Mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) integrates various transport modes into a single accessible platform, emphasizing user convenience and seamless travel experiences. Transportation-as-a-service (TaaS) primarily focuses on vehicle access and ride-sharing options, often highlighting autonomous and electric vehicles. MaaS offers a holistic approach by combining public transit, ride-hailing, biking, and walking options, whereas TaaS centers on providing flexible vehicle usage without ownership.
Table of Comparison
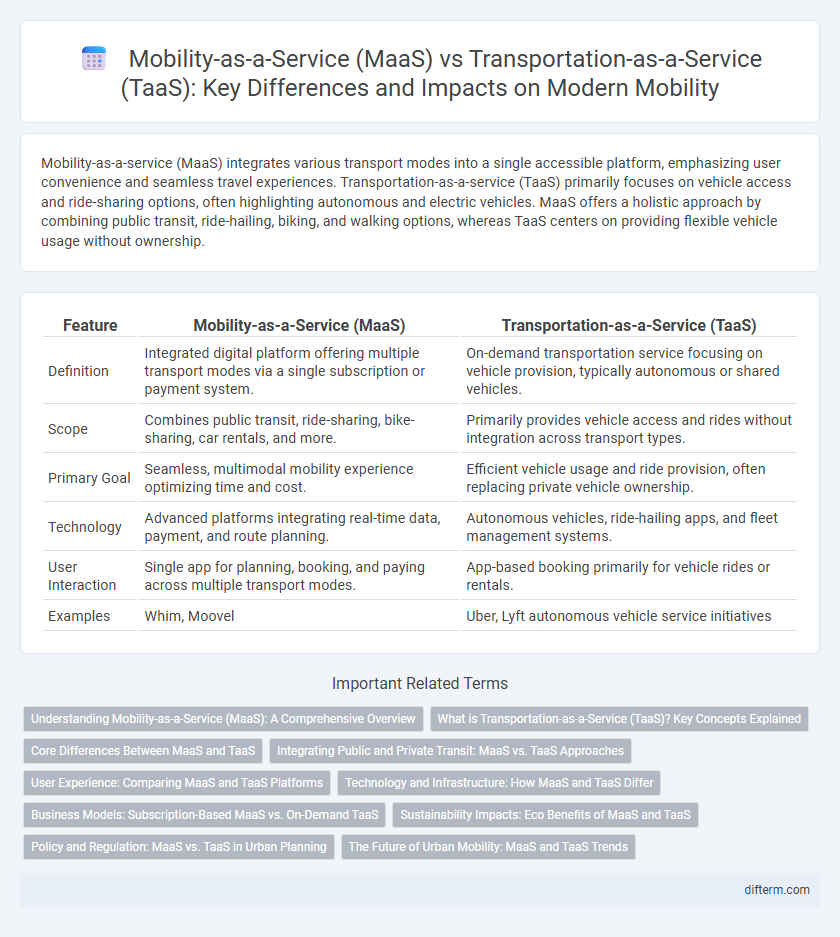
| Feature | Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) | Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated digital platform offering multiple transport modes via a single subscription or payment system. | On-demand transportation service focusing on vehicle provision, typically autonomous or shared vehicles. |
| Scope | Combines public transit, ride-sharing, bike-sharing, car rentals, and more. | Primarily provides vehicle access and rides without integration across transport types. |
| Primary Goal | Seamless, multimodal mobility experience optimizing time and cost. | Efficient vehicle usage and ride provision, often replacing private vehicle ownership. |
| Technology | Advanced platforms integrating real-time data, payment, and route planning. | Autonomous vehicles, ride-hailing apps, and fleet management systems. |
| User Interaction | Single app for planning, booking, and paying across multiple transport modes. | App-based booking primarily for vehicle rides or rentals. |
| Examples | Whim, Moovel | Uber, Lyft autonomous vehicle service initiatives |
Understanding Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS): A Comprehensive Overview
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) integrates various transportation modes such as buses, trains, ride-sharing, and bike rentals into a single digital platform, enhancing user convenience through seamless trip planning and unified payments. Unlike Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS), which primarily focuses on on-demand vehicle access like ride-hailing or car-sharing, MaaS emphasizes multimodal connectivity and holistic travel solutions. Key components of MaaS include real-time data integration, subscription-based models, and personalized mobility options that collectively promote sustainable urban transportation.
