SMART goals provide clear, specific, and measurable targets that enhance individual focus and accountability, promoting steady progress through achievable milestones. OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) align team efforts with broader organizational ambitions, fostering transparency and driving ambitious outcomes by connecting key results to overarching objectives. Combining SMART goals with OKRs effectively balances detailed task management with strategic vision, maximizing productivity at both personal and company levels.
Table of Comparison
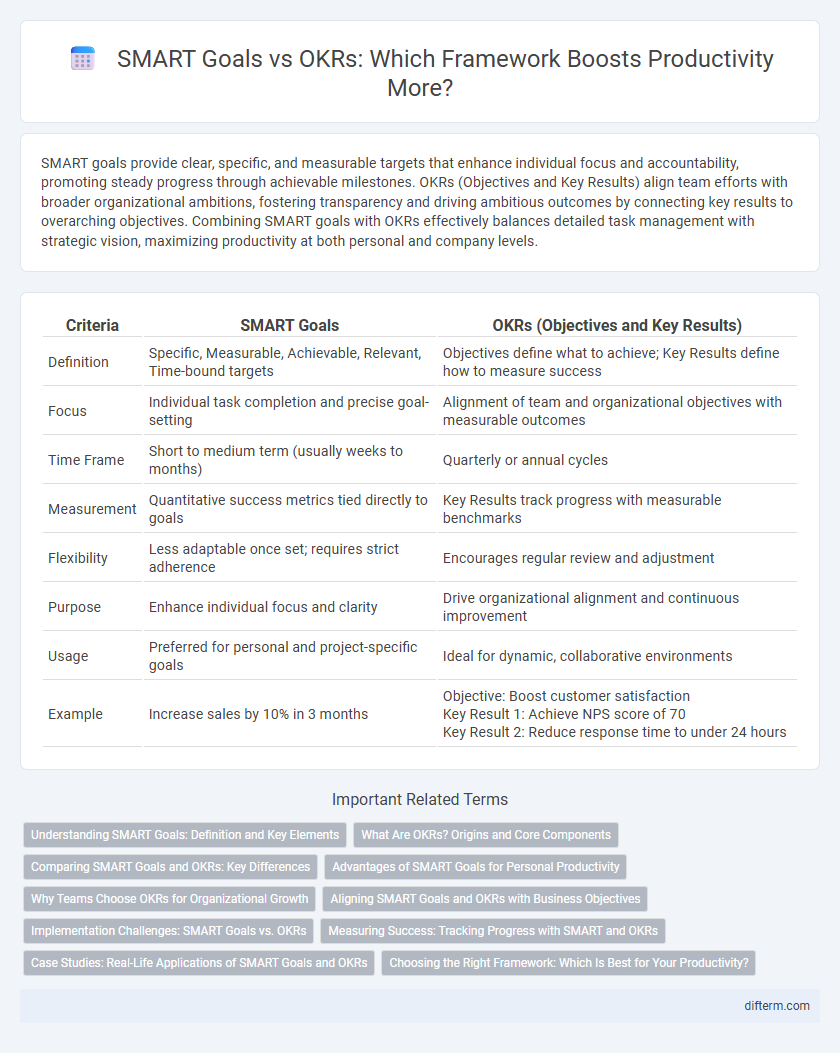
| Criteria | SMART Goals | OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound targets | Objectives define what to achieve; Key Results define how to measure success |
| Focus | Individual task completion and precise goal-setting | Alignment of team and organizational objectives with measurable outcomes |
| Time Frame | Short to medium term (usually weeks to months) | Quarterly or annual cycles |
| Measurement | Quantitative success metrics tied directly to goals | Key Results track progress with measurable benchmarks |
| Flexibility | Less adaptable once set; requires strict adherence | Encourages regular review and adjustment |
| Purpose | Enhance individual focus and clarity | Drive organizational alignment and continuous improvement |
| Usage | Preferred for personal and project-specific goals | Ideal for dynamic, collaborative environments |
| Example | Increase sales by 10% in 3 months | Objective: Boost customer satisfaction Key Result 1: Achieve NPS score of 70 Key Result 2: Reduce response time to under 24 hours |
Understanding SMART Goals: Definition and Key Elements
SMART goals are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound objectives designed to provide clear direction and trackable progress in productivity efforts. Each element ensures goals are well-defined, realistic, aligned with broader aspirations, and constrained by deadlines to enhance accountability. Emphasizing these characteristics creates a structured framework that drives focused action and efficient achievement of desired outcomes.
