Shared mobility involves multiple users accessing a common transportation resource, promoting sustainability and reducing costs, while on-demand mobility provides personalized, flexible transport options tailored to immediate user needs. Shared mobility options, such as carpooling and bike-sharing, optimize vehicle usage and minimize environmental impact by distributing rides among several passengers. On-demand services prioritize convenience and speed, often using technology-driven apps to offer real-time availability and direct routes.
Table of Comparison
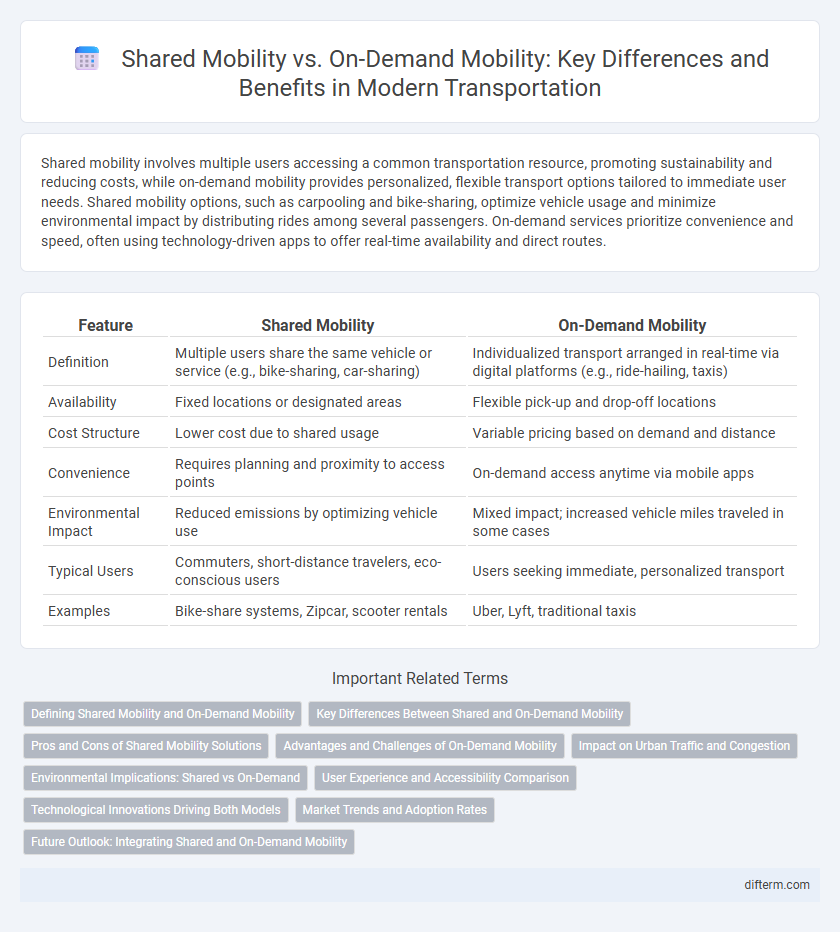
| Feature | Shared Mobility | On-Demand Mobility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple users share the same vehicle or service (e.g., bike-sharing, car-sharing) | Individualized transport arranged in real-time via digital platforms (e.g., ride-hailing, taxis) |
| Availability | Fixed locations or designated areas | Flexible pick-up and drop-off locations |
| Cost Structure | Lower cost due to shared usage | Variable pricing based on demand and distance |
| Convenience | Requires planning and proximity to access points | On-demand access anytime via mobile apps |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced emissions by optimizing vehicle use | Mixed impact; increased vehicle miles traveled in some cases |
| Typical Users | Commuters, short-distance travelers, eco-conscious users | Users seeking immediate, personalized transport |
| Examples | Bike-share systems, Zipcar, scooter rentals | Uber, Lyft, traditional taxis |
Defining Shared Mobility and On-Demand Mobility
Shared mobility refers to transportation services where users share rides, vehicles, or bikes, reducing individual ownership and promoting resource efficiency. On-demand mobility provides personalized transportation options accessible instantly through digital platforms, offering convenience and flexibility. Both models leverage technology but differ in usage patterns and user engagement, shaping urban mobility landscapes.
