Proportional electoral systems allocate seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, promoting fairer representation of diverse political views. Majoritarian systems, on the other hand, emphasize single-winner districts where the candidate with the most votes claims victory, often leading to stronger governments but less diversity. The choice between proportional and majoritarian systems significantly shapes political party dynamics and voter influence.
Table of Comparison
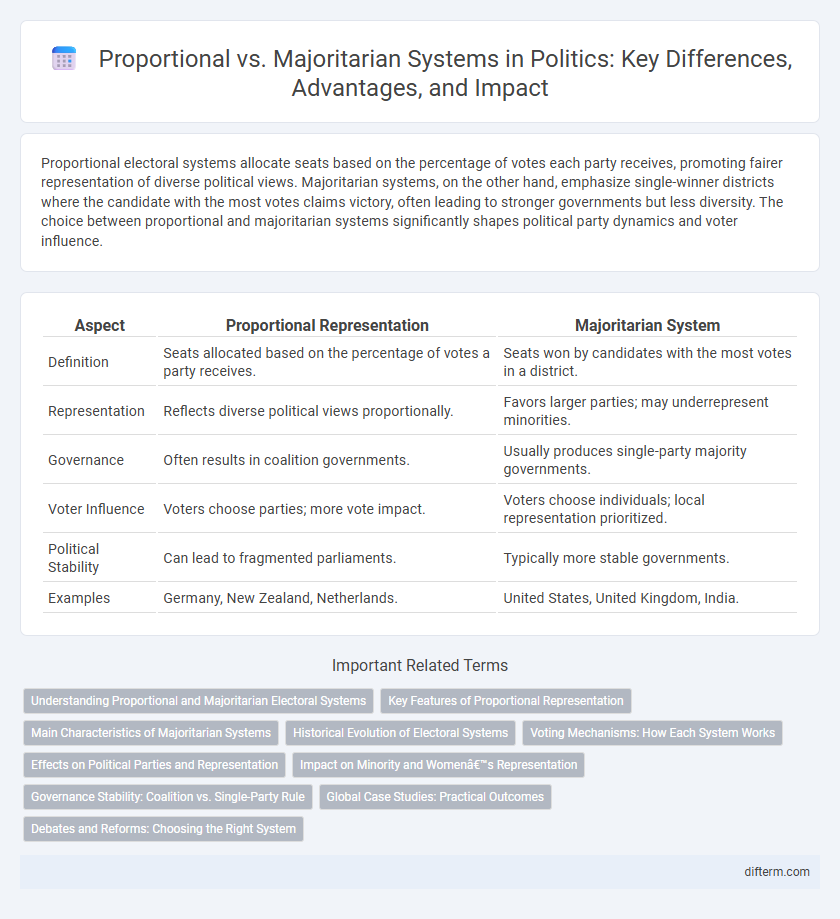
| Aspect | Proportional Representation | Majoritarian System |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seats allocated based on the percentage of votes a party receives. | Seats won by candidates with the most votes in a district. |
| Representation | Reflects diverse political views proportionally. | Favors larger parties; may underrepresent minorities. |
| Governance | Often results in coalition governments. | Usually produces single-party majority governments. |
| Voter Influence | Voters choose parties; more vote impact. | Voters choose individuals; local representation prioritized. |
| Political Stability | Can lead to fragmented parliaments. | Typically more stable governments. |
| Examples | Germany, New Zealand, Netherlands. | United States, United Kingdom, India. |
Understanding Proportional and Majoritarian Electoral Systems
Proportional electoral systems allocate seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring broader representation and reflecting diverse political preferences. Majoritarian systems award seats to candidates who secure the most votes in single-member districts, often leading to clear majorities and stable governments but limited minority representation. Understanding these differences highlights how proportional systems promote inclusivity while majoritarian systems emphasize governability.
Key Features of Proportional Representation
Proportional representation allocates seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring a more accurate reflection of voter preferences. It fosters multi-party systems and coalition governments, enhancing political diversity and representation. This system reduces the likelihood of wasted votes and promotes inclusivity for minority groups and smaller parties.
Main Characteristics of Majoritarian Systems
Majoritarian systems feature single-member districts where the candidate with the most votes wins, often leading to clear majority governments and stable leadership. These systems tend to discourage smaller parties, emphasizing direct accountability between representatives and their constituents. They also promote a two-party system, reducing political fragmentation and simplifying voter choices.
Historical Evolution of Electoral Systems
The historical evolution of electoral systems reveals a shift from majoritarian models, widely used in early democracies such as the United Kingdom and the United States, toward proportional representation systems in many European countries during the 20th century. Proportional representation gained prominence for promoting multi-party inclusion and reflecting diverse voter preferences more accurately, as seen in post-World War II Germany and Sweden. Majoritarian systems, by contrast, have persisted in countries prioritizing strong single-party governance and political stability, highlighting distinct democratic values shaping electoral reforms over time.
Voting Mechanisms: How Each System Works
Proportional voting systems allocate seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, ensuring representation aligns closely with voter preferences. Majoritarian systems, such as first-past-the-post, award seats to candidates who receive the most votes in individual districts, often benefiting larger parties. These mechanisms influence political diversity and governance stability by shaping party strategies and voter engagement.
Effects on Political Parties and Representation
Proportional representation systems tend to foster multi-party systems by allocating seats based on the percentage of votes each party receives, resulting in more accurate representation of diverse political views. Majoritarian systems often favor larger parties, leading to two-party dominance and fewer opportunities for smaller or minority parties to gain representation. This dynamic shapes legislative composition and influences policy-making by either broadening or narrowing the spectrum of political perspectives in government.
Impact on Minority and Women’s Representation
Proportional electoral systems significantly enhance minority and women's representation by allocating seats based on vote share, ensuring diverse voices are reflected in legislatures. Majoritarian systems often marginalize smaller groups and underrepresent women due to winner-takes-all dynamics, limiting political inclusivity. Empirical studies show countries with proportional representation have higher percentages of women and minority lawmakers compared to majoritarian systems.
Governance Stability: Coalition vs. Single-Party Rule
Proportional electoral systems often produce coalition governments that require negotiation among multiple parties, promoting inclusivity but sometimes leading to instability due to conflicting interests. Majoritarian systems typically result in single-party rule, enabling decisive policy implementation and political stability, but risk marginalizing minority voices. Governance stability thus depends on balancing representativeness with effective decision-making in electoral design.
Global Case Studies: Practical Outcomes
Proportional representation systems, as seen in Germany and New Zealand, enhance political diversity by allowing smaller parties to secure legislative seats, leading to coalition governments and broader policy consensus. Majoritarian systems like those in the United States and the United Kingdom tend to produce stable single-party governments but often underrepresent minority parties, limiting political plurality. Empirical studies show that proportional systems generally result in higher voter turnout and greater satisfaction with democratic processes compared to majoritarian frameworks.
Debates and Reforms: Choosing the Right System
Debates around proportional versus majoritarian electoral systems center on representation accuracy and governance stability, with proportional systems promoting inclusivity and majoritarian models emphasizing decisiveness. Reforms often balance voter equity against the potential for fragmented legislatures, influencing party dynamics and policy outcomes. Choosing the right system hinges on national political culture, historical context, and objectives for democratic legitimacy.
proportional vs majoritarian Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com