What Are OKRs? Origins and Core Components
OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) originated at Intel in the 1970s and were popularized by Google to drive focus and alignment in organizations. The core components include a clearly defined Objective, which sets a qualitative goal, and measurable Key Results that track progress toward that goal. Unlike SMART goals, which emphasize Specificity and Realism for individual targets, OKRs foster ambitious, transparent, and collaborative goal-setting across teams.
Comparing SMART Goals and OKRs: Key Differences
SMART goals emphasize Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound criteria to create clear and actionable objectives, fostering individual accountability and short-term focus. OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) consist of ambitious objectives paired with quantifiable key results, promoting alignment, transparency, and continuous progress tracking across teams and organizations. While SMART goals are ideal for precise task management, OKRs drive broader strategic initiatives through collaborative goal-setting and frequent evaluations.
Advantages of SMART Goals for Personal Productivity
SMART goals enhance personal productivity by providing clear, specific, and measurable targets that enable focused effort and easy tracking of progress. Their achievable and relevant criteria foster motivation by ensuring goals are realistic and aligned with individual priorities, reducing overwhelm. Time-bound deadlines create a sense of urgency, driving consistent action and timely completion of tasks.
Why Teams Choose OKRs for Organizational Growth
Teams choose OKRs over SMART goals for organizational growth because OKRs provide a more flexible framework that aligns individual objectives with company-wide key results, enhancing transparency and accountability. OKRs promote continuous progress tracking and allow for quarterly adjustments, ensuring agility in dynamic business environments. This results-focused approach drives collective motivation and sharper alignment with strategic priorities, outperforming the rigidity of SMART goals.
Aligning SMART Goals and OKRs with Business Objectives
Aligning SMART goals and OKRs with business objectives enhances organizational focus by ensuring measurable, specific targets directly support strategic priorities. SMART goals provide clarity through Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound criteria, while OKRs emphasize ambitious Objectives paired with Key Results that track progress. Integrating both frameworks enables teams to translate high-level business goals into actionable, trackable outcomes, driving consistent performance and alignment across all departments.
Implementation Challenges: SMART Goals vs. OKRs
SMART goals often face implementation challenges due to their rigid, specific criteria that can limit adaptability and real-time progress tracking. OKRs offer more flexibility and encourage continuous feedback but require a strong cultural shift and consistent management involvement to be effective. Organizations frequently struggle with aligning OKRs across teams, leading to inconsistent adoption and diluted impact on overall productivity.
Measuring Success: Tracking Progress with SMART and OKRs
SMART goals offer clear, measurable criteria by defining Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound objectives, enabling precise tracking of individual milestones. OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) emphasize ambitious, strategic objectives paired with quantifiable key results to assess progress and align team efforts. Combining SMART goals' detailed metrics with OKRs' broader focus fosters comprehensive measurement of success and accelerates productivity improvements.
Case Studies: Real-Life Applications of SMART Goals and OKRs
Case studies reveal that SMART goals provide clear, measurable benchmarks that enhance individual focus and task completion efficiency, while OKRs drive organizational alignment and ambitious growth through regular progress tracking and transparent communication. Companies like Intel and Google showcase how OKRs foster innovation and cross-team collaboration by setting stretch objectives alongside key results. Conversely, industries with routine tasks benefit from SMART goals to improve accountability and timely goal attainment in customer service and project management.
Choosing the Right Framework: Which Is Best for Your Productivity?
SMART goals provide a clear, structured approach to productivity by emphasizing Specificity, Measurability, Achievability, Relevance, and Time-bound objectives. OKRs focus on ambitious Objectives paired with measurable Key Results, fostering alignment and continuous performance tracking across teams. Selecting the right framework depends on whether your priority is individual task clarity and feasibility (SMART) or organizational alignment and stretch goals (OKRs).
SMART goals vs OKRs Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com