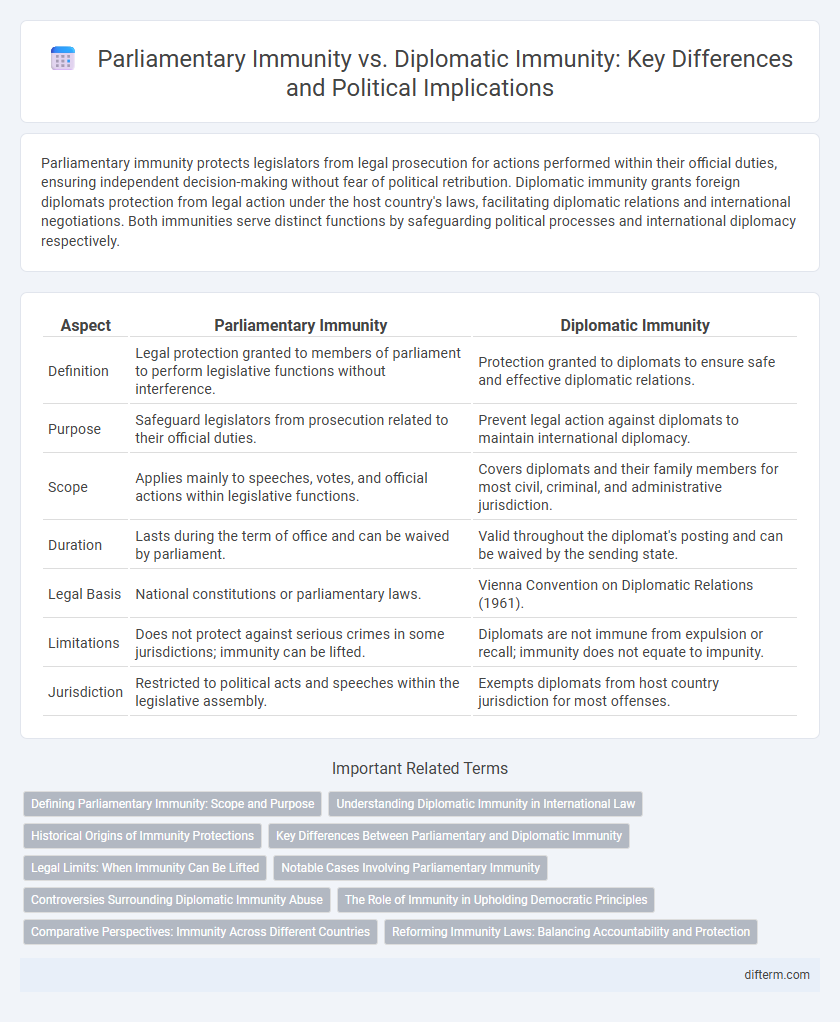
Parliamentary immunity protects legislators from legal prosecution for actions performed within their official duties, ensuring independent decision-making without fear of political retribution. Diplomatic immunity grants foreign diplomats protection from legal action under the host country's laws, facilitating diplomatic relations and international negotiations. Both immunities serve distinct functions by safeguarding political processes and international diplomacy respectively.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Parliamentary Immunity | Diplomatic Immunity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal protection granted to members of parliament to perform legislative functions without interference. | Protection granted to diplomats to ensure safe and effective diplomatic relations. |
| Purpose | Safeguard legislators from prosecution related to their official duties. | Prevent legal action against diplomats to maintain international diplomacy. |
| Scope | Applies mainly to speeches, votes, and official actions within legislative functions. | Covers diplomats and their family members for most civil, criminal, and administrative jurisdiction. |
| Duration | Lasts during the term of office and can be waived by parliament. | Valid throughout the diplomat's posting and can be waived by the sending state. |
| Legal Basis | National constitutions or parliamentary laws. | Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations (1961). |
| Limitations | Does not protect against serious crimes in some jurisdictions; immunity can be lifted. | Diplomats are not immune from expulsion or recall; immunity does not equate to impunity. |
| Jurisdiction | Restricted to political acts and speeches within the legislative assembly. | Exempts diplomats from host country jurisdiction for most offenses. |
Defining Parliamentary Immunity: Scope and Purpose
Parliamentary immunity protects legislators from legal action related to their official duties, ensuring they can perform legislative functions without fear of prosecution or harassment. It extends to speeches, votes, and parliamentary activities but typically excludes crimes unrelated to legislative work. This immunity supports the independence of the legislative branch by safeguarding representatives from external political pressure or judicial interference.
