Prosthetic limbs replace missing limbs, providing mobility and functionality for pets with amputations, while orthotic devices support and stabilize existing limbs affected by injury or weakness. Prosthetics restore basic movement and weight-bearing capabilities, offering a more active lifestyle for pets facing limb loss. Orthotic devices improve comfort and prevent further damage by correcting alignment and supporting proper limb function during recovery or chronic conditions.
Table of Comparison
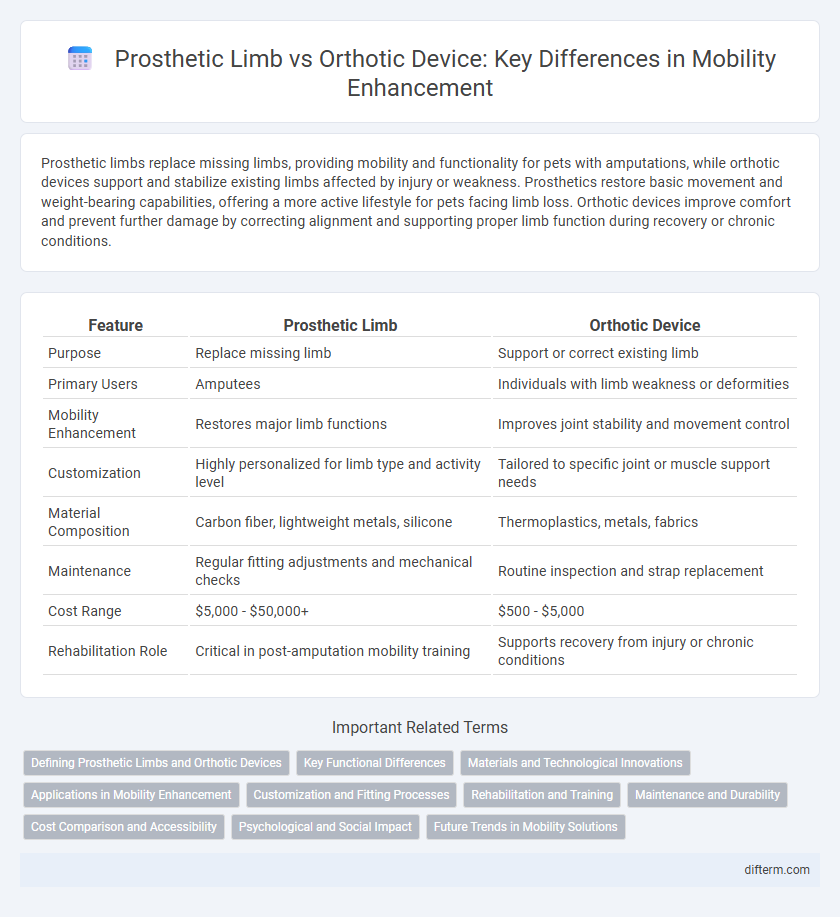
| Feature | Prosthetic Limb | Orthotic Device |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Replace missing limb | Support or correct existing limb |
| Primary Users | Amputees | Individuals with limb weakness or deformities |
| Mobility Enhancement | Restores major limb functions | Improves joint stability and movement control |
| Customization | Highly personalized for limb type and activity level | Tailored to specific joint or muscle support needs |
| Material Composition | Carbon fiber, lightweight metals, silicone | Thermoplastics, metals, fabrics |
| Maintenance | Regular fitting adjustments and mechanical checks | Routine inspection and strap replacement |
| Cost Range | $5,000 - $50,000+ | $500 - $5,000 |
| Rehabilitation Role | Critical in post-amputation mobility training | Supports recovery from injury or chronic conditions |
Defining Prosthetic Limbs and Orthotic Devices
Prosthetic limbs are artificial devices designed to replace missing body parts, restoring mobility and function for individuals with amputations. Orthotic devices are external supports applied to limbs or the spine to correct deformities, improve alignment, and enhance movement without replacing any body part. Both play crucial roles in mobility rehabilitation, with prosthetics focusing on limb replacement and orthotics on support and correction.
