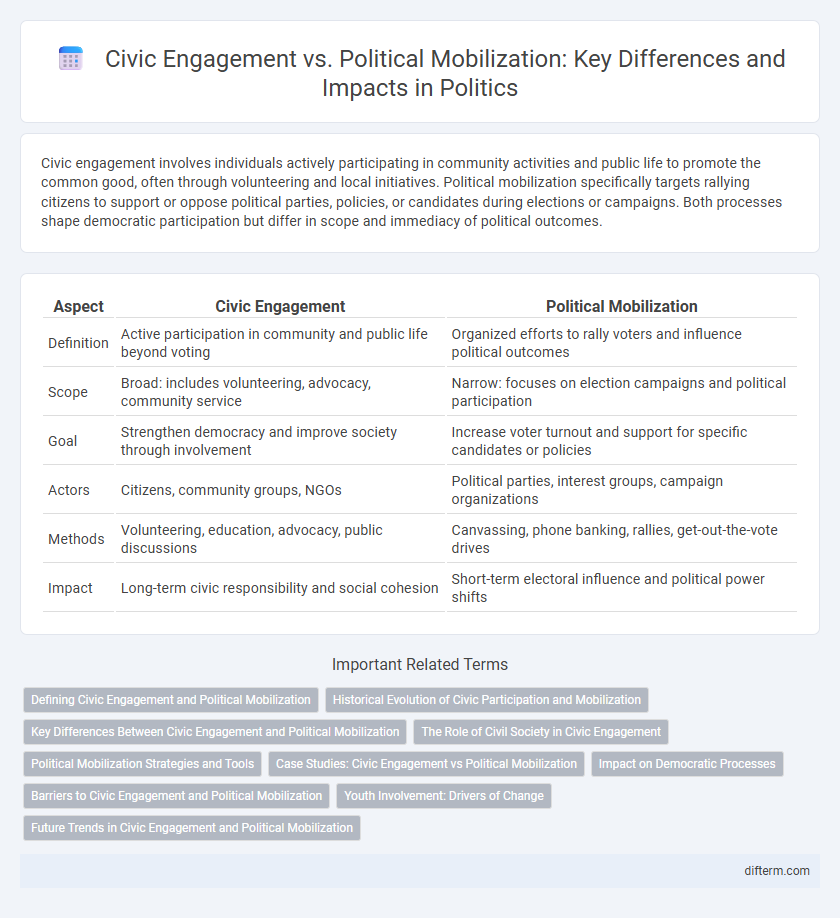
Civic engagement involves individuals actively participating in community activities and public life to promote the common good, often through volunteering and local initiatives. Political mobilization specifically targets rallying citizens to support or oppose political parties, policies, or candidates during elections or campaigns. Both processes shape democratic participation but differ in scope and immediacy of political outcomes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Civic Engagement | Political Mobilization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active participation in community and public life beyond voting | Organized efforts to rally voters and influence political outcomes |
| Scope | Broad: includes volunteering, advocacy, community service | Narrow: focuses on election campaigns and political participation |
| Goal | Strengthen democracy and improve society through involvement | Increase voter turnout and support for specific candidates or policies |
| Actors | Citizens, community groups, NGOs | Political parties, interest groups, campaign organizations |
| Methods | Volunteering, education, advocacy, public discussions | Canvassing, phone banking, rallies, get-out-the-vote drives |
| Impact | Long-term civic responsibility and social cohesion | Short-term electoral influence and political power shifts |
Defining Civic Engagement and Political Mobilization
Civic engagement involves individual and collective actions aimed at identifying and addressing issues of public concern, encompassing activities like voting, volunteering, and community organizing. Political mobilization refers to deliberate efforts by political actors, parties, or organizations to motivate and organize citizens to participate in specific political processes, such as elections or protests. Understanding the distinction highlights how civic engagement is a broader concept of active citizenship, while political mobilization targets strategic participation to achieve particular political outcomes.
