Mind mapping enhances creativity and visual organization by allowing connections between ideas to be easily illustrated, making it ideal for brainstorming sessions. List making offers a straightforward, linear method for task management, promoting clarity and focus on priorities. Choosing between mind mapping and list making depends on whether visual thinking or structured task tracking better suits your productivity style.
Table of Comparison
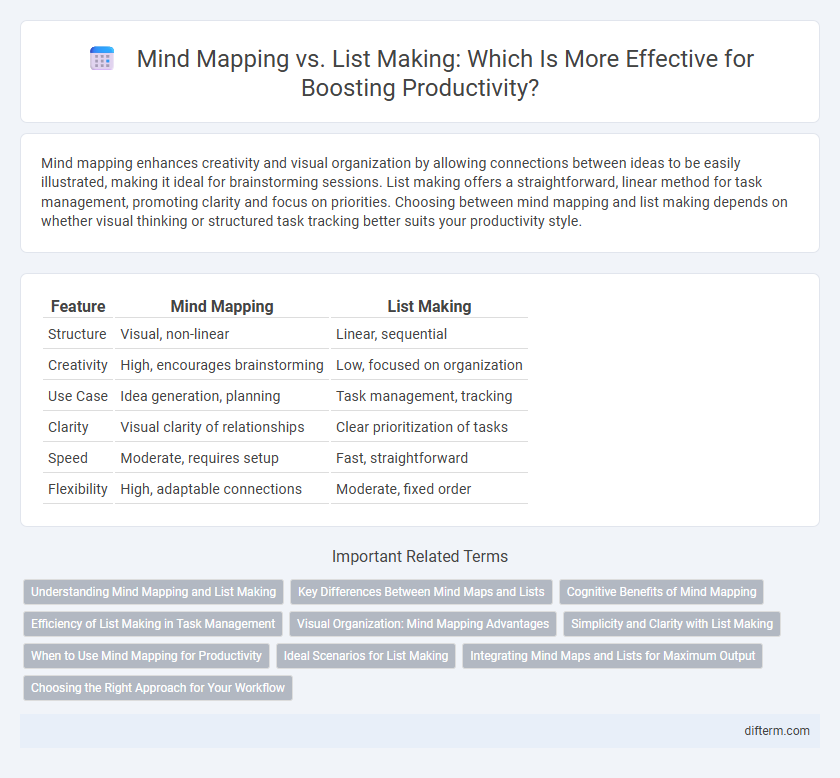
| Feature | Mind Mapping | List Making |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Visual, non-linear | Linear, sequential |
| Creativity | High, encourages brainstorming | Low, focused on organization |
| Use Case | Idea generation, planning | Task management, tracking |
| Clarity | Visual clarity of relationships | Clear prioritization of tasks |
| Speed | Moderate, requires setup | Fast, straightforward |
| Flexibility | High, adaptable connections | Moderate, fixed order |
Understanding Mind Mapping and List Making
Mind mapping enhances productivity by visually organizing ideas, fostering creativity, and establishing connections between concepts for deeper understanding. List making offers straightforward task management and prioritization, making it easier to track progress and complete jobs systematically. Both techniques support effective planning, but mind mapping excels in brainstorming while lists are ideal for concise action steps.
Key Differences Between Mind Maps and Lists
Mind maps visually organize information around a central concept, facilitating creativity and showing hierarchical relationships, whereas lists present data sequentially, emphasizing order and simplicity. Mind maps utilize branches and keywords that stimulate associative thinking, while lists rely on linear, itemized formats that enhance clarity and prioritize tasks. This fundamental difference impacts cognitive processing, with mind maps promoting holistic understanding and lists supporting step-by-step execution.
Cognitive Benefits of Mind Mapping
Mind mapping enhances cognitive function by engaging both hemispheres of the brain, promoting creativity and memory retention through visual and spatial organization of information. Unlike linear list making, mind mapping allows for associative thinking and complex problem-solving by visually connecting ideas and concepts. This method improves information processing efficiency and aids in clearer understanding and recall of tasks.
Efficiency of List Making in Task Management
List making enhances task management efficiency by providing a clear, linear structure that simplifies prioritization and progress tracking. Unlike mind mapping, lists reduce cognitive load by presenting tasks in a straightforward, actionable format that minimizes distractions. This method improves focus and accelerates completion rates, especially in time-sensitive projects.
Visual Organization: Mind Mapping Advantages
Mind mapping offers superior visual organization by enabling users to see relationships between ideas through interconnected nodes and branches. This spatial representation enhances memory retention and creativity compared to linear list making, which can feel rigid and less intuitive. Mind maps facilitate quick identification of key concepts and their associations, improving overall productivity and strategic thinking.
Simplicity and Clarity with List Making
List making enhances productivity by providing simplicity and clarity through its straightforward, linear structure that helps users prioritize tasks efficiently. Unlike mind mapping, which can become visually complex and overwhelming, lists offer direct and concise itemization that minimizes cognitive load and improves focus. This clarity in list making supports quick decision-making and seamless tracking of progress in task management.
When to Use Mind Mapping for Productivity
Mind mapping enhances productivity by visually organizing complex ideas, making it ideal for brainstorming, project planning, and problem-solving where connections between concepts matter. It facilitates creative thinking and memory retention through spatial arrangement and color coding, outperforming linear list making in tasks requiring holistic understanding. Use mind mapping when generating ideas, outlining multifaceted projects, or synthesizing information to boost clarity and efficiency.
Ideal Scenarios for List Making
List making excels in scenarios requiring clear prioritization and sequential task management, such as daily to-do lists and project milestones. It streamlines workflow by breaking down complex objectives into manageable, actionable steps, enhancing focus and accountability. Ideal for deadline-driven environments, list making supports time-sensitive productivity by providing structured clarity.
Integrating Mind Maps and Lists for Maximum Output
Integrating mind maps with list making enhances productivity by combining visual organization and linear task tracking, allowing clearer goal setting and progress monitoring. Mind maps stimulate creativity and big-picture thinking, while lists provide structured, actionable steps that facilitate execution. Employing both tools in tandem creates a dynamic workflow that maximizes focus and efficiency in project management.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Workflow
Mind mapping enhances creativity and visual organization by connecting ideas through diagrams, ideal for brainstorming and complex projects. List making provides a straightforward, linear structure suited for task management and clear prioritization. Selecting the right approach depends on your workflow needs: mind mapping for exploratory thinking and lists for actionable clarity.
Mind mapping vs List making Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com