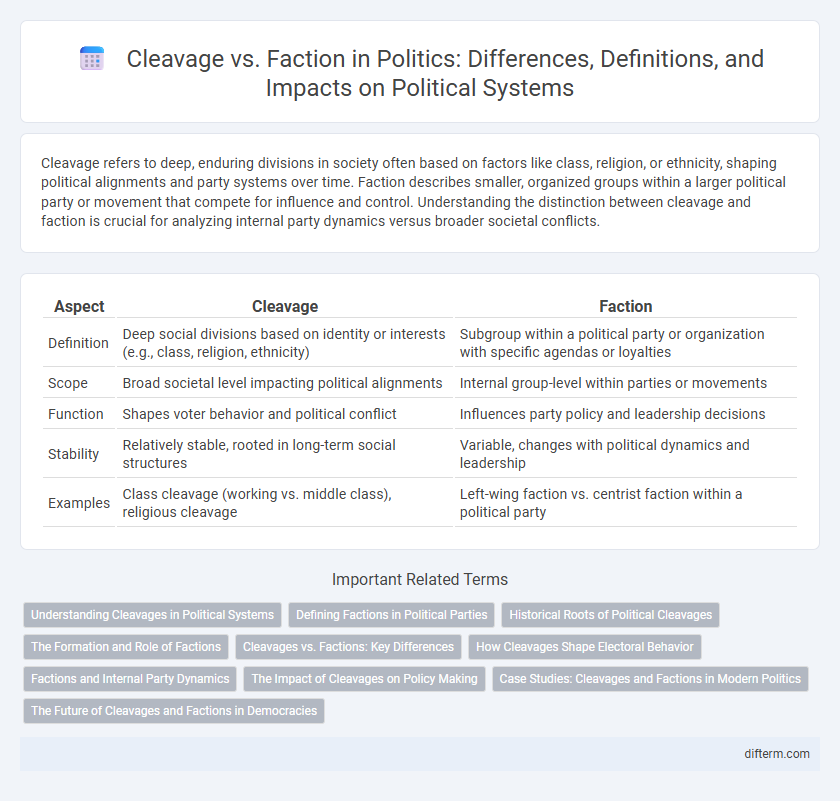
Cleavage refers to deep, enduring divisions in society often based on factors like class, religion, or ethnicity, shaping political alignments and party systems over time. Faction describes smaller, organized groups within a larger political party or movement that compete for influence and control. Understanding the distinction between cleavage and faction is crucial for analyzing internal party dynamics versus broader societal conflicts.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cleavage | Faction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deep social divisions based on identity or interests (e.g., class, religion, ethnicity) | Subgroup within a political party or organization with specific agendas or loyalties |
| Scope | Broad societal level impacting political alignments | Internal group-level within parties or movements |
| Function | Shapes voter behavior and political conflict | Influences party policy and leadership decisions |
| Stability | Relatively stable, rooted in long-term social structures | Variable, changes with political dynamics and leadership |
| Examples | Class cleavage (working vs. middle class), religious cleavage | Left-wing faction vs. centrist faction within a political party |
Understanding Cleavages in Political Systems
Cleavages in political systems represent deep, enduring divisions based on social, economic, or cultural differences that shape voter alignment and party formation. Unlike factions, which are temporary and issue-specific groups within larger political entities, cleavages form the structural basis for political conflict and identity. Recognizing these cleavages is essential for analyzing electoral behavior and the mobilization of political support within diverse societies.
Defining Factions in Political Parties
Factions in political parties represent organized groups that share specific ideological beliefs or policy goals, distinguishing them from broader, more diffuse social cleavages based on ethnicity, class, or religion. These factions actively influence party decisions, leadership contests, and policy platforms by mobilizing supporters within the party structure. Understanding faction dynamics is critical to analyzing party cohesion, intra-party conflicts, and the strategic behavior of political actors.
Historical Roots of Political Cleavages
Political cleavages historically stem from deep-rooted social divisions such as class, religion, ethnicity, and language, shaping party systems and voter alignments. These cleavages provide the structural basis for long-term political behavior, whereas factions typically represent temporary alliances within parties driven by specific issues or leadership contests. Understanding the historical roots of these cleavages reveals patterns of political stability and change across different societies.
The Formation and Role of Factions
Factions form within political parties as organized groups united by shared interests or ideologies, distinct from broader societal cleavages that encompass divisions like class, religion, or ethnicity. While cleavages structure the overall political landscape by delineating persistent social divisions, factions emerge as strategic entities aiming to influence party decisions and policy directions. Factions play a crucial role in shaping legislative agendas, candidate selections, and internal party dynamics by mobilizing support around specific agendas within the larger framework set by cleavages.
Cleavages vs. Factions: Key Differences
Cleavages in politics refer to deep, enduring divisions within society based on social, economic, or cultural factors that shape political alignment, such as class, religion, or ethnicity. Factions are smaller, organized groups within a political party or movement that pursue specific interests or policies, often competing for influence and power. Unlike cleavages, which represent broad societal divisions, factions are more fluid and tactical, focusing on internal party dynamics rather than large-scale societal structures.
How Cleavages Shape Electoral Behavior
Social cleavages such as class, religion, and ethnicity profoundly shape electoral behavior by structuring voter alignments and party competition. These enduring societal divisions create stable voting patterns as individuals tend to support political parties representing their specific group interests. Factions within parties may influence short-term strategic decisions, but underlying cleavages determine long-term electoral dynamics and political allegiance.
Factions and Internal Party Dynamics
Factions within political parties represent organized groups with distinct ideological positions, influencing party cohesion and policy direction. These internal divisions often drive competition for leadership and resources, impacting candidate selection and legislative agendas. Understanding factional dynamics is crucial for analyzing party strategies and electoral outcomes.
The Impact of Cleavages on Policy Making
Cleavages in society, such as ethnic, religious, or class divisions, shape the formation of political factions and influence policy priorities by highlighting competing interests and demands. These deep-rooted social divisions often lead to fragmented policymaking, where coalition-building becomes essential for passing legislation. Understanding the nature and intensity of cleavages enables policymakers to address diverse group needs, foster compromise, and enhance political stability.
Case Studies: Cleavages and Factions in Modern Politics
Cleavages represent deep, structured societal divisions such as class, religion, or ethnicity that shape political alignments over time, while factions are more fluid groups within parties or movements that compete for power and influence. Case studies in modern politics highlight how cleavages in countries like India and Nigeria underpin long-term political stability and conflict, whereas factionalism in parties such as the U.S. Democrats or the UK Labour Party often drives short-term policy disputes and leadership struggles. Understanding the interplay between enduring cleavages and dynamic factions is crucial for analyzing electoral behavior and party system development worldwide.
The Future of Cleavages and Factions in Democracies
Cleavages and factions remain fundamental in shaping democratic dynamics by structuring political competition and voter alignments, often reflecting deep societal divisions such as class, ethnicity, or ideology. The future of democracies depends on managing these cleavages through inclusive institutions that prevent factional polarization from undermining governance and social cohesion. Emerging trends suggest increasing complexity in cleavages, driven by globalization, identity politics, and digital communication, challenging democracies to balance representation with unity.
cleavage vs faction Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com