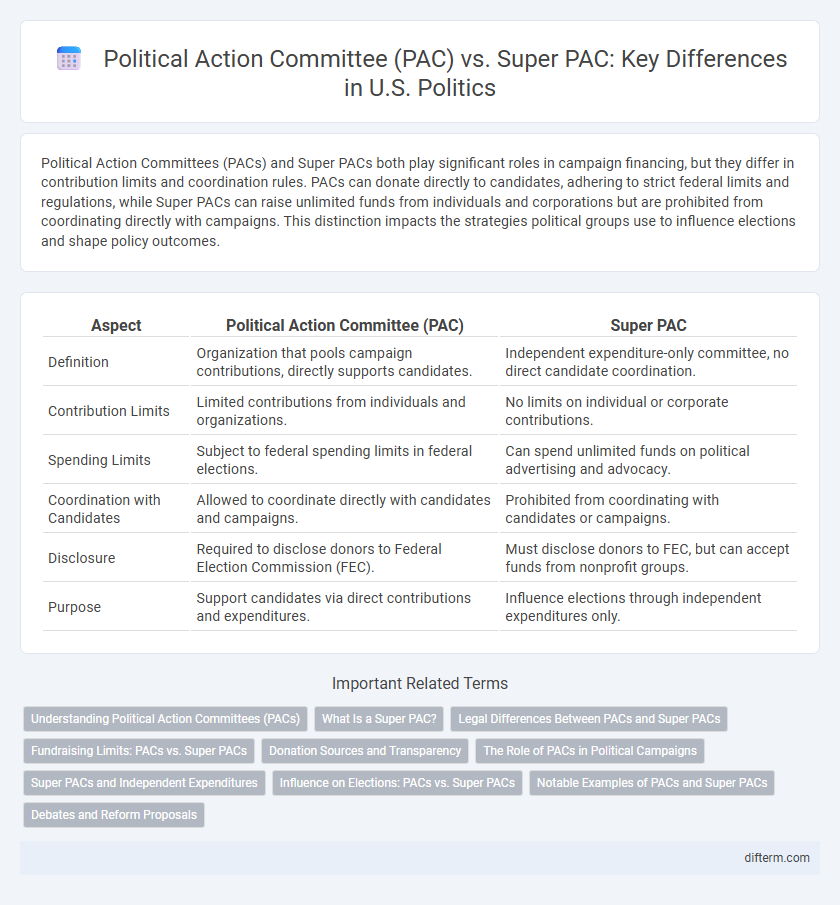
Political Action Committees (PACs) and Super PACs both play significant roles in campaign financing, but they differ in contribution limits and coordination rules. PACs can donate directly to candidates, adhering to strict federal limits and regulations, while Super PACs can raise unlimited funds from individuals and corporations but are prohibited from coordinating directly with campaigns. This distinction impacts the strategies political groups use to influence elections and shape policy outcomes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Political Action Committee (PAC) | Super PAC |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organization that pools campaign contributions, directly supports candidates. | Independent expenditure-only committee, no direct candidate coordination. |
| Contribution Limits | Limited contributions from individuals and organizations. | No limits on individual or corporate contributions. |
| Spending Limits | Subject to federal spending limits in federal elections. | Can spend unlimited funds on political advertising and advocacy. |
| Coordination with Candidates | Allowed to coordinate directly with candidates and campaigns. | Prohibited from coordinating with candidates or campaigns. |
| Disclosure | Required to disclose donors to Federal Election Commission (FEC). | Must disclose donors to FEC, but can accept funds from nonprofit groups. |
| Purpose | Support candidates via direct contributions and expenditures. | Influence elections through independent expenditures only. |
Understanding Political Action Committees (PACs)
Political Action Committees (PACs) are organizations that collect and contribute limited funds directly to political candidates or parties to support their campaigns, adhering to strict federal contribution limits. Unlike Super PACs, which can raise and spend unlimited sums independently without direct coordination with candidates, PACs are subject to legal donation caps and disclosure requirements. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify the regulatory landscape of campaign finance and the influence PACs have on political advocacy and election outcomes.
What Is a Super PAC?
