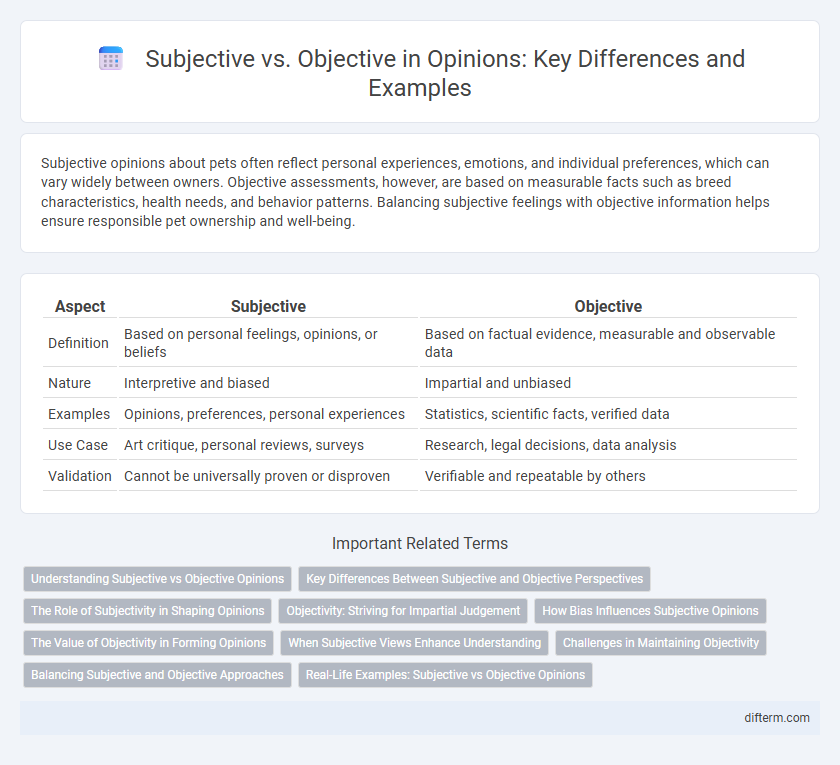
Subjective opinions about pets often reflect personal experiences, emotions, and individual preferences, which can vary widely between owners. Objective assessments, however, are based on measurable facts such as breed characteristics, health needs, and behavior patterns. Balancing subjective feelings with objective information helps ensure responsible pet ownership and well-being.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Subjective | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Based on personal feelings, opinions, or beliefs | Based on factual evidence, measurable and observable data |
| Nature | Interpretive and biased | Impartial and unbiased |
| Examples | Opinions, preferences, personal experiences | Statistics, scientific facts, verified data |
| Use Case | Art critique, personal reviews, surveys | Research, legal decisions, data analysis |
| Validation | Cannot be universally proven or disproven | Verifiable and repeatable by others |
Understanding Subjective vs Objective Opinions
Understanding subjective versus objective opinions hinges on recognizing that subjective opinions stem from personal feelings, beliefs, or preferences, while objective opinions are based on unbiased facts and verifiable evidence. Distinguishing between these types of opinions is essential for critical thinking, enabling individuals to evaluate arguments and make informed decisions. Awareness of this difference fosters clearer communication and reduces misunderstandings in debates and discussions.
Key Differences Between Subjective and Objective Perspectives
Subjective perspectives rely on personal feelings, opinions, and experiences, leading to interpretations influenced by individual biases and emotions. Objective perspectives emphasize facts, measurable data, and unbiased observations, striving for neutrality regardless of personal beliefs. The key difference lies in subjectivity's reliance on internal viewpoints versus objectivity's focus on external, verifiable reality.
The Role of Subjectivity in Shaping Opinions
Subjectivity plays a crucial role in shaping opinions by incorporating personal experiences, emotions, and individual perspectives that influence judgment beyond factual evidence. Unlike objective analysis, subjective viewpoints reflect the unique values and biases of a person, which can lead to diverse interpretations of the same information. This interplay between internal perceptions and external realities underscores the complexity of forming opinions in social and psychological contexts.
Objectivity: Striving for Impartial Judgement
Objectivity demands the exclusion of personal biases, emphasizing evidence-based evaluation and balanced reasoning. Impartial judgment enhances credibility by ensuring decisions are grounded in verifiable facts rather than subjective feelings. Maintaining neutrality fosters trust and clarity in discourse, promoting fair and consistent outcomes.
How Bias Influences Subjective Opinions
Bias significantly shapes subjective opinions by filtering information through individual experiences, emotions, and preconceived notions, leading to personalized interpretations that may deviate from objective facts. Cognitive biases such as confirmation bias and anchoring cause people to favor information that supports their existing beliefs, reinforcing subjective perspectives. This influence challenges the pursuit of neutrality and underscores the importance of critical thinking in evaluating opinions.
The Value of Objectivity in Forming Opinions
Objectivity enhances the credibility and reliability of opinions by grounding them in facts and evidence rather than personal biases or emotions. Subjective views can offer valuable personal insights, but objective perspectives foster clearer understanding and constructive dialogue. Emphasizing objectivity in opinion formation promotes critical thinking and informed decision-making.
When Subjective Views Enhance Understanding
Subjective views enhance understanding by incorporating personal experiences, emotions, and individual perspectives that objective data alone cannot capture. This approach allows for a richer interpretation of complex issues, as it acknowledges the human element behind the facts. In fields like psychology and art, subjective insights illuminate nuanced meanings that quantitative analysis often overlooks.
Challenges in Maintaining Objectivity
Maintaining objectivity presents significant challenges due to inherent cognitive biases and emotional influences that shape individual perspectives. The subjective nature of personal experiences often clouds impartial judgment, making it difficult to separate facts from opinions. Effective strategies to enhance objectivity require rigorous critical thinking and constant self-awareness to minimize these distortions.
Balancing Subjective and Objective Approaches
Balancing subjective and objective approaches involves integrating personal insights with factual evidence to achieve comprehensive understanding. Subjective perspectives enrich analysis with individual experiences and emotions, while objective data provides unbiased, measurable information essential for informed decision-making. Effective judgment emerges from harmonizing these dimensions to address complexity and nuance in various contexts.
Real-Life Examples: Subjective vs Objective Opinions
Subjective opinions reflect personal feelings and individual experiences, such as preferring a particular artist's music over another, which vary widely among people. Objective opinions are based on verifiable facts and evidence, like stating that water boils at 100 degrees Celsius under standard atmospheric conditions. Real-life examples highlight the contrast: a food critic's taste preference is subjective, whereas nutritional information on a food label represents objective data.
subjective vs objective Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com