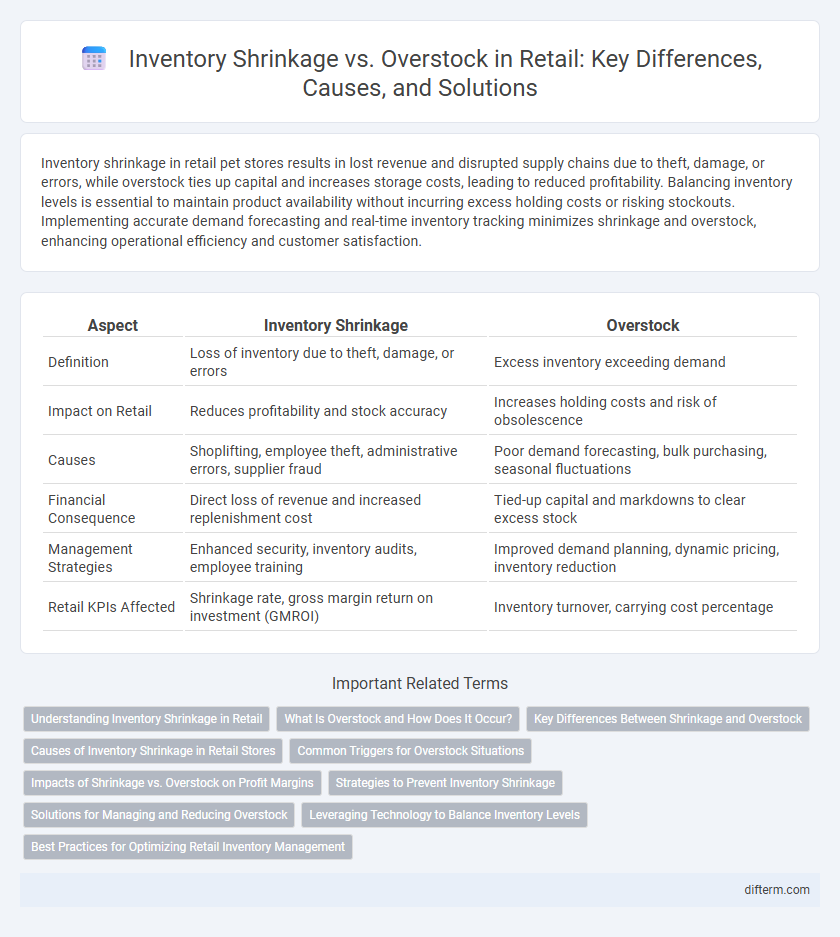
| Aspect | Inventory Shrinkage | Overstock |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Loss of inventory due to theft, damage, or errors | Excess inventory exceeding demand |
| Impact on Retail | Reduces profitability and stock accuracy | Increases holding costs and risk of obsolescence |
| Causes | Shoplifting, employee theft, administrative errors, supplier fraud | Poor demand forecasting, bulk purchasing, seasonal fluctuations |
| Financial Consequence | Direct loss of revenue and increased replenishment cost | Tied-up capital and markdowns to clear excess stock |
| Management Strategies | Enhanced security, inventory audits, employee training | Improved demand planning, dynamic pricing, inventory reduction |
| Retail KPIs Affected | Shrinkage rate, gross margin return on investment (GMROI) | Inventory turnover, carrying cost percentage |
Understanding Inventory Shrinkage in Retail
Inventory shrinkage in retail refers to the loss of products between purchase from suppliers and sale to customers, often caused by theft, damage, or administrative errors. Overstock occurs when excess inventory remains unsold, tying up capital and increasing storage costs. Managing both shrinkage and overstock is essential for optimizing inventory turnover and profitability in retail operations.
What Is Overstock and How Does It Occur?
Overstock occurs when a retailer holds more inventory than consumer demand, leading to excess products that tie up capital and storage space. It commonly arises from inaccurate demand forecasting, poor inventory management, or sudden drops in market demand, causing imbalance between supply and sales. Managing overstock effectively is crucial to minimizing carrying costs and avoiding reduced profitability in the retail sector.
Key Differences Between Shrinkage and Overstock
Inventory shrinkage results from theft, damage, or administrative errors causing stock loss, while overstock occurs when excess inventory exceeds demand, tying up capital and space. Shrinkage directly reduces available sellable goods, impacting profit margins, whereas overstock increases holding costs and risks obsolescence. Retailers must balance accurate demand forecasting and loss prevention strategies to minimize both shrinkage and overstock challenges.
Causes of Inventory Shrinkage in Retail Stores
Inventory shrinkage in retail stores primarily occurs due to shoplifting, employee theft, administrative errors, and supplier fraud. Poor inventory management and lack of effective loss prevention strategies also contribute significantly to unaccounted stock losses. These factors lead to discrepancies between recorded inventory and actual stock, impacting profit margins and operational efficiency.
Common Triggers for Overstock Situations
Overstock situations in retail often stem from inaccurate demand forecasting, leading to excess inventory that ties up capital and storage space. Supplier lead time variability and poor inventory management systems contribute to overordering, resulting in surplus stock. Promotions that fail to stimulate expected sales and sudden changes in consumer trends also trigger overstock challenges.
Impacts of Shrinkage vs. Overstock on Profit Margins
Inventory shrinkage directly reduces profit margins by increasing the cost of goods sold as lost or stolen items disappear from stock without generating revenue. Overstock ties up capital in excess inventory, leading to higher storage costs and potential markdowns that erode profit margins. Effective inventory management balances shrinkage control and demand forecasting to optimize stock levels and maximize profitability.
Strategies to Prevent Inventory Shrinkage
Implementing advanced inventory management systems and regular cycle counts helps detect discrepancies early, reducing inventory shrinkage caused by theft, damage, or administrative errors. Training employees on loss prevention techniques and establishing strict access controls minimizes opportunities for pilferage. Leveraging data analytics to forecast demand improves stock accuracy, preventing overstock while maintaining optimal inventory levels.
Solutions for Managing and Reducing Overstock
Implementing advanced demand forecasting tools and real-time inventory tracking systems helps retailers accurately predict sales trends, preventing overstock accumulation. Cross-channel inventory optimization and dynamic pricing strategies enable efficient stock redistribution and faster turnover. Collaboration with suppliers on flexible ordering and return policies further reduces excess inventory, minimizing holding costs and the risk of obsolescence.
Leveraging Technology to Balance Inventory Levels
Leveraging advanced inventory management systems and real-time analytics helps retailers accurately track stock levels, reducing inventory shrinkage caused by theft, damage, or data errors. Implementing AI-driven demand forecasting allows precise control over ordering processes, minimizing costly overstock situations and optimizing warehouse space. Integrating IoT sensors and automated audits further enhances visibility, balancing inventory levels to maximize profitability and improve customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for Optimizing Retail Inventory Management
Implementing accurate demand forecasting and real-time inventory tracking reduces both inventory shrinkage and overstock risks in retail. Leveraging data analytics and automated replenishment systems helps maintain optimal stock levels, minimizing losses from theft, damage, or obsolescence. Regular cycle counts combined with vendor-managed inventory (VMI) enhance visibility and streamline stock control for efficient retail inventory management.
inventory shrinkage vs overstock Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com