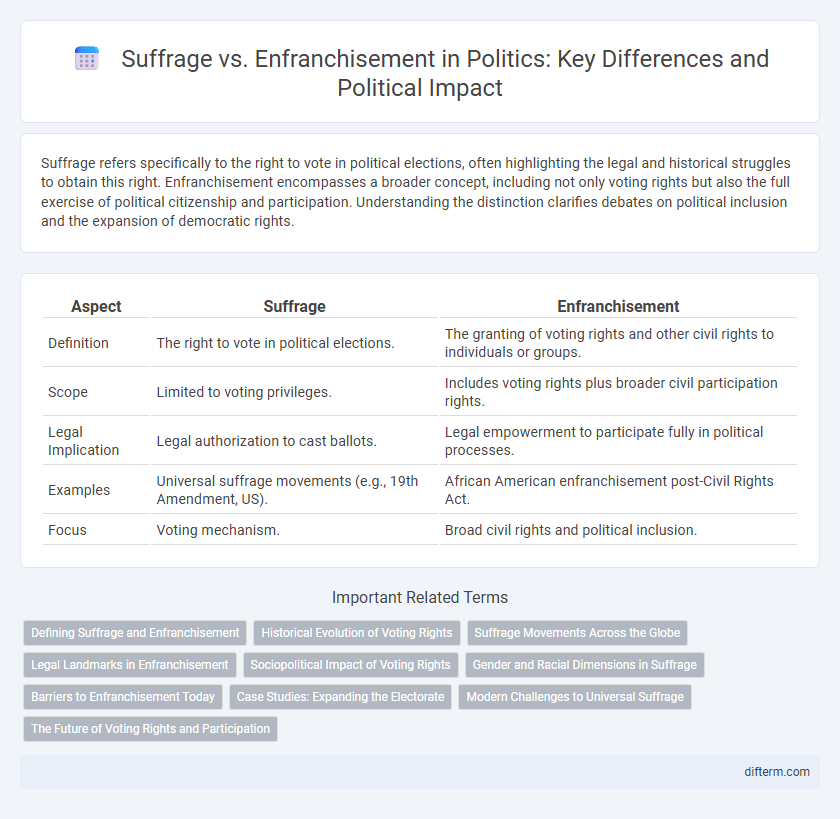
Suffrage refers specifically to the right to vote in political elections, often highlighting the legal and historical struggles to obtain this right. Enfranchisement encompasses a broader concept, including not only voting rights but also the full exercise of political citizenship and participation. Understanding the distinction clarifies debates on political inclusion and the expansion of democratic rights.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Suffrage | Enfranchisement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The right to vote in political elections. | The granting of voting rights and other civil rights to individuals or groups. |
| Scope | Limited to voting privileges. | Includes voting rights plus broader civil participation rights. |
| Legal Implication | Legal authorization to cast ballots. | Legal empowerment to participate fully in political processes. |
| Examples | Universal suffrage movements (e.g., 19th Amendment, US). | African American enfranchisement post-Civil Rights Act. |
| Focus | Voting mechanism. | Broad civil rights and political inclusion. |
Defining Suffrage and Enfranchisement
Suffrage refers specifically to the right to vote in political elections, while enfranchisement encompasses the broader process of granting this right along with associated civil liberties. Enfranchisement involves legal and social mechanisms that extend voting rights to previously excluded groups, often reflecting changes in legislation or societal reforms. Understanding the distinction highlights how suffrage is a subset within enfranchisement, emphasizing active participation in democratic processes.
Historical Evolution of Voting Rights
Suffrage historically referred to the right to vote, initially restricted to property-owning men in many early democracies, whereas enfranchisement expanded to include broader populations such as women and minorities through landmark reforms like the 19th Amendment in the United States and the Representation of the People Acts in the United Kingdom. The gradual expansion of voting rights reflects social and political movements advocating for equality and inclusion, culminating in universal suffrage that encompasses all adult citizens regardless of gender, race, or socioeconomic status. Understanding this evolution highlights the crucial transition from limited suffrage to comprehensive enfranchisement as a foundation of modern democratic systems.
Suffrage Movements Across the Globe
Suffrage movements across the globe have played a crucial role in expanding voting rights and political participation, challenging entrenched systems of exclusion. Key milestones include the women's suffrage campaigns in the United States, the United Kingdom, and India, which progressively secured the franchise for millions. These movements highlight the distinction between suffrage, the right to vote, and enfranchisement, the broader process of granting political rights and inclusion in democratic governance.
Legal Landmarks in Enfranchisement
Legal landmarks in enfranchisement include the 15th Amendment of the U.S. Constitution, which prohibited denying the right to vote based on race, color, or previous condition of servitude, and the 19th Amendment, granting women's suffrage. The Voting Rights Act of 1965 further eliminated discriminatory practices like literacy tests and poll taxes, significantly expanding voter enfranchisement nationwide. These milestones mark critical shifts from the broader concept of suffrage towards legal guarantees ensuring inclusive political participation.
Sociopolitical Impact of Voting Rights
Suffrage refers to the legal right to vote, while enfranchisement encompasses the broader process of granting and exercising that right, often linked to social inclusion and political empowerment. Expanding voting rights has historically altered power structures, enabling marginalized communities to influence policy and advocate for equitable social reforms. The sociopolitical impact of enfranchisement drives democratic legitimacy, fosters civic participation, and shapes governance outcomes through diverse representation.
Gender and Racial Dimensions in Suffrage
Suffrage historically reveals significant gender and racial disparities, with women and racial minorities often excluded from voting rights despite their citizenship. Legal barriers like poll taxes, literacy tests, and gender-based restrictions systematically disenfranchised Black Americans and women, undermining their political participation. Enfranchisement efforts through landmark legislation, including the 15th and 19th Amendments and the Voting Rights Act of 1965, aimed to rectify these injustices by expanding voting access across gender and racial lines.
Barriers to Enfranchisement Today
Barriers to enfranchisement today include stringent voter ID laws, restrictive registration processes, and limited polling access, disproportionately affecting marginalized communities. These obstacles hinder suffrage, which encompasses the right to vote, by imposing practical challenges that reduce voter turnout and political representation. Addressing these barriers is crucial to ensuring equitable participation in democratic processes and upholding the principles of universal suffrage.
Case Studies: Expanding the Electorate
Case studies on expanding the electorate highlight the distinction between suffrage, the legal right to vote, and enfranchisement, the actual empowerment of citizens to participate in elections. Historical examples, such as the 19th Amendment in the United States and the Representation of the People Act 1918 in the United Kingdom, illustrate how legal changes extended suffrage to women but enfranchisement required overcoming social and institutional barriers. These cases demonstrate that expanding suffrage alone does not guarantee full political inclusion without targeted efforts to ensure meaningful enfranchisement.
Modern Challenges to Universal Suffrage
Modern challenges to universal suffrage include voter suppression tactics, such as strict ID laws and gerrymandering, which disproportionately affect marginalized communities. Additionally, misinformation campaigns and digital disenfranchisement undermine the integrity of the electoral process. Access to voting technology and equitable representation remain critical issues in achieving true enfranchisement worldwide.
The Future of Voting Rights and Participation
Suffrage, the right to vote, and enfranchisement, the process of granting that right, remain central to debates on expanding democratic participation. Emerging technologies and legislative reforms aim to address barriers such as voter ID laws, gerrymandering, and disenfranchisement of marginalized communities to enhance inclusivity. The future of voting rights depends on balancing security with accessibility to ensure equitable representation in increasingly diverse societies.
suffrage vs enfranchisement Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com