Conservatism advocates for preserving established institutions and gradual reform to maintain social stability, while reactionism seeks to reverse social and political changes, aiming to return to a previous state of society. Both ideologies resist rapid change, but reactionism often embraces more radical measures to restore perceived lost traditions. Understanding the distinctions between these approaches is crucial for analyzing political dynamics and policy debates.
Table of Comparison
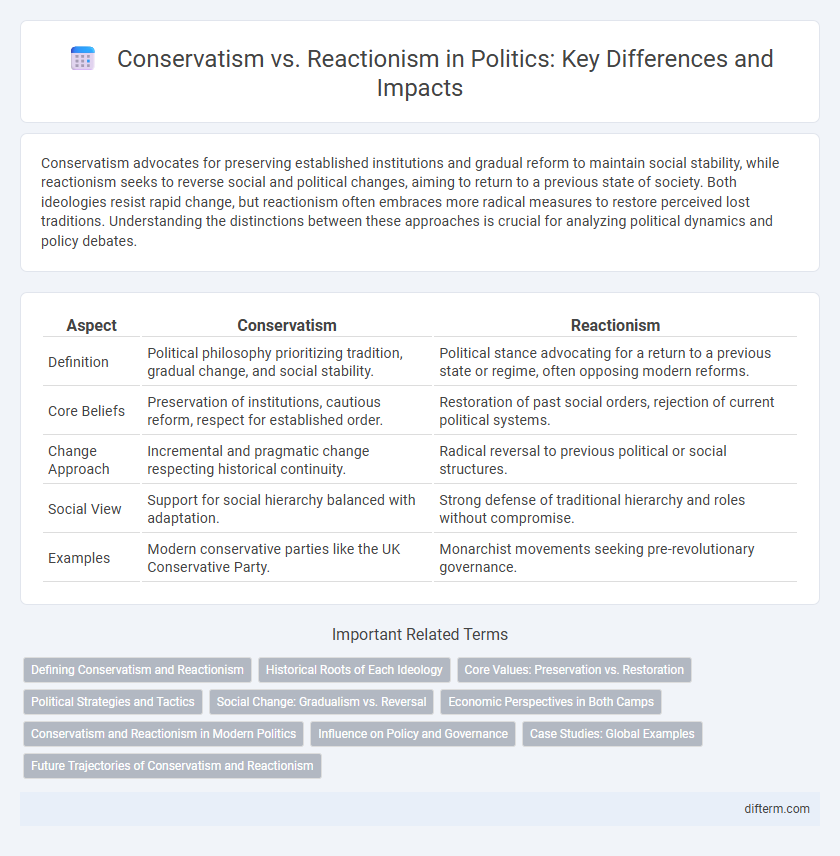
| Aspect | Conservatism | Reactionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Political philosophy prioritizing tradition, gradual change, and social stability. | Political stance advocating for a return to a previous state or regime, often opposing modern reforms. |
| Core Beliefs | Preservation of institutions, cautious reform, respect for established order. | Restoration of past social orders, rejection of current political systems. |
| Change Approach | Incremental and pragmatic change respecting historical continuity. | Radical reversal to previous political or social structures. |
| Social View | Support for social hierarchy balanced with adaptation. | Strong defense of traditional hierarchy and roles without compromise. |
| Examples | Modern conservative parties like the UK Conservative Party. | Monarchist movements seeking pre-revolutionary governance. |
Defining Conservatism and Reactionism
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions, promoting gradual change, and valuing social stability, often rooted in historical continuity and cultural heritage. Reactionism seeks to restore previous social orders and policies, typically advocating for a return to perceived past ideals in response to rapid or revolutionary changes. While conservatism accepts measured adaptation, reactionism resists modernity, aiming to reverse contemporary societal transformations.
Historical Roots of Each Ideology
Conservatism traces its historical roots to the 18th-century response against the radical changes of the French Revolution, emphasizing tradition, social order, and gradual reform. Reactionism emerged as a more extreme political stance, rooted in the desire to restore pre-revolutionary societal structures and resist all forms of modern change. The ideological divide reflects differing attitudes toward progress, with conservatism advocating preservation and cautious adaptation while reactionism demands immediate reversal of political and social transformations.
Core Values: Preservation vs. Restoration
Conservatism emphasizes the preservation of established institutions, traditions, and social orders to maintain societal stability and continuity. Reactionism advocates for the restoration of previous political or social states, often opposing progressive changes and seeking to reverse recent reforms. The core value of conservatism lies in cautious evolution, while reactionism prioritizes reverting to past structures perceived as ideal.
Political Strategies and Tactics
Conservatism emphasizes preserving traditional institutions and gradual reform, employing political strategies that seek stability through measured policy changes and broad coalition-building. Reactionism advocates for a return to previous social or political orders, often utilizing more radical tactics such as mobilizing grassroots movements and leveraging populist rhetoric to resist progressive reforms. Both approaches deploy distinct tactics: conservatism prioritizes legislative negotiation and incrementalism, while reactionism favors direct action and symbolic gestures to catalyze swift political reversal.
Social Change: Gradualism vs. Reversal
Conservatism advocates for gradual social change, emphasizing stability and tradition to adapt societies without abrupt disruptions. Reactionism seeks a reversal to previous social orders, aiming to restore perceived lost values or systems through swift and fundamental shifts. These approaches reflect distinct attitudes toward the pace and direction of social transformation.
Economic Perspectives in Both Camps
Conservatism advocates for free-market principles, limited government intervention, and fiscal responsibility to promote economic stability and growth. Reactionism often seeks to restore past economic structures, favoring protectionist policies and state control to preserve traditional social hierarchies. Both perspectives emphasize economic order but differ in approaches to market regulation and government involvement.
Conservatism and Reactionism in Modern Politics
Conservatism in modern politics emphasizes preserving established institutions, traditions, and values, advocating gradual change to maintain social stability. Reactionism, by contrast, seeks to reverse progressive developments, often promoting a return to perceived past social orders or hierarchies. While conservatism adapts to contemporary challenges with pragmatic reforms, reactionism resists change more rigidly, favoring restoration over evolution.
Influence on Policy and Governance
Conservatism affects policy and governance by emphasizing gradual reform and the preservation of established institutions, promoting stability and continuity within political systems. Reactionism demands a rollback of recent changes to restore prior social or political orders, often resulting in more radical policy reversals and resistance to progressive reforms. Both ideologies shape legislative priorities, with conservatism favoring incremental adjustments and reactionism advocating for swift, fundamental shifts in governance structures.
Case Studies: Global Examples
Conservatism emphasizes gradual social change and the preservation of established institutions, as seen in the UK's post-war political stability under the Conservative Party. Reactionism advocates for a return to a previous state of society, exemplified by France's far-right movements seeking to restore traditional monarchist values. Case studies from Brazil's Bolsonaro administration illustrate a blend of conservative economic policies with reactionary cultural stances, highlighting the global spectrum of right-wing politics.
Future Trajectories of Conservatism and Reactionism
Future trajectories of conservatism emphasize gradual adaptation to societal changes while preserving core cultural and institutional values. Reactionism tends to resist change by advocating a return to past political orders, often opposing modern reforms and progressive policies. The evolving dynamics between these ideologies will shape policy debates on governance, social norms, and national identity in upcoming decades.
conservatism vs reactionism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com