Progressivism advocates for social reform and embraces change to address contemporary issues, emphasizing equality, innovation, and expanded rights. Traditionalism prioritizes maintaining established customs and values, stressing stability, heritage, and gradual evolution within political and social institutions. The clash between these ideologies shapes policy debates on governance, civil liberties, and social justice.
Table of Comparison
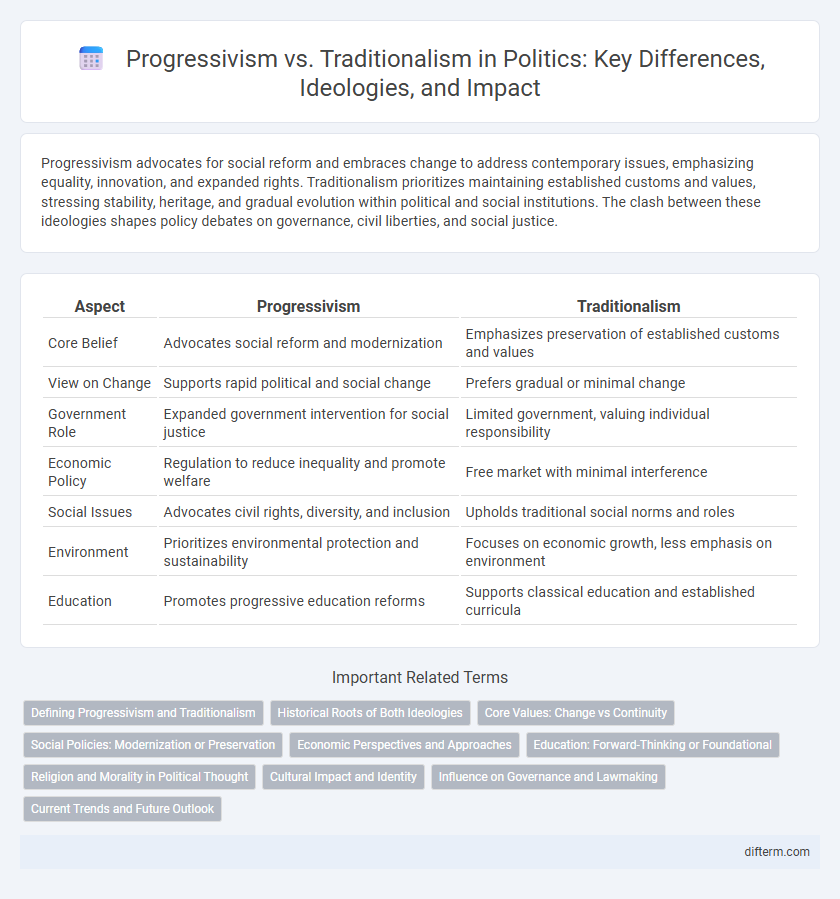
| Aspect | Progressivism | Traditionalism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Belief | Advocates social reform and modernization | Emphasizes preservation of established customs and values |
| View on Change | Supports rapid political and social change | Prefers gradual or minimal change |
| Government Role | Expanded government intervention for social justice | Limited government, valuing individual responsibility |
| Economic Policy | Regulation to reduce inequality and promote welfare | Free market with minimal interference |
| Social Issues | Advocates civil rights, diversity, and inclusion | Upholds traditional social norms and roles |
| Environment | Prioritizes environmental protection and sustainability | Focuses on economic growth, less emphasis on environment |
| Education | Promotes progressive education reforms | Supports classical education and established curricula |
Defining Progressivism and Traditionalism
Progressivism advocates for social reform, emphasizing equality, innovation, and government intervention to address economic and social issues, while traditionalism champions preserving established customs, cultural continuity, and limited change rooted in historical values. Core progressive principles include support for civil rights, environmental protection, and expanded social welfare programs, contrasting with traditionalist priorities like maintaining family structures, religious values, and national heritage. The ideological divide shapes policy debates on education, healthcare, and governance, reflecting differing visions of societal progress and stability.
Historical Roots of Both Ideologies
Progressivism traces its origins to the late 19th and early 20th centuries, emerging as a response to industrialization, urbanization, and social inequalities, emphasizing reform and government intervention. Traditionalism, rooted in conservative thought dating back to the Enlightenment and earlier, values established customs, institutions, and social hierarchies as essential for societal stability. The historical tension between these ideologies centers on how societies should adapt to change versus preserving continuity and inherited cultural norms.
Core Values: Change vs Continuity
Progressivism emphasizes dynamic social reform and innovation, advocating for systemic change to address inequality and promote inclusivity. Traditionalism prioritizes preserving established customs, institutions, and cultural heritage as essential to social stability and identity. The tension between these core values reflects ongoing debates over societal evolution versus maintaining continuity in political and cultural norms.
Social Policies: Modernization or Preservation
Progressivism advocates for the modernization of social policies, emphasizing inclusivity, civil rights expansion, and adaptive reforms to reflect changing societal values. Traditionalism prioritizes the preservation of established social norms, often supporting family structures, cultural heritage, and religious influences as foundational to social stability. These opposing approaches shape legislative agendas and public discourse, influencing education, healthcare, and welfare systems.
Economic Perspectives and Approaches
Progressivism advocates for economic reforms such as wealth redistribution, increased social welfare programs, and government regulation to address inequality and promote social justice. Traditionalism supports free-market principles, limited government intervention, and prioritizes economic stability through conservative fiscal policies. The economic debate centers on balancing regulation with market freedom to achieve growth and equity.
Education: Forward-Thinking or Foundational
Progressivism in education emphasizes student-centered learning, critical thinking, and adaptability to prepare individuals for a rapidly evolving world, often integrating technology and interdisciplinary approaches. Traditionalism focuses on foundational knowledge, structured curricula, and discipline, aiming to preserve cultural heritage and intellectual rigor through classical education models. The debate centers on balancing innovative teaching methods with maintaining essential academic fundamentals to cultivate both creativity and competence in students.
Religion and Morality in Political Thought
Progressivism in political thought advocates for adapting religious and moral values to contemporary societal changes, emphasizing inclusivity and social justice. Traditionalism upholds established religious doctrines and moral frameworks as foundational to political stability and cultural identity. This ideological divide shapes debates on policy issues such as education, civil rights, and governance ethics.
Cultural Impact and Identity
Progressivism advances cultural inclusion by embracing diversity, promoting social equity, and challenging traditional norms to reshape collective identity. Traditionalism upholds historical values and established social structures, emphasizing continuity and cultural heritage as a foundation for societal cohesion. The ongoing tension between these ideologies shapes national identity, influencing policies on education, language, and cultural preservation.
Influence on Governance and Lawmaking
Progressivism drives governance toward embracing reforms that promote social equity, environmental sustainability, and expanded civil rights, often resulting in laws that address systemic inequalities and modern challenges. Traditionalism emphasizes preserving established institutions and cultural norms, advocating for incremental changes that maintain social stability and respect historical legal frameworks. The tension between these ideologies shapes legislative priorities, influencing policy development on issues like healthcare, education, and economic regulation.
Current Trends and Future Outlook
Current trends in politics reveal a growing polarization between progressivism, which emphasizes social equity, environmental sustainability, and technological innovation, and traditionalism, which prioritizes cultural heritage, national sovereignty, and economic stability. Progressive policies are gaining traction in urban centers and among younger demographics, influencing legislation on climate change, social justice, and digital rights. The future outlook suggests this ideological divide will shape electoral strategies and governance approaches, with hybrid models emerging to address complex societal challenges.
progressivism vs traditionalism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com