Hyperpartisanship deepens political divides by prioritizing party loyalty over collaborative problem-solving, often leading to legislative gridlock and decreased public trust in government. Bipartisanship fosters cooperation across party lines, enabling more balanced policy decisions and greater political stability. Emphasizing common goals rather than partisan conflicts can improve governance and strengthen democratic institutions.
Table of Comparison
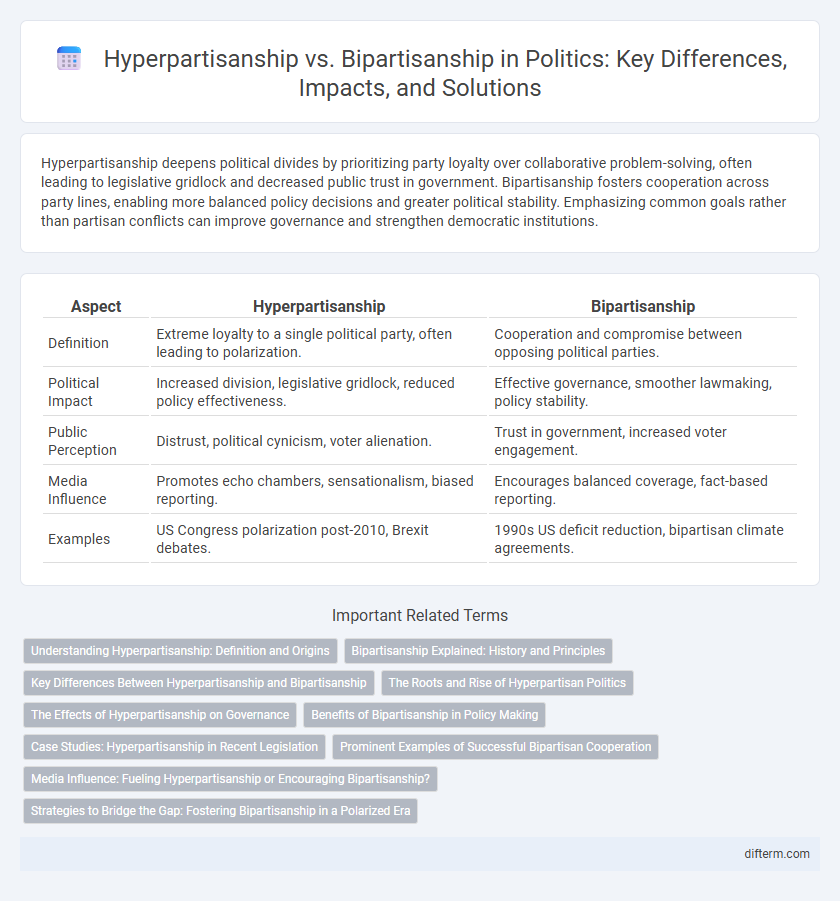
| Aspect | Hyperpartisanship | Bipartisanship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Extreme loyalty to a single political party, often leading to polarization. | Cooperation and compromise between opposing political parties. |
| Political Impact | Increased division, legislative gridlock, reduced policy effectiveness. | Effective governance, smoother lawmaking, policy stability. |
| Public Perception | Distrust, political cynicism, voter alienation. | Trust in government, increased voter engagement. |
| Media Influence | Promotes echo chambers, sensationalism, biased reporting. | Encourages balanced coverage, fact-based reporting. |
| Examples | US Congress polarization post-2010, Brexit debates. | 1990s US deficit reduction, bipartisan climate agreements. |
Understanding Hyperpartisanship: Definition and Origins
Hyperpartisanship refers to an intense and uncompromising allegiance to a political party, often resulting in gridlock and reduced legislative productivity. This phenomenon originates from increasing ideological polarization, media echo chambers, and gerrymandering, which reinforce party loyalty and diminish cross-party dialogue. Understanding hyperpartisanship is critical to addressing political division and fostering effective governance through bipartisan cooperation.
