The 2-minute rule encourages tackling tasks that take two minutes or less immediately to prevent procrastination and build momentum. In contrast, the 5-minute rule involves committing to work on a task for just five minutes, making it easier to start bigger projects by reducing initial resistance. Both methods enhance productivity by breaking down work into manageable time frames, but the 2-minute rule suits quick tasks while the 5-minute rule is better for overcoming inertia on larger activities.
Table of Comparison
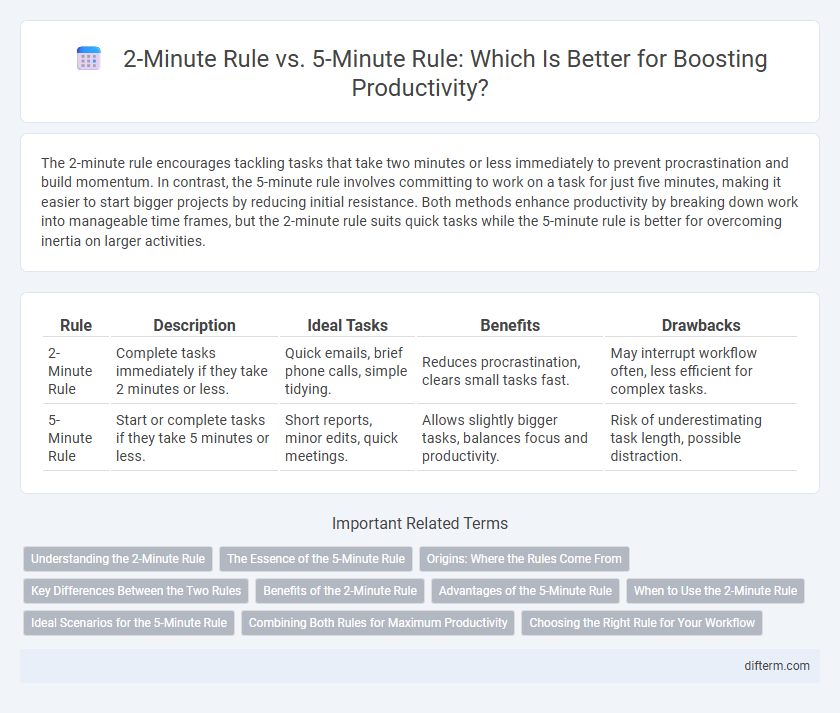
| Rule | Description | Ideal Tasks | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Minute Rule | Complete tasks immediately if they take 2 minutes or less. | Quick emails, brief phone calls, simple tidying. | Reduces procrastination, clears small tasks fast. | May interrupt workflow often, less efficient for complex tasks. |
| 5-Minute Rule | Start or complete tasks if they take 5 minutes or less. | Short reports, minor edits, quick meetings. | Allows slightly bigger tasks, balances focus and productivity. | Risk of underestimating task length, possible distraction. |
Understanding the 2-Minute Rule
The 2-Minute Rule, popularized by productivity expert David Allen, suggests immediately completing any task that takes two minutes or less to prevent buildup and enhance workflow efficiency. This rule leverages quick wins to reduce procrastination and maintain momentum throughout the day. Compared to the 5-Minute Rule, which encourages starting tasks for a minimum of five minutes to overcome inertia, the 2-Minute Rule is more focused on rapid task elimination to streamline daily productivity.
The Essence of the 5-Minute Rule
The 5-minute rule enhances productivity by allowing tasks just beyond the immediate impulse threshold to gain momentum, effectively tackling procrastination and decision fatigue. Unlike the 2-minute rule, which limits attention to quick, easily-completed tasks, the 5-minute rule embraces slightly longer commitments, encouraging consistent progress on more meaningful projects. This approach leverages small increments of dedicated focus, making it easier to transition into deeper work and sustain long-term productivity gains.
Origins: Where the Rules Come From
The 2-minute rule was popularized by productivity expert David Allen in his book "Getting Things Done," emphasizing immediate action on tasks that take two minutes or less to reduce procrastination. The 5-minute rule, often cited in time management circles, originates from the idea that starting a task for just five minutes can overcome inertia and enhance motivation. Both rules stem from behavioral psychology principles aimed at minimizing decision fatigue and promoting task initiation.
Key Differences Between the Two Rules
The 2-minute rule encourages tackling tasks immediately if they can be completed within two minutes, promoting quick wins and reducing procrastination. The 5-minute rule allows starting a task by committing at least five minutes, which helps overcome initial resistance for longer or more complex activities. Key differences lie in task duration focus and psychological commitment, with the 2-minute rule aimed at rapid task clearance and the 5-minute rule designed to build momentum on larger tasks.
Benefits of the 2-Minute Rule
The 2-Minute Rule enhances productivity by promoting immediate action on small tasks, reducing procrastination and mental clutter. By completing tasks that take less than two minutes instantly, it prevents the buildup of minor chores, leading to a more organized and efficient workflow. This rule supports habit formation by integrating quick wins into daily routines, boosting motivation and sustaining momentum throughout the day.
Advantages of the 5-Minute Rule
The 5-minute rule enhances productivity by allowing individuals to commit a manageable chunk of time, reducing the mental barrier to task initiation and fostering consistent progress on complex projects. Unlike the 2-minute rule, the 5-minute approach accommodates more intricate tasks that require deeper focus without overwhelming the individual. This extended duration can improve task momentum, leading to increased motivation and sustained work flow throughout the day.
When to Use the 2-Minute Rule
The 2-minute rule is most effective for tackling small, quick tasks that can be completed immediately, such as responding to emails or organizing your workspace. Applying this rule helps reduce procrastination and prevents minor tasks from accumulating and overwhelming your to-do list. It is ideal for maintaining momentum during focused work sessions without causing significant interruptions.
Ideal Scenarios for the 5-Minute Rule
The 5-minute rule is ideal for tackling tasks that require a bit more time and mental preparation than quick actions like replying to an email or tidying up a desk, which fit the 2-minute rule. It works best for breaking down complex projects into manageable steps, such as outlining a report or brainstorming ideas, where initial momentum is crucial. Using the 5-minute rule enhances focus on tasks that benefit from short, dedicated bursts of attention, increasing overall productivity by reducing procrastination on moderately demanding activities.
Combining Both Rules for Maximum Productivity
Combining the 2-minute and 5-minute rules accelerates task completion by addressing small actions immediately and dedicating focused short bursts to slightly larger tasks. Implementing the 2-minute rule helps clear minor errands or emails quickly, while the 5-minute rule encourages starting more involved tasks without procrastination. This hybrid approach enhances time management efficiency and reduces decision fatigue, driving sustained productivity throughout the day.
Choosing the Right Rule for Your Workflow
The 2-minute rule boosts productivity by encouraging immediate action on tasks that take less than two minutes, reducing procrastination and task accumulation. In contrast, the 5-minute rule suits workflows with more complex or frequent interruptions, allowing a brief commitment to start tasks that may need more time to gain momentum. Selecting the right rule depends on task nature, personal focus levels, and workflow demands, optimizing efficiency and minimizing cognitive load.
2-minute rule vs 5-minute rule Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com