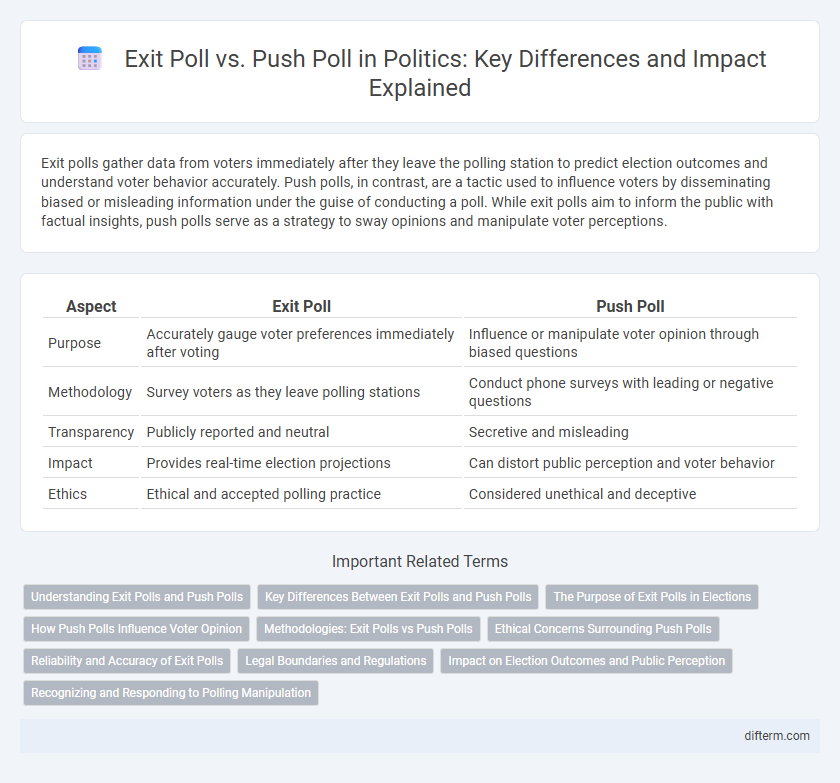
Exit polls gather data from voters immediately after they leave the polling station to predict election outcomes and understand voter behavior accurately. Push polls, in contrast, are a tactic used to influence voters by disseminating biased or misleading information under the guise of conducting a poll. While exit polls aim to inform the public with factual insights, push polls serve as a strategy to sway opinions and manipulate voter perceptions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Exit Poll | Push Poll |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Accurately gauge voter preferences immediately after voting | Influence or manipulate voter opinion through biased questions |
| Methodology | Survey voters as they leave polling stations | Conduct phone surveys with leading or negative questions |
| Transparency | Publicly reported and neutral | Secretive and misleading |
| Impact | Provides real-time election projections | Can distort public perception and voter behavior |
| Ethics | Ethical and accepted polling practice | Considered unethical and deceptive |
Understanding Exit Polls and Push Polls
Exit polls gather voters' actual choices immediately after they leave polling stations to predict election outcomes and analyze voting patterns. Push polls, in contrast, are designed to influence or manipulate voters by presenting biased or misleading information under the guise of a survey. Understanding these differences clarifies how exit polls provide factual data while push polls serve as a campaign strategy aimed at shaping public opinion.
Key Differences Between Exit Polls and Push Polls
Exit polls collect voters' choices immediately after they leave the polling station to provide accurate predictions of election outcomes and voter demographics. Push polls are a form of negative campaigning designed to manipulate voter opinions through biased or misleading questions under the guise of surveying. Key differences include exit polls aiming for unbiased data collection, while push polls seek to influence behavior and perceptions rather than gather genuine electoral information.
The Purpose of Exit Polls in Elections
Exit polls aim to accurately capture voters' choices immediately after they leave polling stations, providing real-time data on election outcomes and voter demographics. These polls help predict winners, analyze voting patterns, and identify trends across different regions and social groups. Unlike push polls, exit polls are designed for objective data collection rather than influencing voter opinions or perceptions.
How Push Polls Influence Voter Opinion
Push polls influence voter opinion by presenting biased or leading questions designed to shape perceptions rather than gather genuine data, often spreading negative information about opponents. Unlike exit polls, which provide neutral voter behavior insights, push polls manipulate respondents to sway decisions before voting. This strategic polling tactic undermines democratic processes by distorting public opinion and campaign narratives.
Methodologies: Exit Polls vs Push Polls
Exit polls use systematic sampling of voters immediately after they leave polling stations to provide statistically representative data on voter behavior and preferences. Push polls employ persuasive, often misleading questions aimed at influencing opinions rather than collecting unbiased data, relying on targeted phone surveys designed to sway rather than measure voters. The methodologies differ fundamentally, with exit polls emphasizing data accuracy and representativeness, while push polls prioritize strategic messaging and voter manipulation.
Ethical Concerns Surrounding Push Polls
Push polls raise significant ethical concerns due to their manipulative nature, often spreading misleading or biased information disguised as survey questions to influence voter opinions. Unlike exit polls, which aim to objectively gather data on voter behavior, push polls prioritize swaying public perception through deceptive tactics. This unethical approach undermines democratic processes by distorting genuine voter sentiment and eroding trust in electoral integrity.
Reliability and Accuracy of Exit Polls
Exit polls collect voter choices immediately after voting, providing highly reliable and accurate reflections of election outcomes when conducted with rigorous sampling methods and transparent procedures. Push polls, by contrast, use biased or leading questions to influence public opinion rather than measure it, significantly compromising reliability and validity. Accurate exit polls are essential for forecasting results and analyzing voter behavior, but their precision depends on methodology, sample size, and adherence to unbiased data collection practices.
Legal Boundaries and Regulations
Exit polls are conducted at polling stations immediately after voters cast their ballots, complying with strict legal boundaries that prohibit influencing voter behavior or misrepresenting data, whereas push polls are often considered deceptive and may violate election laws due to their intent to manipulate voter opinions through biased or leading questions. Legal regulations require exit polls to maintain transparency and neutrality, with oversight to ensure data is collected ethically and released in a manner that does not affect election integrity. Push polls lack standardized regulatory framework and are frequently scrutinized for breaching campaign laws, prompting calls for tighter controls to protect the electoral process from misleading practices.
Impact on Election Outcomes and Public Perception
Exit polls provide statistically reliable data reflecting voter choices immediately after voting, shaping public perception by offering early insights into election outcomes and influencing media narratives and voter behavior. Push polls, by contrast, are designed as manipulative survey techniques that disseminate biased or misleading information to sway opinions, potentially distorting public perception and undermining the integrity of the electoral process. The differential impact of these polling methods highlights the importance of transparency and accuracy in electoral data to maintain trust and legitimacy in democratic systems.
Recognizing and Responding to Polling Manipulation
Exit polls aim to collect accurate voter data immediately after individuals cast ballots, whereas push polls are designed to influence or manipulate voter opinions under the guise of a survey. Recognizing the differences involves analyzing question phrasing, timing, and intent, as exit polls serve transparency while push polls often deploy misleading information to sway results. Effective responses include promoting media literacy, verifying poll sources, and implementing regulations to curb deceptive practices that undermine democratic processes.
Exit poll vs Push poll Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com