Bipartisanship Explained: History and Principles
Bipartisanship, rooted in the United States' political history, emphasizes cooperation and compromise between major political parties to achieve common legislative goals. This principle has guided landmark legislation such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964, demonstrating how cross-party collaboration can result in significant social progress. Bipartisanship fosters stability and promotes democratic governance by encouraging dialogue and mutual respect among diverse political ideologies.
Key Differences Between Hyperpartisanship and Bipartisanship
Hyperpartisanship is characterized by intense loyalty to a single party, often leading to political gridlock and reduced cooperation across the aisle. Bipartisanship involves collaboration between parties to achieve policy goals, promoting compromise and legislative progress. Key differences include the degree of ideological rigidity, willingness to negotiate, and impact on government functionality.
The Roots and Rise of Hyperpartisan Politics
Hyperpartisan politics stem from deep ideological divides and media echo chambers that amplify partisan messages, creating polarized voter bases. The rise of social media platforms has accelerated this trend by enabling targeted misinformation and reinforcing partisanship through algorithm-driven content exposure. Increasing distrust in traditional institutions and growing demographic shifts further entrench hyperpartisanship, undermining efforts at bipartisan cooperation.
The Effects of Hyperpartisanship on Governance
Hyperpartisanship corrodes governance by fostering legislative gridlock and undermining collaborative policymaking, resulting in stalled budgets and delayed reforms. It intensifies political polarization, reducing bipartisan cooperation essential for addressing complex social and economic challenges. The persistent lack of consensus diminishes public trust in democratic institutions and weakens the government's ability to respond effectively to national crises.
Benefits of Bipartisanship in Policy Making
Bipartisanship in policy making fosters sustainable legislation by integrating diverse perspectives, which enhances the quality and durability of laws. It promotes political stability and public trust by encouraging cooperation between parties, reducing polarization and gridlock. Collaborative governance improves policy outcomes through comprehensive debate and consensus-building, ultimately addressing complex societal challenges more effectively.
Case Studies: Hyperpartisanship in Recent Legislation
Recent legislation such as the 2020 COVID-19 relief packages and the 2021 infrastructure bill highlight hyperpartisanship, with intense party-line voting reflecting deep ideological divides. For instance, the CARES Act passed with near-unanimous Democratic support but limited Republican backing, illustrating partisan polarizations impacting legislative efficiency. Contrastingly, moments of bipartisanship occurred when leaders negotiated compromise terms, but these instances remain exceptions amid growing political fragmentation.
Prominent Examples of Successful Bipartisan Cooperation
The 1996 Welfare Reform Act and the 2015 Every Student Succeeds Act illustrate successful bipartisan cooperation, showcasing how cross-party collaboration can yield impactful policy changes. Leaders like Senator Susan Collins and Senator Joe Manchin have played crucial roles in fostering bipartisan dialogue, bridging ideological divides to achieve legislative progress. Such examples demonstrate that despite hyperpartisanship trends, strategic negotiation and shared goals can still drive effective governance.
Media Influence: Fueling Hyperpartisanship or Encouraging Bipartisanship?
Media influence plays a critical role in shaping political discourse by often magnifying hyperpartisanship through echo chambers and sensationalized coverage, which intensifies divisions among audiences. Conversely, platforms that prioritize balanced reporting and feature diverse viewpoints can foster bipartisanship by promoting understanding and dialogue between opposing political groups. The increasing prevalence of algorithm-driven content delivery further complicates media's impact, as personalized feeds frequently reinforce existing biases rather than encouraging cross-partisan engagement.
Strategies to Bridge the Gap: Fostering Bipartisanship in a Polarized Era
Promoting bipartisan cooperation requires structured dialogue platforms where lawmakers from opposing parties engage in regular, solution-oriented discussions to identify mutual goals. Implementing consensus-building techniques such as joint policy workshops and bipartisan committees can dissolve partisan barriers and create shared accountability. Leveraging data-driven approaches to highlight the socioeconomic benefits of bipartisan legislation encourages pragmatic collaboration beyond ideological divides.
hyperpartisanship vs bipartisanship Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com