Big tent parties aim to encompass a wide range of political views to attract diverse voter bases, fostering inclusivity and broad appeal. Narrowcast parties target specific segments or interest groups, delivering focused policies that deeply resonate with their core supporters. The strategic choice between broad coalition-building and specialized advocacy shapes the dynamics and influence of political entities in contemporary democracies.
Table of Comparison
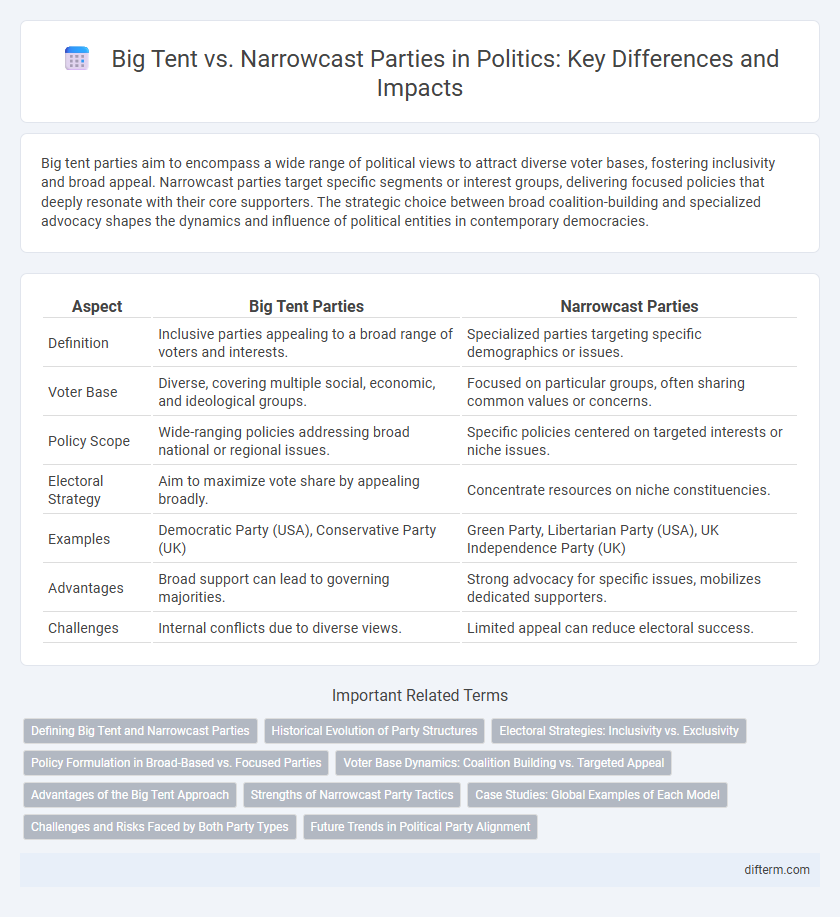
| Aspect | Big Tent Parties | Narrowcast Parties |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inclusive parties appealing to a broad range of voters and interests. | Specialized parties targeting specific demographics or issues. |
| Voter Base | Diverse, covering multiple social, economic, and ideological groups. | Focused on particular groups, often sharing common values or concerns. |
| Policy Scope | Wide-ranging policies addressing broad national or regional issues. | Specific policies centered on targeted interests or niche issues. |
| Electoral Strategy | Aim to maximize vote share by appealing broadly. | Concentrate resources on niche constituencies. |
| Examples | Democratic Party (USA), Conservative Party (UK) | Green Party, Libertarian Party (USA), UK Independence Party (UK) |
| Advantages | Broad support can lead to governing majorities. | Strong advocacy for specific issues, mobilizes dedicated supporters. |
| Challenges | Internal conflicts due to diverse views. | Limited appeal can reduce electoral success. |
Defining Big Tent and Narrowcast Parties
Big tent parties seek to attract a broad spectrum of voters across multiple demographics and ideologies, promoting inclusivity and diverse policy platforms to maximize electoral appeal. Narrowcast parties focus on specific segments of the electorate, addressing specialized interests or ideological niches with targeted messaging and policies. This strategic distinction influences party organization, campaign strategies, and policy priorities in political systems.