Historical Evolution of Civic Participation and Mobilization
The historical evolution of civic participation and political mobilization reveals shifting strategies from localized, community-based efforts to broad, organized campaigns driven by political parties and interest groups. Early civic engagement emphasized grassroots activism and voluntary associations, while modern political mobilization increasingly relies on digital platforms and data analytics to target and mobilize voters. These developments reflect an ongoing transformation in how citizens interact with political processes and influence policy outcomes.
Key Differences Between Civic Engagement and Political Mobilization
Civic engagement encompasses a broad range of activities aimed at improving community well-being, including volunteering, participating in local meetings, and promoting social causes, while political mobilization specifically targets rallying voters and influencing electoral outcomes through campaigns and advocacy. Civic engagement is sustained by individual initiative and long-term involvement, contrasted with political mobilization's focus on short-term, targeted efforts to drive immediate political action. Understanding these distinctions clarifies their unique roles in democratic processes and effective policy influence.
The Role of Civil Society in Civic Engagement
Civil society organizations play a pivotal role in fostering civic engagement by creating platforms for community participation and promoting public discourse. These entities empower citizens to express their interests and hold political actors accountable, thereby bridging the gap between individuals and formal political institutions. By facilitating grassroots involvement and enhancing political literacy, civil society strengthens democratic processes and encourages sustained political mobilization.
Political Mobilization Strategies and Tools
Political mobilization strategies encompass targeted outreach methods such as grassroots campaigning, digital advertising, and data analytics to efficiently activate and motivate voter participation. Utilizing micro-targeting tools and social media algorithms allows campaigns to tailor messages that resonate with specific demographic groups, enhancing engagement and turnout. Effective mobilization also integrates coalition-building and community organizing to sustain long-term political influence beyond election cycles.
Case Studies: Civic Engagement vs Political Mobilization
Case studies reveal distinct outcomes between civic engagement and political mobilization, where civic engagement fosters sustained community involvement through education and dialogue, while political mobilization often targets immediate electoral outcomes using rallies and voter drives. For example, the 2018 Midterm Elections in the United States showcased political mobilization's effectiveness in increasing voter turnout, whereas the participatory budgeting initiatives in Brazil highlight civic engagement's role in empowering citizens to influence local governance. These cases underscore the importance of balancing both approaches for robust democratic participation and policy impact.
Impact on Democratic Processes
Civic engagement fosters sustained public participation through education and community involvement, strengthening democratic institutions by promoting informed decision-making and accountability. Political mobilization often targets short-term voter turnout and issue advocacy, influencing electoral outcomes and policy debates with immediate impact. Both dynamics shape democratic processes by balancing long-term civic responsibility and critical episodic political action, enhancing governance legitimacy.
Barriers to Civic Engagement and Political Mobilization
Barriers to civic engagement often include socioeconomic disparities, lack of access to educational resources, and systemic disenfranchisement, which limit individuals' awareness and participation in democratic processes. Political mobilization faces challenges such as partisan polarization, voter suppression tactics, and mistrust in political institutions, hindering collective action and grassroots activism. Overcoming these obstacles requires targeted strategies to increase inclusivity, enhance political education, and protect voting rights to strengthen democratic participation.
Youth Involvement: Drivers of Change
Youth involvement in politics acts as a critical driver of change, with civic engagement fostering long-term democratic values and political mobilization catalyzing immediate action on pressing issues. High levels of youth civic participation correlate with increased voter turnout and policy advocacy, while mobilization campaigns effectively address social justice and environmental concerns. Empowering young people through education and digital platforms strengthens their role as influential agents in reshaping political landscapes.
Future Trends in Civic Engagement and Political Mobilization
Emerging digital platforms and AI-driven analytics are reshaping future trends in civic engagement and political mobilization by enabling hyper-targeted outreach and real-time participation tracking. Increased reliance on social media algorithms and virtual town halls facilitates sustained public involvement while raising concerns about information echo chambers and data privacy. Integrating blockchain technology promises enhanced transparency and trust in electoral processes, potentially transforming citizen-state interactions.
civic engagement vs political mobilization Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com