A Super PAC, or independent expenditure-only committee, is a political action committee that can raise and spend unlimited amounts of money to advocate for or against political candidates, without direct coordination with their campaigns. Unlike traditional PACs, Super PACs are required to disclose their donors, but they play a significant role in influencing elections by funding advertisements and other political activities. The emergence of Super PACs has transformed campaign financing, making their impact a focal point in discussions about political transparency and influence.
Legal Differences Between PACs and Super PACs
Political Action Committees (PACs) are subject to contribution limits and can donate directly to candidates, while Super PACs operate independently and can raise unlimited funds but are prohibited from coordinating with campaigns. PACs must disclose donor information regularly, adhering to Federal Election Commission (FEC) regulations, whereas Super PACs also disclose donors but leverage the ability to spend independently on political advertising. The legal distinctions between PACs and Super PACs define their fundraising capacity, operational scope, and compliance requirements under U.S. campaign finance law.
Fundraising Limits: PACs vs. Super PACs
Political Action Committees (PACs) face strict fundraising limits, capping contributions at $5,000 per donor per year, and direct coordination with candidates is permitted under federal law. Super PACs, or independent expenditure-only committees, can raise unlimited funds from individuals, corporations, and unions but are prohibited from coordinating directly with candidates or parties. These differentiated fundraising rules allow PACs to operate within controlled financial bounds while Super PACs influence elections through vast, unrestricted spending on independent political activities.
Donation Sources and Transparency
Political Action Committees (PACs) are limited to donating directly to candidates and must adhere to strict contribution limits and disclosure requirements, ensuring transparency about their donation sources. Super PACs, or independent expenditure-only committees, can raise unlimited sums from individuals, corporations, and unions but are prohibited from coordinating directly with candidates, while still required to disclose donor information publicly. The key difference lies in Super PACs' capacity to receive unlimited funds and engage in independent expenditures without donating directly to campaigns, raising ongoing concerns about the transparency and influence of their funding sources.
The Role of PACs in Political Campaigns
Political Action Committees (PACs) play a crucial role in political campaigns by directly contributing to candidates' campaign funds, subject to legal limits on donations. Super PACs, unlike traditional PACs, can raise and spend unlimited amounts of money independently to advocate for or against political candidates, without direct coordination with campaigns. These entities influence electoral outcomes through substantial funding of advertising, voter mobilization efforts, and issue advocacy, shaping the political landscape significantly.
Super PACs and Independent Expenditures
Super PACs, or independent-expenditure only committees, can raise and spend unlimited funds to influence federal elections but must operate independently from candidates and political parties. Their expenditures focus on independent communications, such as advertisements and outreach, that expressly advocate for the election or defeat of a candidate without direct coordination. This legal distinction allows Super PACs to wield substantial financial influence in political campaigns through unrestricted contributions from corporations, unions, and individuals.
Influence on Elections: PACs vs. Super PACs
Political Action Committees (PACs) contribute directly to candidates with statutory limits, influencing elections through regulated financial support and coordinated campaigns. Super PACs, by contrast, can raise and spend unlimited funds independently, exerting greater impact through unrestricted advertising and voter outreach efforts. The distinction in regulatory constraints leads to Super PACs playing a more dominant role in shaping electoral outcomes and candidate viability.
Notable Examples of PACs and Super PACs
Notable Political Action Committees (PACs) include the American Israel Public Affairs Committee (AIPAC) and the National Rifle Association Political Victory Fund, both influential in funding candidates aligned with their policy goals. In contrast, Super PACs such as Priorities USA Action and Senate Majority PAC have leveraged their ability to raise unlimited contributions to independently support candidates, often shaping high-profile elections with extensive media campaigns. The distinction between PACs and Super PACs lies in their contribution limits and coordination restrictions, with Super PACs playing a more dominant role in recent federal elections due to their expansive fundraising capabilities.
Debates and Reform Proposals
Political Action Committees (PACs) and Super PACs differ significantly in their influence on debates and reform proposals, with PACs directly contributing to candidates and Super PACs independently spending unlimited funds to influence elections. Reform proposals often target Super PACs for their potential to amplify wealthy interests and undermine campaign finance transparency, advocating for stricter disclosure rules and contribution limits. Debates around these entities emphasize the need for balancing free speech with preventing corruption and ensuring equitable political competition.
political action committee vs super PAC Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com