What is Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS)? Key Concepts Explained
Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS) refers to the on-demand delivery of various transportation options through digital platforms, integrating services like ride-sharing, car rentals, public transit, and micro-mobility under one seamless system. It emphasizes user-centric access, flexibility, and efficiency by leveraging connected technologies and real-time data to optimize route planning, vehicle usage, and multimodal travel. Unlike Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS), which broadly includes mobility-related services beyond transport, TaaS specifically targets transportation modes as a unified, service-driven solution.
Core Differences Between MaaS and TaaS
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) integrates various transportation modes into a single accessible platform, emphasizing user-centric trip planning, booking, and payment services. Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS) primarily focuses on providing vehicles or transport units, often autonomous, as on-demand services without necessarily integrating multiple transit options. The core difference lies in MaaS being a comprehensive mobility solution enhancing user convenience across multiple transport services, while TaaS centers on vehicle provisioning and operational efficiency.
Integrating Public and Private Transit: MaaS vs. TaaS Approaches
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) integrates public and private transit options through a unified digital platform, enabling users to plan, book, and pay for multi-modal journeys seamlessly. Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS) primarily focuses on on-demand vehicle services such as ride-hailing and car-sharing, often operating independently from public transit systems. MaaS promotes comprehensive urban mobility by combining buses, trains, bikes, and ride-sharing into a single service, while TaaS emphasizes vehicle access and operational efficiency without necessarily integrating diverse transit modes.
User Experience: Comparing MaaS and TaaS Platforms
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms provide seamless integration of multiple transportation modes, enhancing user experience through personalized trip planning and unified payment systems. Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS) platforms typically focus on single-service offerings like ride-hailing or car-sharing, limiting the scope of user interaction and convenience. MaaS delivers a holistic approach with real-time updates and multi-modal connectivity, significantly improving accessibility and satisfaction compared to the more fragmented TaaS experience.
Technology and Infrastructure: How MaaS and TaaS Differ
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) integrates various transportation modes into a single digital platform, leveraging advanced software and real-time data analytics to provide seamless, user-centric travel planning and payment solutions. Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS) emphasizes the use of autonomous vehicles and connected infrastructure, focusing on vehicle fleet management and on-demand ride services powered by cutting-edge sensor technology and AI. The key technological distinction lies in MaaS's software-driven integration of existing transport systems versus TaaS's infrastructure-centric deployment of autonomous and smart vehicle operations.
Business Models: Subscription-Based MaaS vs. On-Demand TaaS
Subscription-based Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) offers customers a bundled access plan to multiple transport modes through a single platform, enhancing convenience and cost predictability. On-demand Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS) focuses on individual trip requests, providing flexible, pay-per-use solutions primarily driven by ride-hailing and micro-mobility services. Businesses adopting MaaS models benefit from steady revenue streams and customer loyalty, while TaaS models capitalize on dynamic pricing and scalability to meet fluctuating demand.
Sustainability Impacts: Eco Benefits of MaaS and TaaS
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) integrates multiple sustainable transport options, reducing private car dependence and lowering carbon emissions by optimizing routes and modes based on real-time data. Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS), often involving shared autonomous vehicles or electric fleets, minimizes vehicle ownership and promotes energy efficiency, leading to significant reductions in urban air pollution and fossil fuel consumption. Both MaaS and TaaS contribute to sustainable urban mobility by enhancing accessibility while supporting emissions reduction targets and advancing cleaner transportation ecosystems.
Policy and Regulation: MaaS vs. TaaS in Urban Planning
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) integrates multiple transportation modes under a single digital platform, requiring policy frameworks that emphasize data sharing, user privacy, and interoperability standards to ensure seamless urban mobility. Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS) involves on-demand vehicle services like ride-hailing and autonomous fleets, necessitating regulations focused on safety, vehicle standards, and congestion management within city infrastructures. Urban planning must balance MaaS's collaborative ecosystem with TaaS's operational complexities by developing adaptive policies that foster innovation while safeguarding public interests.
The Future of Urban Mobility: MaaS and TaaS Trends
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) integrates multiple transportation modes into a single accessible platform, enhancing user convenience with real-time data and seamless payments. Transportation-as-a-Service (TaaS) emphasizes on-demand vehicle access, including autonomous and electric fleets, driving efficiency and sustainability in urban environments. Emerging trends highlight MaaS's role in reducing private car ownership while TaaS advances shared, eco-friendly transport solutions, collectively shaping the future of smart city mobility ecosystems.
mobility-as-a-service vs transportation-as-a-service Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com