Centrism in politics advocates for balanced policies that incorporate moderate views from both the left and right, aiming to promote stability and gradual progress. Radicalism pushes for profound and rapid systemic change, often challenging established institutions and norms to address perceived injustices. The tension between centrism and radicalism shapes political discourse by influencing strategies for reform and governance.
Table of Comparison
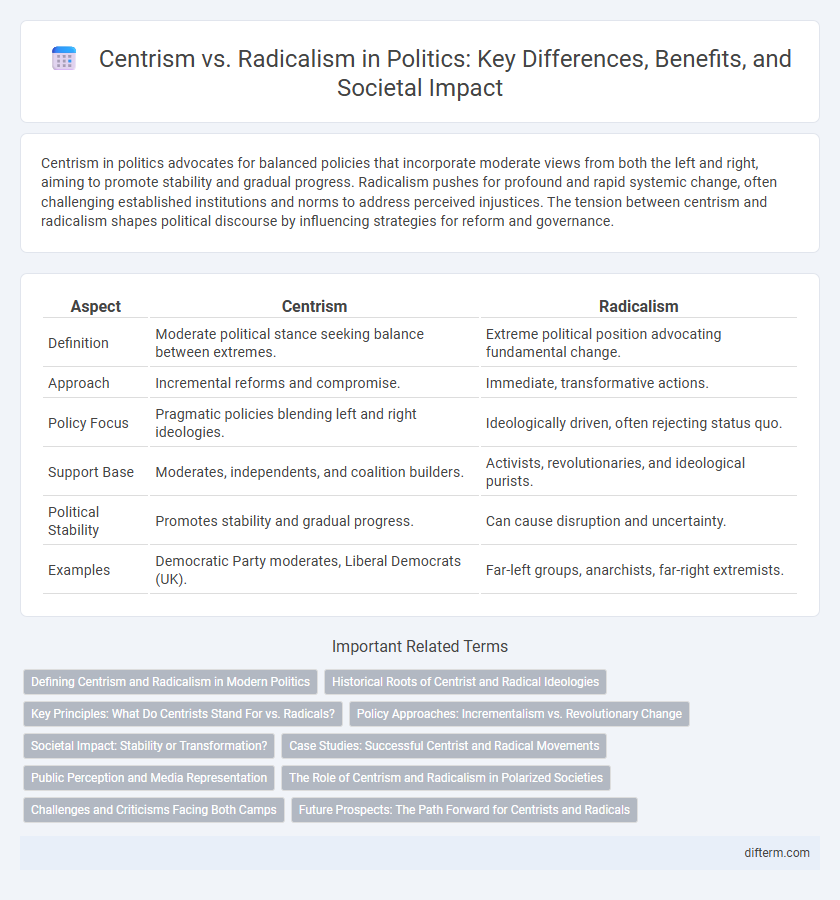
| Aspect | Centrism | Radicalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Moderate political stance seeking balance between extremes. | Extreme political position advocating fundamental change. |
| Approach | Incremental reforms and compromise. | Immediate, transformative actions. |
| Policy Focus | Pragmatic policies blending left and right ideologies. | Ideologically driven, often rejecting status quo. |
| Support Base | Moderates, independents, and coalition builders. | Activists, revolutionaries, and ideological purists. |
| Political Stability | Promotes stability and gradual progress. | Can cause disruption and uncertainty. |
| Examples | Democratic Party moderates, Liberal Democrats (UK). | Far-left groups, anarchists, far-right extremists. |
Defining Centrism and Radicalism in Modern Politics
Centrism in modern politics advocates for moderate policies that balance progressive and conservative values, seeking pragmatic solutions to complex issues. Radicalism pushes for fundamental changes to the political system, often challenging established institutions and advocating for transformative reforms. The tension between centrism's emphasis on incremental progress and radicalism's demand for swift systemic overhaul shapes contemporary political debates worldwide.
