Last-mile delivery robots offer precise navigation on sidewalks and doorsteps, providing efficient package drop-offs directly to customers' homes. Autonomous vans cover larger delivery volumes and distances, optimizing route planning for suburban and urban areas. Combining both technologies enhances flexibility and speed in last-mile logistics, improving overall customer satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
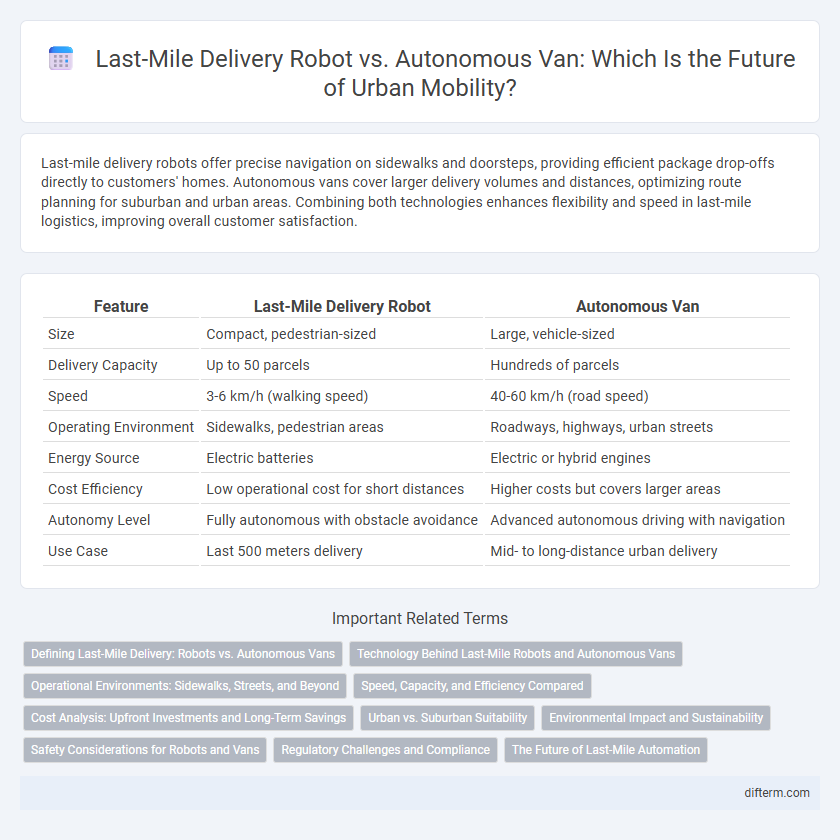
| Feature | Last-Mile Delivery Robot | Autonomous Van |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Compact, pedestrian-sized | Large, vehicle-sized |
| Delivery Capacity | Up to 50 parcels | Hundreds of parcels |
| Speed | 3-6 km/h (walking speed) | 40-60 km/h (road speed) |
| Operating Environment | Sidewalks, pedestrian areas | Roadways, highways, urban streets |
| Energy Source | Electric batteries | Electric or hybrid engines |
| Cost Efficiency | Low operational cost for short distances | Higher costs but covers larger areas |
| Autonomy Level | Fully autonomous with obstacle avoidance | Advanced autonomous driving with navigation |
| Use Case | Last 500 meters delivery | Mid- to long-distance urban delivery |
Defining Last-Mile Delivery: Robots vs. Autonomous Vans
Last-mile delivery robots excel in navigating urban sidewalks for small parcel deliveries, ensuring precise, contactless drop-offs within short distance ranges. Autonomous vans offer greater cargo capacity and speed, efficiently handling bulkier shipments over longer urban and suburban routes. Choosing between robots and autonomous vans depends on delivery density, payload size, and infrastructure compatibility for optimized last-mile logistics.
