Drop shipping in retail pet allows sellers to list products without holding inventory, as suppliers ship directly to customers, reducing upfront costs and storage needs. Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) involves the seller managing inventory and shipping, offering greater control over packaging and shipping times but requiring more resources. Choosing between these models depends on the seller's capacity to handle logistics and desired level of customer service.
Table of Comparison
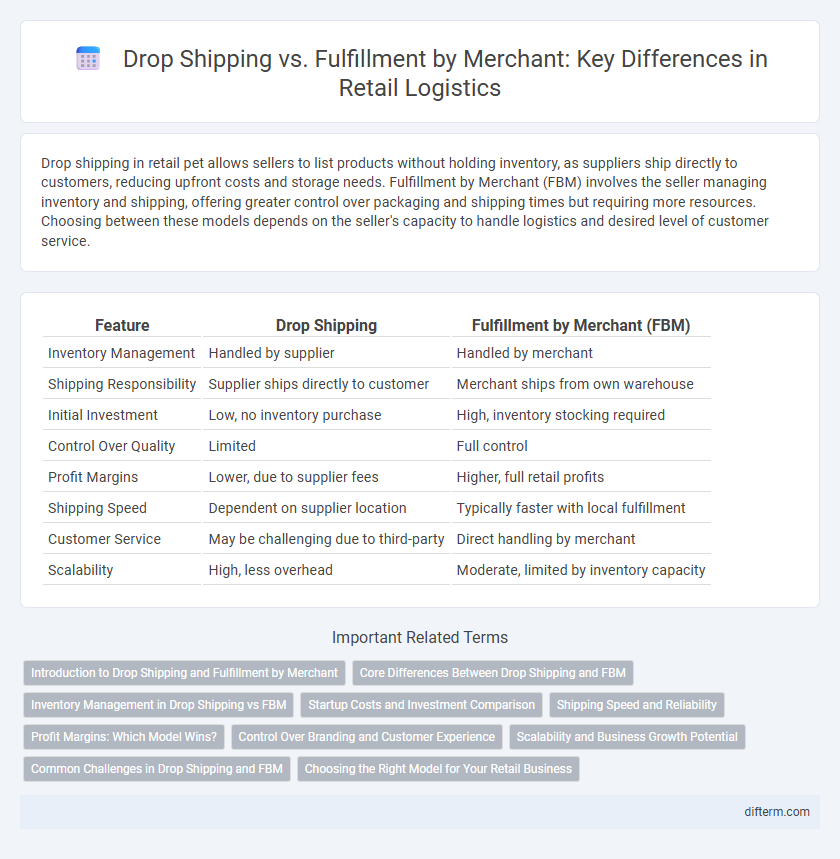
| Feature | Drop Shipping | Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Management | Handled by supplier | Handled by merchant |
| Shipping Responsibility | Supplier ships directly to customer | Merchant ships from own warehouse |
| Initial Investment | Low, no inventory purchase | High, inventory stocking required |
| Control Over Quality | Limited | Full control |
| Profit Margins | Lower, due to supplier fees | Higher, full retail profits |
| Shipping Speed | Dependent on supplier location | Typically faster with local fulfillment |
| Customer Service | May be challenging due to third-party | Direct handling by merchant |
| Scalability | High, less overhead | Moderate, limited by inventory capacity |
Introduction to Drop Shipping and Fulfillment by Merchant
Drop shipping is a retail fulfillment method where the merchant doesn't keep products in stock but instead transfers customer orders and shipment details to a manufacturer, wholesaler, or another retailer who then ships the goods directly to the customer. Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) involves the seller storing inventory, managing orders, and handling shipping processes independently without relying on third-party fulfillment services. Understanding these models helps retailers optimize inventory management, reduce upfront costs, and control customer experience in e-commerce operations.
Core Differences Between Drop Shipping and FBM
Drop shipping involves a retailer selling products without holding inventory, as suppliers ship directly to customers, while Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) requires the seller to store, pack, and ship products themselves. In drop shipping, the retailer avoids upfront inventory costs but has less control over shipping times and product quality. FBM allows sellers to manage inventory and customer service directly, offering greater control but requiring more operational resources and storage space.
Inventory Management in Drop Shipping vs FBM
Drop shipping eliminates the need for retailers to hold inventory, as suppliers manage stock and ship products directly to customers, reducing overhead costs and inventory risks. In contrast, Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) requires sellers to maintain and manage their own inventory, offering greater control over stock levels and shipping times but increasing storage and handling responsibilities. Effective inventory management in drop shipping depends on supplier reliability, while FBM relies on accurate stock tracking and timely order processing to prevent stockouts or overselling.
Startup Costs and Investment Comparison
Drop shipping eliminates inventory investment by allowing retailers to sell products directly from suppliers without upfront stock purchases, resulting in minimal startup costs. Fulfillment by Merchant requires significant capital to purchase and store inventory, manage warehousing, and handle shipping logistics, increasing initial investment. Entrepreneurs choosing drop shipping benefit from lower financial risk and faster time-to-market compared to the higher capital demands and operational involvement of fulfillment by merchant.
Shipping Speed and Reliability
Drop shipping often results in longer and less predictable shipping times due to reliance on third-party suppliers, impacting overall reliability and customer satisfaction. Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) enables sellers to control inventory and shipping processes directly, often leading to faster and more consistent delivery speeds. Direct control in FBM also improves tracking accuracy and reduces the risk of delays compared to drop shipping models.
Profit Margins: Which Model Wins?
Drop shipping typically offers lower profit margins due to higher wholesale and shipping costs, while fulfillment by merchant (FBM) allows retailers to control inventory and shipping expenses, often resulting in higher margins. FBM enables bulk purchasing and better pricing negotiations, increasing profitability but requiring more upfront investment and management. Retailers prioritizing profit margins often favor FBM for greater margin control despite the added operational responsibilities.
Control Over Branding and Customer Experience
Drop shipping offers limited control over branding and customer experience since products are shipped directly from suppliers, often resulting in inconsistent packaging and slower delivery times. Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) allows retailers greater control over packaging, branding, and customer service, enhancing brand consistency and customer satisfaction. Retailers using FBM can customize unboxing experiences and manage shipping speed, directly impacting buyer perception and loyalty.
Scalability and Business Growth Potential
Drop shipping offers scalability with minimal upfront inventory investment, allowing retailers to quickly expand product offerings and reach global markets without warehousing costs. Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) enables greater control over inventory and customer experience, supporting sustainable business growth through personalized service and brand differentiation. Businesses seeking rapid scaling often prefer drop shipping, while those prioritizing brand loyalty and consistent quality lean towards FBM for long-term growth.
Common Challenges in Drop Shipping and FBM
Drop shipping and Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) both present challenges such as inventory management discrepancies and delayed shipping times that impact customer satisfaction. Drop shipping often struggles with supplier reliability and lack of quality control, while FBM faces issues around warehouse capacity and order accuracy. Both models require efficient communication and robust tracking systems to minimize order errors and returns.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Retail Business
Choosing between drop shipping and fulfillment by merchant (FBM) depends on your retail business's control preferences and inventory management capabilities. Drop shipping allows retailers to sell products without holding inventory, minimizing upfront costs but potentially sacrificing shipping speed and customer experience. FBM offers greater control over inventory, packaging, and shipping, which can enhance brand loyalty but requires more investment in warehousing and logistics.
Drop Shipping vs Fulfillment by Merchant Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com