Historical Roots of Centrist and Radical Ideologies
Centrist ideologies emerged in the aftermath of the French Revolution as a moderate response seeking to balance order and progress, drawing from Enlightenment principles and promoting gradual reform within existing political structures. Radical ideologies originated concurrently, emphasizing profound societal transformation through immediate and sweeping changes, often challenging established institutions and advocating for broader democratic or socialist principles. The historical tension between centrism and radicalism reflects divergent approaches to political change, with centrists prioritizing stability and incrementalism, while radicals focus on systemic overhaul rooted in early 19th-century revolutionary movements.
Key Principles: What Do Centrists Stand For vs. Radicals?
Centrists prioritize pragmatic governance, seeking a balanced approach that incorporates moderate policies from both left and right to promote social stability and economic growth. Radicals advocate for sweeping systemic changes, often challenging existing political structures to address deep inequalities and power imbalances. The core principle for centrists is compromise and incremental reform, whereas radicals emphasize revolutionary action and transformational justice.
Policy Approaches: Incrementalism vs. Revolutionary Change
Centrism advocates for incrementalism, favoring gradual policy adjustments that build consensus and ensure stability within democratic institutions. Radicalism supports revolutionary change, seeking rapid, fundamental restructuring of political, economic, or social systems to address systemic inequalities and injustices. Policy approaches rooted in centrism often emphasize pragmatism and compromise, while radicalism prioritizes transformative reforms that challenge the status quo.
Societal Impact: Stability or Transformation?
Centrism promotes societal stability by advocating incremental reforms and consensus-building, which helps maintain social cohesion and prevent polarization. Radicalism seeks profound transformation through rapid, fundamental changes, often challenging established institutions to address systemic inequalities. The balance between these approaches shapes political dynamics, affecting how societies manage conflict, progress, and adaptation to evolving challenges.
Case Studies: Successful Centrist and Radical Movements
Centrist movements like Germany's CDU have demonstrated success by advocating pragmatic policies that appeal to a broad electorate, promoting stability and incremental reform. In contrast, radical movements such as France's Yellow Vests harness grassroots mobilization and direct action to challenge established political structures and demand systemic change. These case studies reveal how centrism leverages consensus-building while radicalism thrives on urgency and disruption to achieve political goals.
Public Perception and Media Representation
Public perception often paints centrism as pragmatic and stable, attracting moderate voters seeking compromise within polarized political landscapes. Media representation tends to oscillate, framing radicalism as either a vital force for necessary change or a disruptive threat to social order. This dichotomy influences voter engagement and policy debates, shaping the perceived legitimacy of political movements.
The Role of Centrism and Radicalism in Polarized Societies
Centrism promotes compromise and pragmatic solutions, serving as a stabilizing force in highly polarized societies by bridging divides between opposing ideologies. Radicalism fuels political momentum by advocating for fundamental changes and challenging entrenched systems, often intensifying polarization in the process. Both centrism and radicalism play pivotal roles in shaping political discourse and policy outcomes during periods of societal polarization.
Challenges and Criticisms Facing Both Camps
Centrism faces criticism for perceived indecisiveness and an inability to address urgent issues decisively, often being labeled as overly cautious or compromising essential values. Radicalism encounters challenges related to its polarizing nature, risking social division and resistance from established institutions unwilling to accept rapid or extreme reforms. Both camps struggle with balancing effective policy implementation while maintaining public support amid increasing political polarization worldwide.
Future Prospects: The Path Forward for Centrists and Radicals
The future prospects for centrists involve advocating balanced policies that appeal to a broader electorate seeking stability and pragmatic solutions amid growing political polarization. Radicals push for transformative changes addressing systemic issues with urgency, often mobilizing grassroots support for comprehensive reforms. Collaborative approaches between centrists and radicals could foster innovative governance models, combining measured progress with bold initiatives to address complex societal challenges.
centrism vs radicalism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com