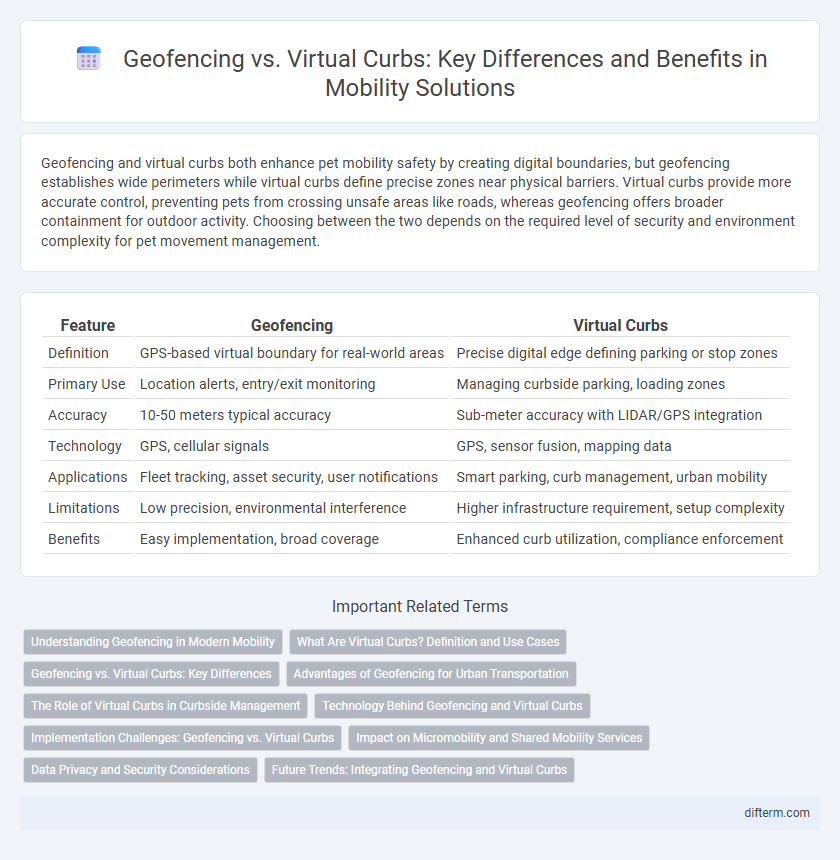
Geofencing and virtual curbs both enhance pet mobility safety by creating digital boundaries, but geofencing establishes wide perimeters while virtual curbs define precise zones near physical barriers. Virtual curbs provide more accurate control, preventing pets from crossing unsafe areas like roads, whereas geofencing offers broader containment for outdoor activity. Choosing between the two depends on the required level of security and environment complexity for pet movement management.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Geofencing | Virtual Curbs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | GPS-based virtual boundary for real-world areas | Precise digital edge defining parking or stop zones |
| Primary Use | Location alerts, entry/exit monitoring | Managing curbside parking, loading zones |
| Accuracy | 10-50 meters typical accuracy | Sub-meter accuracy with LIDAR/GPS integration |
| Technology | GPS, cellular signals | GPS, sensor fusion, mapping data |
| Applications | Fleet tracking, asset security, user notifications | Smart parking, curb management, urban mobility |
| Limitations | Low precision, environmental interference | Higher infrastructure requirement, setup complexity |
| Benefits | Easy implementation, broad coverage | Enhanced curb utilization, compliance enforcement |
Understanding Geofencing in Modern Mobility
Geofencing in modern mobility leverages GPS and RFID technology to create virtual boundaries around predefined geographic areas, enabling precise location-based services such as automated alerts, fleet management, and ride-hailing optimization. Virtual curbs enhance this concept by designating specific zones for pick-up and drop-off, improving traffic flow and pedestrian safety in urban environments. Both technologies are integral to smart transportation systems, enabling efficient vehicle routing, reducing congestion, and enhancing user experience in mobility-as-a-service platforms.
