Entering a flow state dramatically enhances productivity by promoting deep focus and seamless task engagement, whereas a distracted state fragments attention and reduces work quality. Minimizing interruptions and creating an environment conducive to concentration helps sustain the flow state. This balance between flow and distraction is crucial for maximizing efficiency and achieving high-performance outcomes.
Table of Comparison
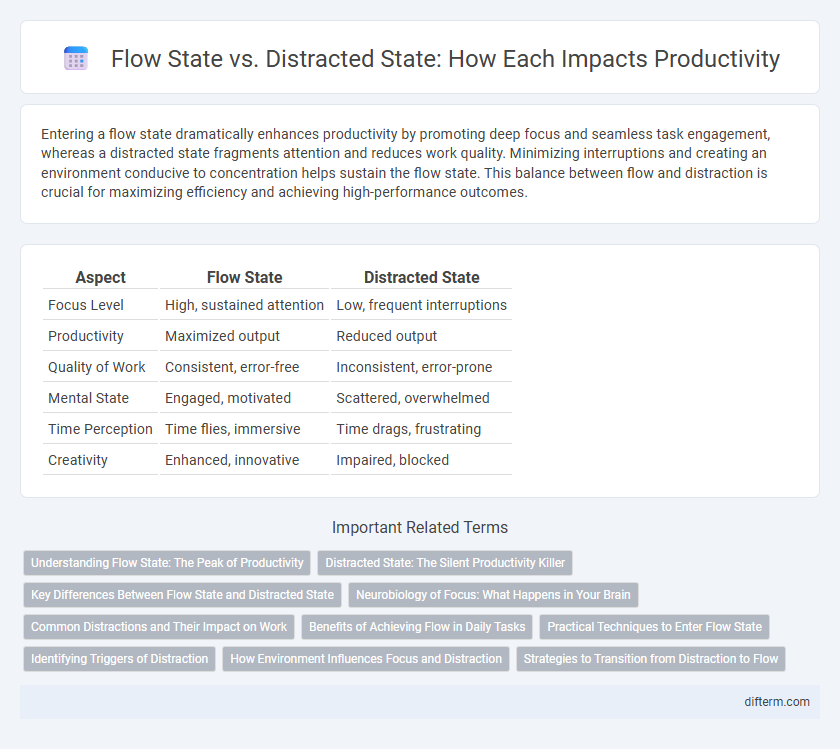
| Aspect | Flow State | Distracted State |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Level | High, sustained attention | Low, frequent interruptions |
| Productivity | Maximized output | Reduced output |
| Quality of Work | Consistent, error-free | Inconsistent, error-prone |
| Mental State | Engaged, motivated | Scattered, overwhelmed |
| Time Perception | Time flies, immersive | Time drags, frustrating |
| Creativity | Enhanced, innovative | Impaired, blocked |
Understanding Flow State: The Peak of Productivity
Flow state represents the peak of productivity, characterized by complete immersion and heightened focus on tasks, leading to enhanced creativity and efficiency. Distractions disrupt this cognitive rhythm, causing fragmented attention and decreased performance. Understanding the neurological basis of flow, including dopamine release and synchronization of brain waves, helps optimize work environments to sustain deep concentration and maximize output.
Distracted State: The Silent Productivity Killer
The distracted state disrupts cognitive processes by fragmenting attention and increasing task-switching, which reduces overall efficiency and prolongs task completion. Studies show that frequent distractions can decrease productivity by up to 40%, leading to increased errors and mental fatigue. Minimizing interruptions through environment control and digital tools is crucial to maintain sustained focus and optimize work output.
Key Differences Between Flow State and Distracted State
Flow state features heightened concentration, effortless engagement, and seamless progress toward goals, resulting in peak productivity and creativity. In contrast, a distracted state involves fragmented attention, frequent interruptions, and reduced task completion, leading to increased errors and longer work duration. Understanding these differences allows individuals to cultivate environments and habits that favor sustained focus and optimal performance.
Neurobiology of Focus: What Happens in Your Brain
During the flow state, the brain exhibits increased activity in the prefrontal cortex, particularly in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, enhancing sustained attention and working memory capacity. Dopamine and norepinephrine levels surge, optimizing cognitive function and promoting a deep sense of immersion and productivity. In contrast, the distracted state triggers heightened activity in the default mode network, causing mind-wandering and reduced executive control, which disrupts focus and decreases overall efficiency.
Common Distractions and Their Impact on Work
Common distractions such as smartphone notifications, background noise, and multitasking severely disrupt the flow state, reducing cognitive performance and work efficiency. These interruptions fragment attention, increase stress levels, and extend task completion times, ultimately lowering overall productivity. Minimizing exposure to such distractions is crucial for maintaining deep focus and achieving optimal work outcomes.
Benefits of Achieving Flow in Daily Tasks
Achieving flow in daily tasks enhances productivity by fostering deep concentration and minimizing errors, leading to higher quality work. This state stimulates creativity and accelerates problem-solving, allowing individuals to complete tasks more efficiently. Sustained flow also boosts motivation and satisfaction, reducing mental fatigue and promoting consistent performance.
Practical Techniques to Enter Flow State
Deep work and time blocking help cultivate flow state by minimizing distractions and structuring focused work periods. Techniques such as setting clear goals, using the Pomodoro method, and practicing mindfulness enhance attention and cognitive engagement. Regular breaks, environmental optimization, and eliminating multitasking are proven to sustain flow and boost productivity.
Identifying Triggers of Distraction
Identifying triggers of distraction involves recognizing environmental, emotional, and digital factors that interrupt flow state productivity. Common distractions include noisy surroundings, multitasking demands, and constant notifications from devices. Developing awareness of these triggers allows individuals to implement strategies that minimize interruptions and sustain focused attention.
How Environment Influences Focus and Distraction
Workspace design significantly impacts the ability to enter a flow state, with minimal noise and organized surroundings enhancing concentration. Cluttered and noisy environments increase cognitive load and trigger distractions, reducing productivity levels. Natural light and ergonomic furniture further support sustained focus by improving comfort and reducing fatigue.
Strategies to Transition from Distraction to Flow
Implementing time-blocking and mindfulness techniques enhances cognitive control, facilitating the transition from distraction to flow state. Reducing multitasking and setting clear, achievable goals increases sustained attention and immersion in tasks. Utilizing environmental cues such as minimizing notifications and creating dedicated workspaces supports maintaining flow by limiting external interruptions.
flow state vs distracted state Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com