Key Functional Differences
Prosthetic limbs replace missing body parts, providing mobility and functionality similar to natural limbs, while orthotic devices support, align, or correct existing limbs to improve movement and reduce pain. Prosthetics enable advanced activities such as walking, running, or grasping by mimicking limb mechanics, whereas orthotics primarily stabilize joints and enhance biomechanical efficiency. The key functional difference lies in prosthetics' role as limb replacements, contrasted with orthotics' function as supportive devices for impaired but present limbs.
Materials and Technological Innovations
Prosthetic limbs commonly utilize advanced carbon fiber composites and titanium alloys to achieve lightweight durability and enhanced performance, while orthotic devices often incorporate thermoplastics and lightweight metals for customizable support and flexibility. Recent technological innovations in prosthetics include microprocessor-controlled joints and sensor integration for adaptive movement, whereas orthotics have seen developments in 3D printing and smart materials that improve patient comfort and dynamic responsiveness. These materials and technologies significantly enhance mobility outcomes by providing tailored solutions that meet specific functional requirements in both prosthetic and orthotic applications.
Applications in Mobility Enhancement
Prosthetic limbs restore mobility by replacing missing body parts, enabling individuals to walk, run, and perform complex movements with improved independence. Orthotic devices support and align existing limbs, enhancing function and reducing pain in conditions such as cerebral palsy, stroke, and musculoskeletal disorders. Both technologies play critical roles in mobility enhancement, with prosthetics focusing on limb replacement and orthotics optimizing natural limb performance.
Customization and Fitting Processes
Prosthetic limbs involve complex customization processes including detailed anatomical measurements, 3D scanning, and digital modeling to ensure precise socket fit and functional alignment tailored to individual limb loss. Orthotic devices require customized molding and biomechanical assessment to optimize support and correction for existing limbs, focusing on pressure distribution and joint stabilization. Advanced materials and iterative fitting sessions enhance comfort and mobility outcomes in both prosthetic and orthotic applications.
Rehabilitation and Training
Prosthetic limbs provide dynamic restoration of lost limbs, enabling patients to regain functional mobility through targeted rehabilitation programs that emphasize strength, coordination, and gait training. Orthotic devices support or correct impaired musculoskeletal function, facilitating improved movement patterns and reducing pain during rehabilitation. Customized training protocols for both prosthetics and orthotics maximize patient outcomes by enhancing muscle adaptation, balance, and proprioception during recovery.
Maintenance and Durability
Prosthetic limbs require regular maintenance such as cleaning, alignment adjustments, and component replacements to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Orthotic devices, typically made from durable materials like carbon fiber and thermoplastics, demand less frequent maintenance but must be inspected for wear and fit to prevent discomfort or injury. Both devices benefit from professional evaluations to sustain durability and functionality in daily mobility activities.
Cost Comparison and Accessibility
Prosthetic limbs typically incur higher costs than orthotic devices due to advanced materials and custom technology, with prices ranging from $5,000 to over $50,000 depending on complexity. Orthotic devices, designed to support or correct musculoskeletal issues, generally cost between $500 and $5,000, making them more accessible for a broader population. Accessibility to prosthetics remains limited in low-income regions due to expensive manufacturing and fitting processes, while orthotics benefit from wider availability and lower costs, enhancing mobility for users with budget constraints.
Psychological and Social Impact
Prosthetic limbs often enhance psychological well-being by restoring a sense of normalcy and boosting self-esteem through improved mobility and appearance. Orthotic devices, while primarily focused on support and correction, can also positively influence mental health by reducing pain and increasing functional independence. Both prosthetics and orthotics play crucial roles in social integration, enabling users to participate more actively in community and work activities, thereby reducing feelings of isolation and enhancing quality of life.
Future Trends in Mobility Solutions
Advancements in prosthetic limb technology increasingly integrate AI-driven sensors and lightweight materials, enhancing user adaptability and comfort while improving biomechanical function. Emerging orthotic devices emphasize smart materials and real-time biomechanical feedback to dynamically support mobility and reduce injury risk. The convergence of these technologies promises personalized, responsive mobility solutions that adapt seamlessly to individual movement patterns and environments.
prosthetic limb vs orthotic device Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com