Pro-inflammatory foods such as processed meats, refined sugars, and trans fats can trigger chronic inflammation, increasing the risk of diseases like arthritis, heart disease, and diabetes. Anti-inflammatory foods, including leafy greens, fatty fish, nuts, and berries, help reduce inflammation by providing essential antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids. Incorporating more anti-inflammatory options into your diet supports overall health and reduces the likelihood of inflammation-related conditions.
Table of Comparison
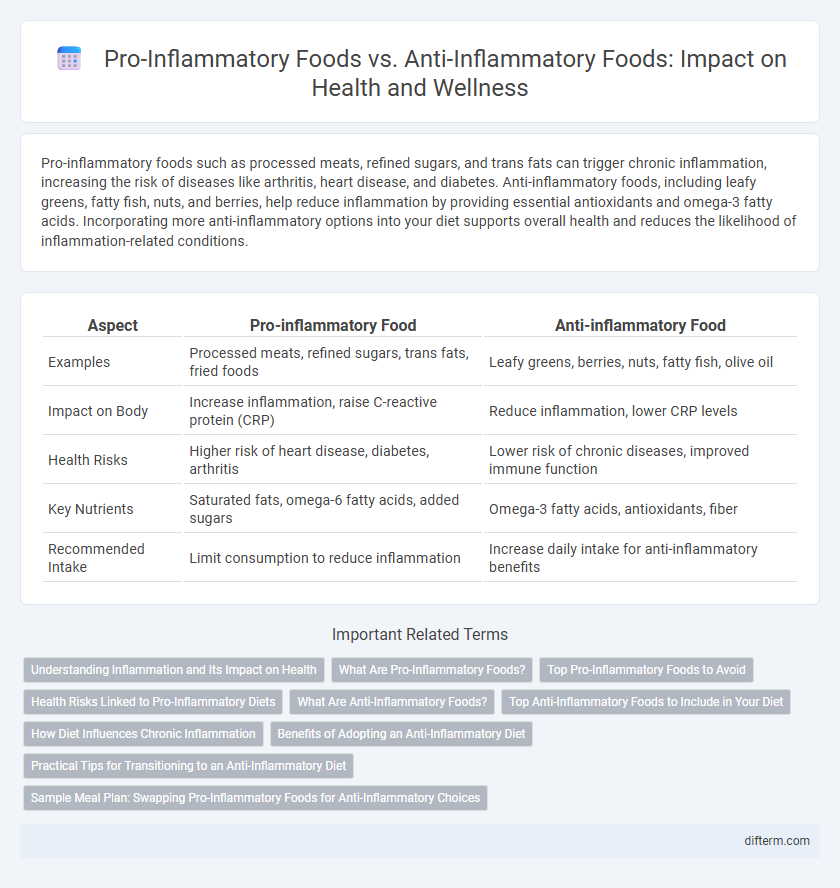
| Aspect | Pro-inflammatory Food | Anti-inflammatory Food |
|---|---|---|
| Examples | Processed meats, refined sugars, trans fats, fried foods | Leafy greens, berries, nuts, fatty fish, olive oil |
| Impact on Body | Increase inflammation, raise C-reactive protein (CRP) | Reduce inflammation, lower CRP levels |
| Health Risks | Higher risk of heart disease, diabetes, arthritis | Lower risk of chronic diseases, improved immune function |
| Key Nutrients | Saturated fats, omega-6 fatty acids, added sugars | Omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, fiber |
| Recommended Intake | Limit consumption to reduce inflammation | Increase daily intake for anti-inflammatory benefits |
Understanding Inflammation and Its Impact on Health
Pro-inflammatory foods such as refined sugars, trans fats, and processed meats trigger cytokine production, leading to chronic inflammation linked to diseases like diabetes and heart conditions. In contrast, anti-inflammatory foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and phytochemicals--found in berries, fatty fish, and leafy greens--help reduce inflammatory markers and support immune regulation. Understanding the balance between these food types is crucial for managing systemic inflammation and preventing long-term health complications.
What Are Pro-Inflammatory Foods?
Pro-inflammatory foods are types of food that trigger or exacerbate inflammation within the body, often contributing to chronic health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. These foods typically include processed meats, refined sugars, trans fats, and highly processed carbohydrates, all of which increase levels of inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and cytokines. Consuming these pro-inflammatory foods frequently can disrupt the body's immune response, leading to persistent inflammation and associated health risks.
Top Pro-Inflammatory Foods to Avoid
Top pro-inflammatory foods to avoid include processed meats such as sausages and bacon, which contain high levels of saturated fats and nitrates that trigger inflammation. Refined carbohydrates like white bread and pastries spike blood sugar levels, promoting inflammatory responses in the body. Excessive consumption of sugary beverages and fried foods rich in trans fats further exacerbates chronic inflammation linked to various health issues.
Health Risks Linked to Pro-Inflammatory Diets
Pro-inflammatory diets rich in processed foods, sugars, and trans fats significantly increase the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. Elevated markers of systemic inflammation, including C-reactive protein and interleukin-6, are consistently observed in individuals consuming high levels of pro-inflammatory foods. Replacing these with anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids can mitigate inflammation and reduce associated health risks.
What Are Anti-Inflammatory Foods?
Anti-inflammatory foods are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that help reduce inflammation and promote overall health. Common examples include fatty fish like salmon, leafy greens such as spinach and kale, berries, nuts, and olive oil. Incorporating these foods into a balanced diet can lower the risk of chronic diseases linked to inflammation, including heart disease and arthritis.
Top Anti-Inflammatory Foods to Include in Your Diet
Leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale, rich in antioxidants and polyphenols, effectively reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. Fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel provide high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, which lower pro-inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein. Berries, nuts, and olive oil also contribute anti-inflammatory compounds that support immune health and reduce chronic disease risk.
How Diet Influences Chronic Inflammation
Pro-inflammatory foods such as refined sugars, trans fats, and excessive red meat can exacerbate chronic inflammation by triggering the release of cytokines and promoting oxidative stress. In contrast, anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, leafy greens, and berries help reduce inflammatory markers by supplying antioxidants and modulating immune responses. Diet plays a crucial role in managing chronic inflammation, impacting the risk of conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
Benefits of Adopting an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids helps reduce chronic inflammation, lowering the risk of diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. Anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens, nuts, and fatty fish provide essential antioxidants and phytochemicals that support immune function and promote cellular repair. This dietary approach enhances overall health by improving metabolic function and reducing markers of inflammation in the body.
Practical Tips for Transitioning to an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Incorporate more anti-inflammatory foods such as leafy greens, berries, fatty fish rich in omega-3s, and nuts into daily meals while reducing intake of pro-inflammatory items like processed meats, refined sugars, and trans fats. Prioritize cooking methods like steaming or grilling instead of frying to preserve nutrient integrity and minimize inflammation. Gradually replacing sugary beverages with herbal teas or water infused with lemon supports hydration and further reduces inflammation risk.
Sample Meal Plan: Swapping Pro-Inflammatory Foods for Anti-Inflammatory Choices
Swapping pro-inflammatory foods like processed meats, refined sugars, and fried snacks for anti-inflammatory choices such as fatty fish, leafy greens, and nuts can reduce chronic inflammation effectively. A sample meal plan might include grilled salmon with spinach and quinoa for lunch, a snack of walnuts and berries, and dinner featuring turmeric-spiced roasted vegetables alongside brown rice. Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber supports immune health and lowers inflammation markers.
Pro-inflammatory food vs Anti-inflammatory food Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com