Historical Evolution of Party Structures
Big tent parties have historically evolved to encompass a broad spectrum of social groups and political ideologies, aiming to maximize electoral support by appealing to diverse constituencies. Narrowcast parties emerged as a response to increasing political polarization and the desire for more ideologically cohesive platforms, focusing on specific demographic or interest groups. This evolution reflects shifting political landscapes where broad-based coalitions compete with specialized, identity-driven movements for influence and voter loyalty.
Electoral Strategies: Inclusivity vs. Exclusivity
Big tent parties employ electoral strategies centered on inclusivity, aiming to attract a broad coalition of voters across diverse demographics and ideological spectrums to maximize electoral appeal. Narrowcast parties adopt exclusivity as a strategic approach, targeting specific, often homogeneous voter segments with tailored messaging to consolidate loyalty and ensure high voter turnout within niche groups. These contrasting strategies shape campaign messaging, candidate selection, and policy platforms, influencing overall party competitiveness and representation in legislatures.
Policy Formulation in Broad-Based vs. Focused Parties
Big tent parties often engage diverse interest groups, leading to policy formulation that balances conflicting priorities to maintain wide electoral appeal. Narrowcast parties concentrate on specific demographics or issues, allowing more precise and ideologically consistent policy development tailored to their target base. This focused approach can result in clearer policy agendas but may limit broader coalition-building and electoral reach.
Voter Base Dynamics: Coalition Building vs. Targeted Appeal
Big tent parties attract diverse voter bases by embracing broad coalitions across multiple demographics, enhancing electoral stability through inclusive policy platforms. Narrowcast parties focus on targeted appeals to specific segments, fostering intense loyalty but limiting mass appeal and coalition potential. Voter base dynamics reveal that coalition building in big tent parties supports governance viability, while narrowcast strategies drive issue-specific mobilization and niche influence.
Advantages of the Big Tent Approach
The big tent approach in politics offers the advantage of broader voter appeal by encompassing diverse ideological perspectives within a single party, fostering inclusivity and greater electoral support. It enhances political stability by reducing polarization and promoting consensus-building among varied interest groups. This strategy also increases adaptability to changing political landscapes, making the party more resilient during fluctuating public opinion.
Strengths of Narrowcast Party Tactics
Narrowcast party tactics excel in targeting specific voter segments with tailored messaging, increasing engagement and loyalty among niche constituencies. These strategies enable precise data-driven campaigns that maximize resource efficiency and voter turnout within specialized demographics. By leveraging focused communications, narrowcast parties cultivate deeper trust and clearer identities, enhancing their influence despite limited broader appeal.
Case Studies: Global Examples of Each Model
Big tent parties like the Democratic Party in the United States and the Indian National Congress effectively mobilize diverse social groups by embracing broad policy platforms. In contrast, narrowcast parties such as Germany's Alternative for Germany (AfD) and Brazil's Social Liberal Party emphasize targeted appeals to specific ideological or demographic bases. These global examples illustrate how party structures shape electoral strategies and voter engagement in contemporary democracies.
Challenges and Risks Faced by Both Party Types
Big tent parties face challenges in maintaining internal cohesion as diverse factions compete for influence, risking ideological dilution and voter alienation. Narrowcast parties struggle with limited electoral appeal and vulnerability to changes in niche issue relevance, which can undermine long-term sustainability. Both party types encounter risks of fragmentation and policy inconsistency, complicating governance and electoral success.
Future Trends in Political Party Alignment
Big tent parties are expected to evolve by incorporating diverse ideological perspectives to appeal to a broader electorate, leveraging data analytics and social media to tailor messages effectively. Narrowcast parties will likely intensify focus on specific demographic or interest groups, enhancing engagement through targeted digital campaigns and grassroots mobilization. Future political realignment may witness increased hybrid models where parties balance broad coalition-building with specialized messaging to optimize voter reach and loyalty.
big tent vs narrowcast parties Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com