What Are Virtual Curbs? Definition and Use Cases
Virtual curbs are digital boundaries established through GPS and sensor technologies to control vehicle access and parking in specific areas, enhancing urban mobility management. They enable precise regulation of loading zones, ride-hailing pickup points, and restricted parking areas without physical barriers, improving traffic flow and safety. Use cases include managing delivery vehicle stops, ride-share passenger pickups, and reserved parking spaces in congested city environments.
Geofencing vs. Virtual Curbs: Key Differences
Geofencing creates invisible boundaries using GPS or RFID technology to trigger alerts when a device enters or exits a defined area, primarily supporting location-based services in urban mobility. Virtual curbs employ advanced sensors and real-time data integration to dynamically manage curb spaces for parking, loading, and ride-sharing, enhancing curbside accessibility and traffic flow. The key difference lies in geofencing's broader location-based triggers versus virtual curbs' precise, context-sensitive curb space management.
Advantages of Geofencing for Urban Transportation
Geofencing enhances urban transportation by enabling precise area-based controls, improving traffic flow and safety through automated vehicle restrictions in designated zones. It supports dynamic route optimization and real-time monitoring, reducing congestion and emissions in crowded city centers. This technology allows for scalable management of mobility solutions, ensuring compliance with local regulations while adapting to changing urban environments.
The Role of Virtual Curbs in Curbside Management
Virtual curbs play a critical role in curbside management by creating dynamic, programmable zones that regulate parking, loading, and passenger pickups without physical barriers. Unlike traditional geofencing, virtual curbs integrate real-time traffic data and vehicle communication systems to optimize space utilization and reduce congestion. This technology enhances urban mobility by enabling precise control over curb access, facilitating efficient rideshare operations and last-mile deliveries.
Technology Behind Geofencing and Virtual Curbs
Geofencing technology relies on GPS, RFID, Wi-Fi, and cellular data to create virtual boundaries that trigger specific actions when a device enters or exits a predefined area. Virtual curbs enhance this concept by integrating LiDAR, computer vision, and real-time data analytics to enforce parking and loading zones dynamically, improving urban mobility management. Both technologies leverage IoT connectivity and machine learning algorithms to optimize traffic flow and ensure compliance with city regulations.
Implementation Challenges: Geofencing vs. Virtual Curbs
Implementing geofencing faces challenges such as GPS accuracy limitations and high dependency on satellite signals, leading to potential location errors in dense urban areas. Virtual curbs require sophisticated sensor integration and real-time data processing to effectively manage dynamic boundaries and ensure safety around pedestrian zones. Both technologies demand robust infrastructure and continuous calibration to maintain operational reliability in varied mobility environments.
Impact on Micromobility and Shared Mobility Services
Geofencing enhances micromobility and shared mobility services by creating virtual boundaries that trigger automated actions like speed control or parking restrictions, improving safety and compliance without physical infrastructure. Virtual curbs provide dynamic, location-specific regulations that adapt to real-time conditions, optimizing space allocation for scooters and bikes, reducing sidewalk clutter, and enhancing user experience. Together, these technologies enable municipalities and operators to better manage fleet distribution, enforce usage policies, and support sustainable urban mobility solutions.
Data Privacy and Security Considerations
Geofencing relies on GPS data that can expose users to location tracking risks, necessitating robust encryption and strict access controls to protect sensitive information. Virtual curbs utilize proximity sensors and localized data processing, reducing reliance on external networks and enhancing user privacy by limiting data transmission. Both technologies demand comprehensive compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA to ensure secure handling of personal mobility data.
Future Trends: Integrating Geofencing and Virtual Curbs
Future trends in mobility emphasize the integration of geofencing and virtual curbs to enhance urban traffic management and pedestrian safety. By combining geofencing's location-based triggers with virtual curbs' dynamic boundary definitions, cities can enable adaptive traffic zones and more precise curbside management for autonomous vehicles and delivery robots. This integration leverages real-time data and AI to optimize flow, reduce congestion, and improve accessibility in smart city environments.
geofencing vs virtual curbs Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com