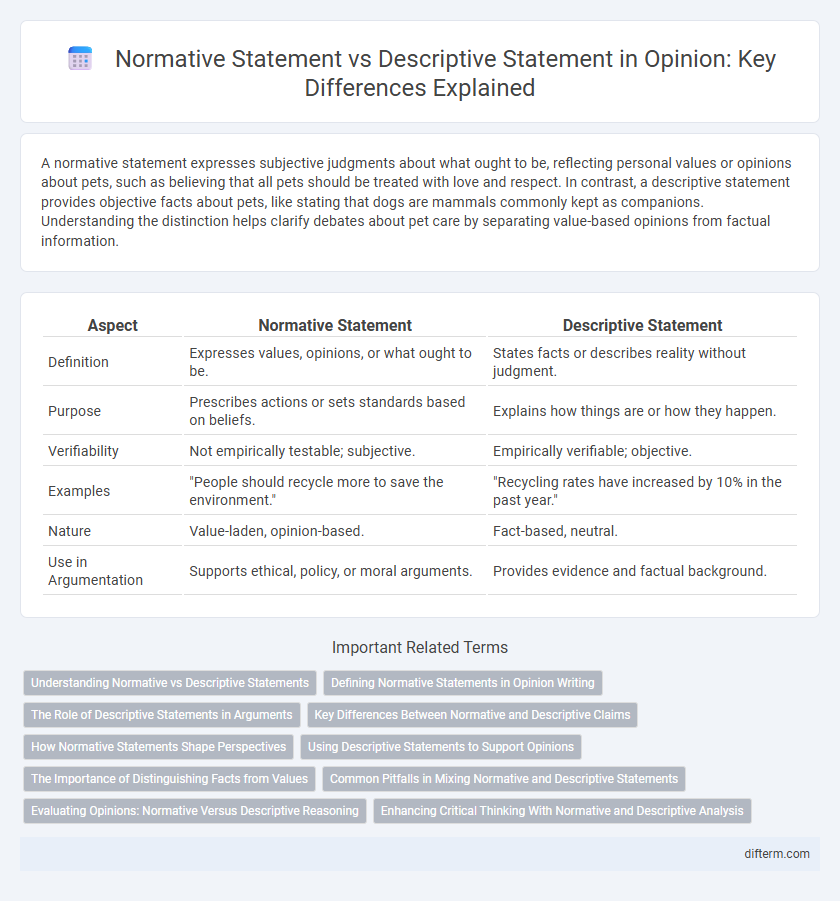
A normative statement expresses subjective judgments about what ought to be, reflecting personal values or opinions about pets, such as believing that all pets should be treated with love and respect. In contrast, a descriptive statement provides objective facts about pets, like stating that dogs are mammals commonly kept as companions. Understanding the distinction helps clarify debates about pet care by separating value-based opinions from factual information.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Normative Statement | Descriptive Statement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expresses values, opinions, or what ought to be. | States facts or describes reality without judgment. |
| Purpose | Prescribes actions or sets standards based on beliefs. | Explains how things are or how they happen. |
| Verifiability | Not empirically testable; subjective. | Empirically verifiable; objective. |
| Examples | "People should recycle more to save the environment." | "Recycling rates have increased by 10% in the past year." |
| Nature | Value-laden, opinion-based. | Fact-based, neutral. |
| Use in Argumentation | Supports ethical, policy, or moral arguments. | Provides evidence and factual background. |
Understanding Normative vs Descriptive Statements
Normative statements express value judgments about what ought to be, reflecting opinions and ethical considerations, while descriptive statements convey objective facts describing how things are without judgment. Understanding the distinction is crucial for clear communication, as normative claims cannot be proven true or false through empirical evidence, unlike descriptive claims. This differentiation helps in debates by separating facts from personal or societal values, preventing conflation of opinion with objective data.
Defining Normative Statements in Opinion Writing
Normative statements in opinion writing express value judgments about what ought to be, reflecting subjective beliefs and ethical considerations. These statements often use modal verbs like "should," "must," or "ought to," indicating prescriptions rather than facts. Unlike descriptive statements that describe empirical reality, normative statements guide opinions and decision-making based on cultural, moral, or personal standards.
The Role of Descriptive Statements in Arguments
Descriptive statements provide objective information about facts and reality, forming the foundation for evaluating normative claims within arguments. They establish empirical evidence that helps distinguish subjective preferences from objective conditions, enhancing clarity and coherence in debates. Accurate descriptive statements enable sound reasoning by grounding normative statements in observable phenomena.
Key Differences Between Normative and Descriptive Claims
Normative statements express value judgments about what ought to be, rooted in ethics and subjective opinions, while descriptive statements objectively describe facts or reality without judgment. Normative claims are prescriptive, guiding behavior or policy based on ideals, whereas descriptive claims are empirical, verifiable through observation or evidence. The key difference lies in normative statements being inherently subjective and evaluative, contrasting with descriptive statements' neutrality and factual basis.
How Normative Statements Shape Perspectives
Normative statements influence perspectives by expressing values and what ought to be, guiding ethical judgments and decision-making processes. These statements shape societal norms by embedding subjective beliefs into policy debates, differentiating them from descriptive statements that merely present objective facts. By framing issues through a moral lens, normative statements drive public discourse and influence cultural and legal standards.
Using Descriptive Statements to Support Opinions
Using descriptive statements to support opinions enhances credibility by grounding subjective views in observable facts and evidence. Descriptive statements provide clear, objective information that helps clarify the basis of normative claims, enabling more persuasive and logically sound arguments. Incorporating empirical data and factual observations into opinion writing facilitates a balanced analysis and strengthens the overall argumentation.
The Importance of Distinguishing Facts from Values
Normative statements prescribe how things ought to be, reflecting values and subjective judgments, while descriptive statements convey objective facts about the world. Distinguishing facts from values is crucial for clear reasoning and effective debate, ensuring that discussions are grounded in evidence rather than personal beliefs. This separation helps policymakers and individuals make informed decisions by recognizing when an argument shifts from empirical observation to value-based opinion.
Common Pitfalls in Mixing Normative and Descriptive Statements
Confusing normative statements, which express judgments about what ought to be, with descriptive statements, which detail what is, leads to flawed reasoning and unclear arguments. Common pitfalls include treating opinions as facts and deriving prescriptive conclusions solely from empirical data without ethical consideration. Clear distinction enhances critical analysis by ensuring evaluative claims are not mistaken for objective descriptions.
Evaluating Opinions: Normative Versus Descriptive Reasoning
Normative statements express value judgments about what ought to be, relying on ethical or moral principles that cannot be empirically tested. Descriptive statements provide objective observations based on factual evidence and can be verified or falsified through empirical data. Evaluating opinions requires distinguishing between these two types of reasoning to understand whether a claim reflects subjective values or objective reality.
Enhancing Critical Thinking With Normative and Descriptive Analysis
Normative statements, which express value judgments about what ought to be, challenge individuals to evaluate beliefs and ethical principles, fostering deeper critical thinking. Descriptive statements provide empirical data and observable facts that establish a foundation for analyzing reality without bias. Combining normative and descriptive analysis sharpens reasoning skills by requiring the assessment of both factual information and subjective values in decision-making processes.
normative statement vs descriptive statement Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com