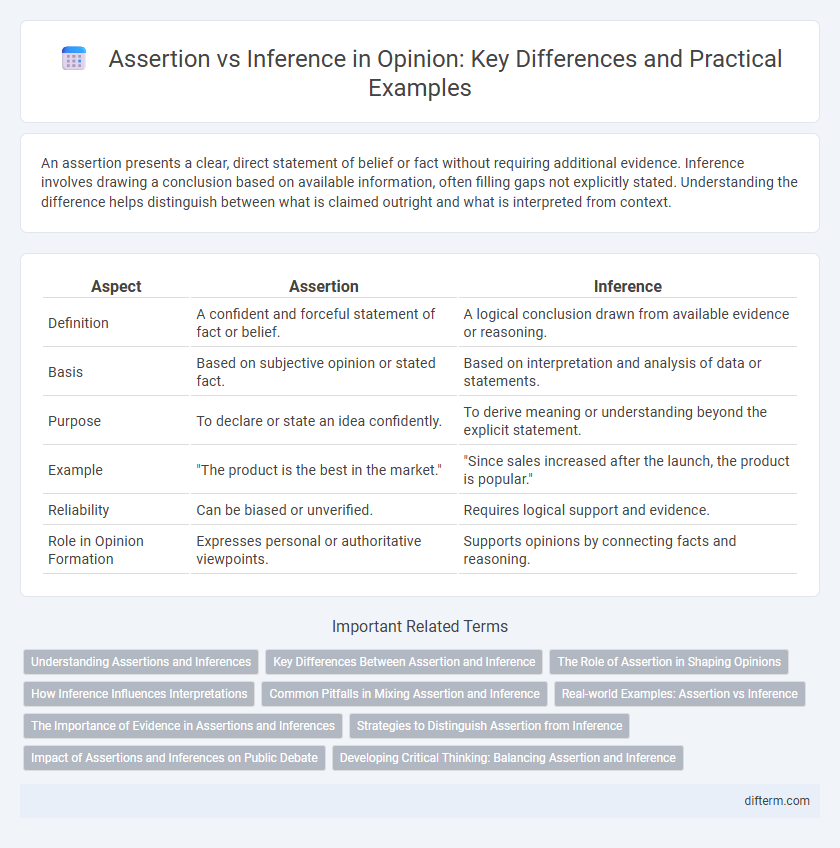
An assertion presents a clear, direct statement of belief or fact without requiring additional evidence. Inference involves drawing a conclusion based on available information, often filling gaps not explicitly stated. Understanding the difference helps distinguish between what is claimed outright and what is interpreted from context.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Assertion | Inference |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A confident and forceful statement of fact or belief. | A logical conclusion drawn from available evidence or reasoning. |
| Basis | Based on subjective opinion or stated fact. | Based on interpretation and analysis of data or statements. |
| Purpose | To declare or state an idea confidently. | To derive meaning or understanding beyond the explicit statement. |
| Example | "The product is the best in the market." | "Since sales increased after the launch, the product is popular." |
| Reliability | Can be biased or unverified. | Requires logical support and evidence. |
| Role in Opinion Formation | Expresses personal or authoritative viewpoints. | Supports opinions by connecting facts and reasoning. |
Understanding Assertions and Inferences
Assertions present definitive statements or claims that express a viewpoint or fact, often requiring evidence for validation. Inferences involve drawing logical conclusions based on available information, interpreting underlying meanings beyond explicit expressions. Distinguishing between assertions and inferences enhances critical thinking and effective communication by clarifying what is directly stated versus what is implied.
Key Differences Between Assertion and Inference
Assertion is a confident and forceful statement presented as a fact, often without requiring proof, while inference is a logical conclusion drawn from available evidence or premises. Assertions state beliefs or claims directly, whereas inferences interpret information to reach a reasoned judgment. Understanding the distinction between these concepts is crucial for critical thinking and effective argument analysis.
The Role of Assertion in Shaping Opinions
Assertion plays a crucial role in shaping opinions by expressing a clear and confident statement that influences how information is perceived and accepted. Unlike inferences, which rely on reasoning and evidence, assertions provide definitive claims that often guide the audience's beliefs and attitudes without requiring immediate validation. This authoritative presentation can strongly impact opinion formation by framing perspectives in a way that appears unquestionable or self-evident.
How Inference Influences Interpretations
Inference significantly influences interpretations by allowing individuals to derive meaning beyond explicit statements, enhancing comprehension in complex texts. It enables readers to connect disparate pieces of information, forming coherent conclusions that shape their understanding and opinions. This cognitive process plays a crucial role in critical thinking, aiding in the evaluation of arguments and the detection of underlying implications.
Common Pitfalls in Mixing Assertion and Inference
Confusing assertions with inferences often leads to flawed reasoning, as assertions are statements presented as facts while inferences draw conclusions based on evidence. A common pitfall is treating an inference as an unquestionable truth without verifying the underlying data or assumptions. This mix-up can undermine critical thinking and weaken arguments by obscuring the distinction between observed facts and interpreted meanings.
Real-world Examples: Assertion vs Inference
Assertions are statements presented as facts without supporting evidence, such as a news anchor claiming, "Crime rates have doubled this year," while inferences involve drawing conclusions based on available data, like deducing from statistical reports that increased unemployment may contribute to rising crime. In courtroom settings, prosecutors assert a defendant's guilt, whereas juries infer verdicts by interpreting evidence and testimonies. Understanding the distinction between assertion and inference is crucial for critical thinking and evaluating the validity of arguments in everyday decision-making.
The Importance of Evidence in Assertions and Inferences
Assertions and inferences rely heavily on evidence to establish credibility and accuracy; assertions state a belief or claim, while inferences draw conclusions based on available data. Robust evidence strengthens assertions by providing factual support and guides inferences through logical reasoning from observed information. Without solid evidence, both assertions and inferences risk being flawed or misleading, emphasizing the critical role of verified data in sound judgment.
Strategies to Distinguish Assertion from Inference
Effective strategies to distinguish assertion from inference involve analyzing the evidence supporting a statement and identifying whether the claim is directly stated or logically derived. Assertions present explicit facts or opinions without requiring additional interpretation, while inferences rely on implied information or reasoning based on observed data. Critical evaluation techniques such as questioning the source's intent, verifying factual accuracy, and scrutinizing the logical connections improve the reliability of differentiating between assertion and inference in complex texts.
Impact of Assertions and Inferences on Public Debate
Assertions shape public debate by presenting definitive claims that can polarize opinions and steer discussions toward binary positions. Inferences, grounded in interpretation and evidence, foster critical thinking and nuanced dialogue, allowing for exploration of multiple perspectives. The interplay between assertions and inferences significantly influences the depth and quality of public discourse, impacting policy decisions and societal understanding.
Developing Critical Thinking: Balancing Assertion and Inference
Developing critical thinking requires balancing assertion and inference by grounding statements in evidence while exploring underlying assumptions. Assertions present clear, confident claims, whereas inferences extend reasoning to draw conclusions from available information. Mastery involves evaluating the validity of both, enhancing analysis and informed decision-making.
assertion vs inference Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com