Understanding Diplomatic Immunity in International Law
Diplomatic immunity, established under the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations (1961), grants diplomats protection from prosecution in the host country to ensure uninterrupted diplomatic functions. Unlike parliamentary immunity, which protects legislators from legal action within their own country to safeguard legislative independence, diplomatic immunity emphasizes international relations and sovereign equality. This immunity covers criminal and civil jurisdiction protections, allowing diplomats to perform their duties without fear of harassment or legal entanglement abroad.
Historical Origins of Immunity Protections
Parliamentary immunity originated in medieval England as a safeguard for lawmakers to debate and legislate without fear of royal retribution, solidifying its role in protecting democratic processes. Diplomatic immunity traces back to ancient civilizations like Greece and Rome, where envoys were granted safe passage and protection to ensure peaceful interstate communication. Both immunities evolved from distinct historical needs: parliamentary immunity shields legislative independence, while diplomatic immunity upholds international relations and the inviolability of diplomats.
Key Differences Between Parliamentary and Diplomatic Immunity
Parliamentary immunity protects legislators from legal actions related to speech and votes conducted within their official duties, ensuring independence in legislative functions. Diplomatic immunity grants diplomats protection from prosecution under the host country's laws, safeguarding diplomatic agents' functions and maintaining international relations. Key differences lie in scope and beneficiaries: parliamentary immunity applies to elected representatives within domestic legislative processes, while diplomatic immunity covers foreign diplomats residing abroad.
Legal Limits: When Immunity Can Be Lifted
Parliamentary immunity can be lifted through a formal vote by the legislative body, allowing legal proceedings against members for criminal acts unrelated to their official duties. Diplomatic immunity, codified under the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, is more rigid, generally only lifted by the diplomat's home country waiving immunity to permit prosecution. Both immunities aim to protect official functions, but legal limits depend on institutional authority and international agreements governing their suspension.
Notable Cases Involving Parliamentary Immunity
Notable cases involving parliamentary immunity highlight its role in protecting legislators from prosecution for actions related to their official duties, as seen in the case of French President Emmanuel Macron, who benefited from immunity as a former parliamentarian during investigations. Unlike diplomatic immunity, which shields diplomats from legal action in foreign countries, parliamentary immunity primarily safeguards lawmakers within their own national legal system, ensuring legislative independence. The Brazilian Supreme Court's ruling on former President Dilma Rousseff's parliamentary immunity emphasized the limits and conditions under which such protections apply, marking a critical precedent in balancing accountability and legislative privilege.
Controversies Surrounding Diplomatic Immunity Abuse
Diplomatic immunity, designed to protect diplomats from prosecution, often faces criticism due to frequent abuses where individuals evade legal responsibility for serious crimes. Parliamentary immunity, while also controversial, primarily aims to safeguard legislators from politically motivated prosecutions rather than criminal acts. The core controversy revolves around diplomatic immunity's exploitation, which undermines justice and fuels diplomatic tensions between states.
The Role of Immunity in Upholding Democratic Principles
Parliamentary immunity safeguards legislators by protecting their freedom of speech and actions within parliamentary duties, ensuring open debate and accountability essential for democratic governance. Diplomatic immunity protects diplomats from legal prosecution in host countries, facilitating international relations and peaceful negotiations without fear of local interference. Both immunities play crucial roles in upholding democratic principles by balancing legal protections with the need for transparency and justice in political and international arenas.
Comparative Perspectives: Immunity Across Different Countries
Parliamentary immunity safeguards legislators from prosecution or legal action during their official duties, varying significantly between countries such as France, where it offers broad protections, and the United States, which applies more limited immunity focused on speech. Diplomatic immunity, governed by the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, provides diplomats inviolability from criminal jurisdiction universally but is interpreted and enforced differently by states like the United Kingdom and China in cases involving serious crimes or diplomatic misconduct. Comparative analysis reveals that while parliamentary immunity centers on preserving legislative independence, diplomatic immunity emphasizes state sovereignty and international relations, resulting in diverse legal interpretations and practical applications worldwide.
Reforming Immunity Laws: Balancing Accountability and Protection
Reforming immunity laws requires carefully balancing parliamentary immunity, which protects legislators from prosecution during their terms to ensure legislative independence, with diplomatic immunity, which shields diplomats from legal action to maintain international relations. Enhanced legal frameworks must define clear limits and conditions for lifting immunity, preventing abuse while preserving essential protections that support political functions and diplomatic missions. Transparent accountability mechanisms and rigorous oversight can reconcile the need for immunity with democratic principles and rule of law.
Parliamentary immunity vs Diplomatic immunity Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com