Technology Behind Last-Mile Robots and Autonomous Vans
Last-mile delivery robots utilize advanced sensors, computer vision, and AI algorithms to navigate urban environments autonomously, enabling precise door-to-door package delivery. Autonomous vans integrate LiDAR, radar, and GPS technologies, combined with machine learning, to safely manage complex traffic scenarios over longer distances. Both platforms leverage edge computing and real-time data processing to optimize route efficiency and reduce delivery times in the mobility ecosystem.
Operational Environments: Sidewalks, Streets, and Beyond
Last-mile delivery robots excel in navigating sidewalks and pedestrian zones with compact designs and obstacle avoidance systems, ensuring efficient package drop-offs in dense urban areas. Autonomous vans operate primarily on streets and highways, leveraging advanced sensors and mapping technologies to handle longer distances and larger cargo loads in mixed traffic environments. Both solutions complement each other by optimizing delivery operations across diverse urban landscapes and regulatory frameworks.
Speed, Capacity, and Efficiency Compared
Last-mile delivery robots excel in navigating congested urban areas with higher speed on short routes, while autonomous vans offer greater capacity for bulk shipments over longer distances. Delivery robots maintain energy efficiency due to smaller size and lower power consumption, contrasting with autonomous vans that require more fuel or battery resources for larger loads. Efficiency varies with delivery context, where robots reduce congestion and emissions in dense zones, whereas autonomous vans optimize route planning for volume and distance.
Cost Analysis: Upfront Investments and Long-Term Savings
Last-mile delivery robots require lower upfront investments due to compact design and minimal infrastructure needs, while autonomous vans involve higher initial costs for vehicle acquisition and advanced sensor integration. Long-term savings from delivery robots emerge through reduced labor expenses and energy efficiency in urban environments, whereas autonomous vans offer scalability and higher payload capacity, potentially lowering per-package transportation costs over time. Cost analysis must consider factors like maintenance frequency, regulatory compliance expenses, and operational flexibility in diverse delivery scenarios.
Urban vs. Suburban Suitability
Last-mile delivery robots excel in dense urban environments due to their compact size and ability to navigate sidewalks and pedestrian areas, enhancing efficiency in congested city streets. Autonomous vans suit suburban settings better, where wider roads and longer distances make vehicle capacity and speed essential for timely deliveries. Both technologies optimize last-mile logistics by adapting to the specific mobility demands of urban and suburban landscapes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Last-mile delivery robots produce significantly lower carbon emissions compared to autonomous vans due to their smaller size and electric powertrains, contributing to reduced urban air pollution and energy consumption. These robots require fewer resources for manufacturing and operation, leading to a smaller ecological footprint and supporting sustainable logistics practices. In contrast, autonomous vans, while efficient for larger loads, generally consume more energy and generate higher emissions over comparable distances, highlighting the importance of integrating micro-mobility solutions for environmentally responsible last-mile delivery.
Safety Considerations for Robots and Vans
Last-mile delivery robots enhance pedestrian safety through low speeds and obstacle detection sensors, reducing collision risks in crowded urban areas. Autonomous vans incorporate advanced LiDAR, radar, and AI-driven fail-safe systems to navigate complex traffic scenarios and ensure passenger and pedestrian protection. Both platforms require rigorous safety validation and real-time monitoring to mitigate operational hazards and comply with regulatory standards.
Regulatory Challenges and Compliance
Last-mile delivery robots face stringent regulatory challenges related to sidewalk usage, pedestrian safety, and local ordinances that vary widely between municipalities. Autonomous vans encounter complex compliance requirements involving road safety standards, federal vehicle regulations, and permissions for mixed traffic operation on public roads. Both technologies must navigate evolving legal frameworks to achieve scalable, lawful deployment in urban delivery networks.
The Future of Last-Mile Automation
Last-mile delivery robots offer precise urban navigation and cost-efficient solutions for small parcel deliveries, enhancing delivery speed and reducing traffic congestion. Autonomous vans provide larger cargo capacity and extended range, supporting bulk deliveries and scalability in suburban and rural areas. Future last-mile automation will integrate these technologies to optimize route efficiency, environmental impact, and customer satisfaction across diverse delivery scenarios.
Last-mile delivery robot vs autonomous van Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com