Key Differences Between Shared and On-Demand Mobility
Shared mobility involves multiple users accessing a common vehicle or transportation system, promoting resource efficiency and reducing individual vehicle ownership. On-demand mobility provides personalized, real-time transportation services tailored to individual user requests, often leveraging app-based platforms for dynamic routing. Key differences lie in usage models, with shared mobility emphasizing collective access and on-demand mobility focusing on immediate, user-specific convenience.
Pros and Cons of Shared Mobility Solutions
Shared mobility solutions offer cost-effective, environmentally friendly transportation by reducing the number of vehicles on the road and promoting resource efficiency through carpooling and bike-sharing programs. However, shared mobility can face challenges such as inconsistent availability, limited coverage areas, and concerns about hygiene and personal space, which may deter some users. Balancing these pros and cons is crucial for cities aiming to integrate shared mobility into their broader transportation ecosystems.
Advantages and Challenges of On-Demand Mobility
On-demand mobility offers significant advantages such as increased convenience, real-time responsiveness, and reduced wait times by leveraging advanced technology and data analytics to match supply with dynamic user demand. It enhances urban accessibility and optimizes fleet utilization, contributing to decreased private car ownership and lower traffic congestion, yet challenges include scalability, regulatory compliance, and the need for robust digital infrastructure to ensure seamless service delivery. Balancing user privacy concerns and integrating with existing transportation networks remain critical hurdles for widespread adoption and sustainability.
Impact on Urban Traffic and Congestion
Shared mobility reduces the number of private vehicles on roads by increasing ride occupancy, effectively lowering urban traffic congestion and parking demand. On-demand mobility offers flexible, real-time transportation options but can sometimes increase vehicle miles traveled due to deadheading and repositioning of vehicles. Studies show that integrating shared mobility with efficient on-demand services can optimize urban traffic flow and minimize congestion hotspots.
Environmental Implications: Shared vs On-Demand
Shared mobility significantly reduces carbon emissions by maximizing vehicle occupancy, decreasing the number of cars on the road, and promoting fewer trips overall. On-demand mobility, while convenient, often leads to increased vehicle miles traveled (VMT) due to deadheading and inefficient trip patterns, thereby contributing to higher greenhouse gas emissions. Optimizing shared mobility systems with electric vehicles and integrated transit can further amplify environmental benefits and mitigate urban air pollution.
User Experience and Accessibility Comparison
Shared mobility services, such as bike-sharing and carpooling, offer cost-effective and eco-friendly transportation options with fixed availability, often requiring prior scheduling or station-based access that may limit spontaneous use. On-demand mobility platforms, including ride-hailing and microtransit, enhance user experience by providing real-time, door-to-door service with flexible scheduling through mobile apps, improving accessibility for users with varying mobility needs. Both models contribute to reducing urban congestion, but on-demand mobility tends to offer superior convenience and accessibility, especially in underserved or low-density areas.
Technological Innovations Driving Both Models
Technological innovations such as advanced telematics, AI-powered routing algorithms, and seamless mobile app integration are pivotal in shaping both shared mobility and on-demand mobility models. Shared mobility benefits from IoT-enabled vehicle tracking and real-time data analytics to optimize fleet utilization, while on-demand mobility leverages dynamic pricing models and autonomous vehicle technology to enhance user convenience and efficiency. The convergence of 5G connectivity and machine learning accelerates the scalability and responsiveness of these mobility solutions, transforming urban transportation landscapes.
Market Trends and Adoption Rates
Shared mobility services, including car-sharing and bike-sharing, have seen steady growth driven by urbanization and environmental concerns, with global adoption rates expected to reach 30% by 2028. On-demand mobility, such as ride-hailing and microtransit, experiences rapid expansion in metropolitan areas, fueled by advances in smartphone technology and consumer preference for convenience, capturing a market share projected at 45% by 2028. Market trends indicate a convergence of these models as integrated platforms offer seamless multimodal options, accelerating overall adoption in smart city initiatives.
Future Outlook: Integrating Shared and On-Demand Mobility
The future outlook for urban transportation emphasizes the integration of shared mobility and on-demand mobility to create seamless, efficient, and sustainable transit solutions. Advanced technologies like AI and IoT enable dynamic routing and real-time vehicle allocation, optimizing resource utilization and reducing traffic congestion. Collaborative platforms will enhance user accessibility by combining ride-sharing, bike-sharing, and autonomous shuttles, fostering a connected mobility ecosystem.
shared mobility vs on-demand mobility Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com